1. Name the products of tyrosine putrefaction
A. phenol and cresol
B. ornithine and oxyproline
C. scatol and indol
D. methyl mercaptan and hydrogen sulphide
E. scatol and phenol
2. Matching
Match the following site of protein digestion with corresponding proteolytic enzymes
The place of synthesis Enzymes
1. stomach A. pepsin
2. small intestine B. trypsin
C. carboxypeptidase
D. chymotrypsin
3. Name the characteristic of glutamic acid
A. diaminomonocarbonic, glyco-ketogenic, non-essential
B. monoaminomonocarbonic, essential, ketogenic
C. monoaminodicarbonic, essential, ketogenic
D. monoaminodicarbonic, non-essential, glycogenic
E. monoaminomonocarbonic, glycogenic, non-essential
4. S-adenosylmethionine takes part in the reaction of
A. hydroxylation
B. methylation
C. carboxylation
D. phosphorylation
E. acetylation
5. All characteristics of ornithine are true except
A. it takes part in detoxification of ammonia
B. it is not included in proteins
C. it is a mono-amino mono-carboxylic acid
D. in neutral medium ornithine has positive charge
6. Matching
Match the following substrates of decarboxylation reaction with their products
Substrates Products
1. Aspartate A. αalanine
2. Glutamate B. phenylacetic acid
3. 5-hydroxytryptophan C. histamine
D. gamma-aminobutyric acid
E. serotonine
7. Matching
Match the following substrates of oxidative deamination reaction with their products
substratesproducts
1. Aspartate A. αketoglutarate
2. Phenylalanine B. pyruvate
3. Alanine C. oxaloacetate
D. phenylpyruvate
E. α-ketobutyric acid
8. Matching
Match the following amino acids with their products in the process of putrefaction
1. Lysine A. phenol and cresol
2. Tyrosine B. indole and skatole
C. cadaverine
D. putrescine
E. skatole and phenol
9. Matching
Match the following amino acids with their products in the process of putrefaction
1. Tryptophan A. phenol and cresol
2. Ornithine B. indole and skatole
C. cadaverine
D. phenol and indol
E. putrescine
10. Matching
Match the following zymogenes with the types of their activation
Zymogenes Activation types
1. Pepsinogen A. HCl and autocatalysis
2. Trypsinogen B. autocatalysis only
3. Chymotrypsinogen C. enterokinase and autocatalysis
D. ttrypsin only
E. H3PO4
11. Name the biologic functions of hydrochloric acid
A. activation of pepsinogen
B. provision for optimal ph of pepsin in gastric juce
C. denaturation of food proteins
D. bactericidal action
E. all of the above mentioned
12. Pepsin exerts a fast cleavage of protein endo-peptide bonds formed mainly by the carboxyl groups of
A. phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
B. histidine, valine, threonine
C. serine, glycine, alanine
D. lysine, methionine, arginine
E. all of the abovementioned
13. Name the possible pathways of amino acids consumption in the liver
A. synthesis of the blood coagulation factors
B. synthesis of non-proteinic nitrogenous compounds
C. synthesis of carbohydrates
D. synthesis of lipids
E. oxidation of amino acids to the end products
F. all of the abovementioned
14. Name the common product of all deamination types
A. ammonia
B. fatty acids
C. hydroxy acids
D. alphaketo acids
E. unsaturated acids
F. all of the abovementioned
15. Name the enzyme taking part in transdeamination reaction
A. glutamate dehydrogenase
B. aspartate dehydrogenase
C. pyruvate dehydrogenase
D. succinate dehydrogenase
E. glutamate decarboxylase
16. Matching
Match the following substrates of decarboxylation reaction with their products
Substrates of decarboxylation Products
1. Glutamate A. αketoglutarate
2. Aspartate B. gammaaminobutyric acid
C. serotonine
D. histamine
E. bettaalanine
17. Matching
Match the following enzymes with their catalysed reactions
EnzymesReactions
1. Aspartate aminotransferase A. Aspartate + α-ketoglutarate oxaloacetate
+ glutamate
2. Alanine aminotransferase B. Alanine + oxaloacetate →
pyruvate + aspartate
C. Alanine → pyruvate
D. Glutamate → γ-aminobutyric acid
E. Aspartate → oxaloacetate
18. Matching
Match the following states of nitrogen balance with corresponding physiologic and pathologic situations
1. positive nitrogen balance A. young growing organism
2. negative nitrogen balance B. female organism in pregnancy
3. nitrogen equilibrium C. in starvation
D. in protein deficiency
E. healthy adult organism
19. Name the class of enzyme catalysing deamination reaction
A. isomerases
B. transferases
C. oxydoreductases
D. lyases
E. ligases
Ammonia detoxification
1. Cycle metabolite of urea shown in the figure

