Текстовой глоссарий:
| interfere - вмешиваться swallow – глотать inhale – вдыхать inject - вводить absorb - поглощать detection - обнаружение ingestion - при прогла-тывании inhalation – вдыхание regardless of - независимо cleaning supplies – мою-щие средства vehicle - транспортное средство the use of multiple drugs - использование нескольких препаратов paint thinner – раствори-тель для краски the venom – яд occupational exposure – про-фессиональное воздействие, контакт insecticides – инсекти-циды nausea – тошнота vomiting – рвота giddiness –головок руже-ние irritability – раздражи-тельность palpitations – сердцеби-ение muscle twitching – мы-шечные судороги induce vomiting – вызыва-ние рвоты to counteract the poison - противодействовать яду law enforcement authorities – правоохр. органы saline solution – физ.-раствор seizures - судороги convulsions – судороги | lead dust - свинцовая пыль carbon monoxide - окись углерода bee stings - пчелиные укусы snake bites - укусы змей absorption or surface contact - поглощение или контакт с поверх-ностью alkalies – щелочей salmonella exposure – воздействие сальмо-неллы car fluids - автомобиль жидкостей mental confusion – спу-танность сознания pain relievers – болеу-толяющие suicide attempts – попытки само убий-ства escherichia coli – ки-шелная палочка cleaning detergents/paints - моющие средства / краски gas from furnace - газа из печи skin rashes - кожные вы-сыпания drowsiness – сонли-вость abdominal pain - боль в животе bladder - мочевой пу-зырь the esophagus – пище-вод activated charcoal – ак-тивированный уголь gastric lavage – промы-вание желудка |
Poisoning
Poisoning occurs when any substance interferes with normal body functions after it is swallowed, inhaled, injected, or absorbed. The branch of medicine that deals with the detection and treatment of poisons is known as toxicology.
There are 4 main types of poisoning.
§ Ingestion (eating, drinking, swallowing)
§ Inhalation (drugs, lead dust, chemical dust, natural gas, carbon monoxide)
§ Injection (bee stings, snake bites, drug use, overdose on normal medications)
§ Absorption or surface contact (chemical dust, plants, alkalies) regardless of the poison type.
The most common way people get poisoned is through the food supply: through the fast food and pet food salmonella exposure.
Children are the second common victimsof poisoning in the cosmetics, cleaning supplies, pesticides, and car fluids. Kids are surely attracted to all the bright, pretty colors of vehicle fluids, shampoo, bubble bath, and make up.
The elderly are the third most likely group to be poisoned. Mental confusion, poor eyesight, and the use of multiple drugs, pain relievers, sleeping meds, antidepressants, and street drugs are the leading reasons this group has a high rate of accidental poisoning. A substantial number of poisonings also occur as suicide attempts or drug overdoses.
Poisons are common in the home and workplace, yet there are basically two major types. One group consists of products that were never meant to be ingested or inhaled, such as shampoo, paint thinner, pesticides, houseplant leaves, and carbon monoxide.
The other group contains products that can be ingested in small quantities, but which are harmful if taken in large amounts, such as pharmaceuticals, medicinal herbs, or alcohol. Other types of poisons include the bacterial toxins that cause food poisoning, such as Escherichia coli; heavy metals, such as the lead found in the paint on older houses; and the venom found in the bites and stings of some animals and insects.
Causes
· Medications
· Drug overdose
· Occupational exposure
· Cleaning detergents/paints
· Carbon mono oxide gas from furnace, heaters
· Insecticides
· Certain cosmetics
· Certain household plants, animals
· Food poisoning (Botulism)
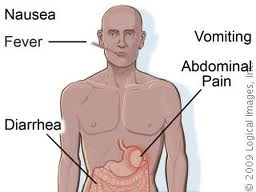
Symptoms
Severity of symptoms can range from headache and nausea to convulsions and death. The type of poison, the amount and time of exposure, and the age, size, and health of the victim are all factors which taken together determine the severity of symptoms and the chances for recovery.
· Blue lips
· Skin Rashes
· Difficulty in breathing
· Diarrhea
· Vomiting/Nausea
· Fever
· Head ache
· Giddiness/drowsiness
·  Double vision
Double vision
· Abdominal/chest pain
· Palpitations/Irritability
· Loss of appetite/bladder control
· Numbness
· Muscle twitching 



· Seizures 
· Weakness
· Loss of consciousness
 Poisoning first aid
Poisoning first aid
Immediate first aid is very important in a poisoning emergency. The first aid you give  before getting medical help can save a person's life. Treatment for poisoning depends on the poison swallowed or inhaled.
before getting medical help can save a person's life. Treatment for poisoning depends on the poison swallowed or inhaled.
·  Seek immediate medical help
Seek immediate medical help
Meanwhile,
· Try and identify the poison if possible
· Check for signs like burns around mouth, breathing difficulty or vomiting
· Induce vomiting if poison swallowed
· In case of convulsions, protect the person from self injury
· If the vomit falls on the skin, wash it thoroughly
· Position the victim on the left till medical help arrives
Treatment
For acid, alkali, or petroleum product poisonings, the person should not vomit. Acids and alkalis can burn the esophagus if they are vomited, and petroleum products can be inhaled into the lungs during vomiting, resulting in pneumonia.
Once the victim is under medical care, doctors have the option of treating the person with a specific remedy to counteract the poison (antidote) or with activated charcoal to absorb the substance inside the individual's digestive system. In some instances, pumping the stomach may be required.
This technique, which is known as gastric lavage, involves introducing 20 to 30 mL of tap water or 9 percent saline solution into the person's digestive tract and removing the stomach contents with a siphon or syringe. The process is repeated until the washings are free of poison. Medical personnel will also provide supportive care as needed, such as intravenous fluids or mechanical ventilation.
If the doctor suspects that the poisoning was not accidental, he or she is required to notify law enforcement authorities.
Упражнения
I. Прочитайте и переведите текст с помощью глоссария и ответьте на вопросы по содержанию текста.
1. When does poisoning occur?
2. What branch of medicine deals with the detection and treatment of poisons?
3. How many typesof poisoning are there? What are they?
4. What is the most common way people get poisoned?
5. Who are the second common victims of poisoning?
6. What are thecausesof poisoning? Count them.
7. What determines the severity of symptoms and the chances for recovery?
8. Why can the first aid you give before getting medical help be so important?
9. What does treatment for poisoning depend on?
II. Дайте русские эквиваленты следующих фраз:
Common victims, car fluids (vehicle fluids), bubble bath, mental confusion, poor eyesight, multiple drugs, sleeping meds, street drugs, suicide attempts, drug overdoses, houseplant leaves, digestive system, cleaning supplies, paint thinner, bee stings, pain relievers, skin rashes, abdominal pain, gastric lavage, saline solution, activated charcoal.