A. argininosuccinate
B. arginine
C. aspartate
D. carbamoyl-phosphate
E. ornithine
2. Indicatethe right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea shown in the figure

A. arginine
B. citrulline
F. carbamoyl-phosphate
C. argininosuccinate
D. fumarate
3. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea shown in thefigure
A. argininosuccinate
B. carbamoyl-phosphate
C. aspartate
D. urea
E. citrulline
4. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea shown in thefigure

A. citrulline
B. fumarate
C. ornithine
D. aspartate
E. argininosuccinate
5. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea shown in the figure

A. citrulline
B. fumarate
C. carbamoyl-phosphate
D. urea
E. argininosuccinate
6. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea shown in the figure

A. citrulline
B. arginine
C. carbamoyl-phosphate
D. aspartate
E. argininosuccinate
7. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea shown in thefigure

A. citrulline
B. arginine
C. carbamoyl-phosphate
D. aspartate
E. argininosuccinate
8. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea shown inthe figure

A. ornithine
B. arginine
C. carbamoyl-phosphate
D. urea
E. argininosuccinate
9. Indicate the stage of the cycle with the action of urea ornitine carbamoyltransferase

10. Indicatethe stage of the cycle with the action of urea argininosuccinate synthetase

11. Indicate the stage of the cycle with the action of urea argininosuccinate lyase

12. Indicate the stages of urea cycle with the action of arginase
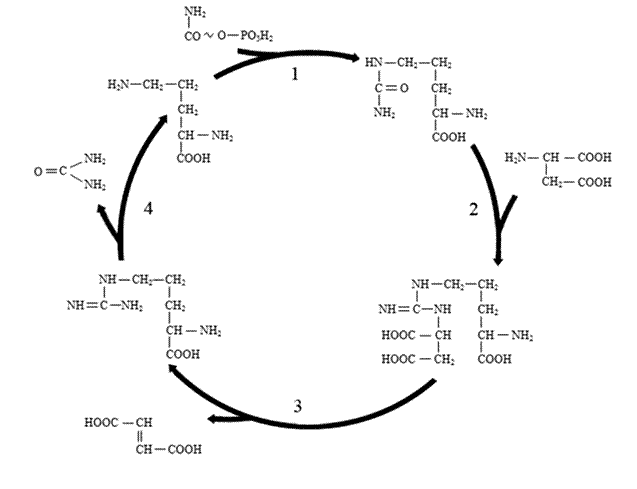
13. Name the amino acids produced as a result of α-keto- acid reductive amination of
1. α-ketoglutarate A. serine
2. pyruvate B. alanine
3. oxaloacetate C. glutamic acid
D. lysine
E. aspartic acid
F. valine
14. Ammonia is produced by
A. deamination of amino acids
B. deamination of biogenic amines
C. deamination of purine bases
D. deamination of amino acids amides
E. all of the above mentioned
15. How many ATP molecules are required to produce one urea molecule?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
16. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea carbamoyl-phosphate

17. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite of urea citrulline

18. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite aspartateof urea

19. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite argininosuccinateof urea

20. Indicate theright answer
Cycle metabolite fumarateof urea

21. Indicate theright answer
Cycle metabolitearginineof urea

22. Indicate the right answer
The metabolite ofurea cycle

23. Indicate the right answer
Cycle metabolite ornithine of urea

24. Indicate the right answer
The enzyme which catalyzes the given reaction of urea cycle


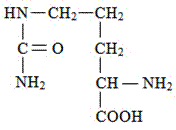
ornitine carbamoyltransferase
A. argininosuccinate synthetase
B. argininosuccinate lyase
C. arginase
D. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
25. Indicate the right answer
The enzyme which catalyzes the given reaction of urea cycle



A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
26. Indicate the right answer
The enzyme which catalyzes the given reaction of urea cycle



A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
27. Indicate the right answer
The enzyme which catalyzes the given reaction of urea cycle


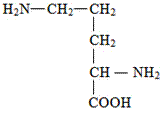
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
28. Indicate the right answer to fill in the missing word
The enzymes catalyze this reaction of urea cycle
Ornithine  Citrulline
Citrulline
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. aarbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
29. Indicate the right answer to fill in the missing word
The enzymes catalyze this reaction of urea cycle
Citrulline  Argininosuccinate
Argininosuccinate
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. arbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
30. Indicate the right answer to fill in the missing word
The enzymes catalyze this reaction of urea cycle
Argininosuccinate  arginine
arginine
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
31. Indicate the right answer to fill in the missing word
The enzymes catalyze this reaction of urea cycle
Arginine  Ornithine
Ornithine
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
32. Reductive amination proceeds mainly with the use of
A. α-ketoglutarate
B. pyruvate
C. oxaloacetate
D. acetone
E. α-ketobutyrate
33. Name the enzyme, which defect result in hyperargininemia
A. оrnitine carbamoyltransferase
B. аrgininosuccinate synthetase
C. аrgininosuccinate lyase
D. аrginase
E. сarbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
34. Name the enzyme, which defect result incitrullinemia
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
35. Name the enzyme, which defect result inargininosuccinic aciduria
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
36. Name the enzyme, which defect result inhyperammoniemia
A. ornitine carbamoyltransferase
B. argininosuccinate synthetase
C. argininosuccinate lyase
D. arginase
E. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase
37. Name the metabolite which binds cytric acid cycle with urea cycle
A. malate
B. citrate
C. oxaloacetate
D. fumarate
E. succinate
38. The mechanism of ammonia neutralization includes
A. production of urea
B. reductive amination
C. production of amino acids amides
D. production of ammonia salts
E. all of the above mentioned
39. Argininosuccinate splits by argininosuccinate lyase to produce arginine and
A. fumarate
B. urea
C. ornithine
D. asparagine
E. lysine
40. In the liver urea is formed from
A. ammonia and carbon monoxide
B. ammonia and carbon dioxide
C. ammonia and hydrochloric acid
D. ammonia and phosphate
E. all of the abovementioned
41. Name the sources for urea molecule atoms
A. H2O, NH3, CO2, aspartate
B. NH3, H3PO4, CO2, glutamate
C. aspartate, glutamate, NH, CO,
D. H2O, H3PO4, NH3, aspartate
E. CO2, H2O, aspartate, ATP
42. The source of ammonia in the body is not
A. amino
B. urea
C. biogenic amines
D. purine bases
E. cytosine
43. Indicate the rightanswer
Carbamoylphosphateis located
A. In the mitochondria
B. In the lysosomes
C. In the cytoplasm
D. In the Golgi
E. In the endoplasmic reticulum
44. Alanine is synthesized from pyruvate with the participation of
A. vitamine B6
B. vitamine B5
C. vitamine B3
D. vitamine B2
E. vitamine B7
45. The mechanism of ammonia neutralization includes
A. production of urea
B. reductive amination
C. production of amino acids amides
D. production of ammonia salts
E. all of the abovementioned




