If you don’t know, find the answer in the text. What information was new for you? Share your opinions if oil and gas can be formed nowadays.
Translate the following derivatives
1) Sediment (sedimentary, sedimentation)
2) To accumulate (accumulative, accumulator, accumulation)
3) To move (move, movable (moveable), movement)
Glossary
1. Remains (of smth) – 1. the parts of ancient objects and buildings that have survived and are discovered in the present days; 2. the body of a dead person or animal.
2. to decay – to be destroyed gradually by natural processers; to destroy smth in this way.
3. Compound – a thing consisting of two or more separate things combined together.
4. Sediment – the solid material that settles at the bottom of a liquid.
Translate the text using the given vocabulary.
Anticline антиклиналь heating oil печное топливо
Cap rock покрывающая порода impermeable непроницаемый
Compound структура, смесь kerosene керосин
Consumption потребление layer слой
Crude oil сырая нефть limestone известняк
To decay разлагаться marble мрамор
To distill перегонять, извлекать petroleum нефть
To drill down бурить pinching out вытеснение
Enormous огромный, чудовищный porous пористый,губчатый
To exert оказывать давление pumping выкачивание насосом
Exploration разведка remains останки
Faulting сбросообразование reservoir rock порода-коллектор
Fine-grained мелкозернистый sandstone песчаник
Fold складка, изгиб sedimentary осадочный
Folding складкообразование shale сланец
Formation образование, формация silt ил
Gasoline амер. бензин to trap здесь удерживать
To gush out фонтанировать well скважина
| How Oil Drilling Works |
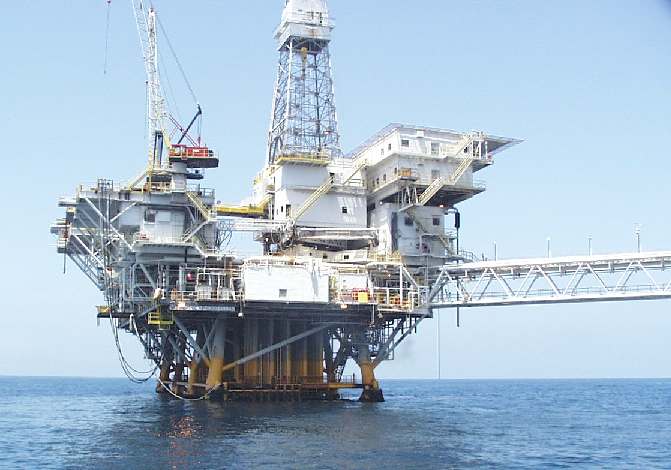 Offshore oil rig
Offshore oil rig
|
Crude oil gets refined into gasoline, kerosene, heating oil and other products. To keep up with our consumption, oil companies must constantly look for new sources of petroleum, as well as improve the production of existing wells.
How does a company go about finding oil and pumping it from the ground? You may have seen images of black crude oil gushing out of the ground, or seen an oil well in movies and television shows like “Giant”, “Oklahoma Crude”, “Armageddon” and “Beverly Hillbillies”. But modern oil production is quite different from the way it's portrayed in the movies. In this article, we will examine how modern oil exploration and drilling works.
Forming oil
Oil is formed from the remains of tiny plants and animals (plankton) that died in ancient seas between 10 million and 600 million years ago. After the organisms died, they sank into the sand and mud at the sea bottom.

| Tiny sea plants and animals died and were buried on the ocean floor. Over time, they were covered by layers of silt and sand. | Over millions of years, the remains were buried deeper and deeper. The enormous heat and pressure turned them into oil and gas. | Today, we drill down throw layers of sand, silt and rock to reach the rock formations that certain oil and gas deposits. |
| 
| 
|
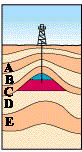
| Oil reservoir rocks and natural gas can be trapped by folding (left picture), faulting (middle picture) or pinching out (right picture) |
Over the years, the organisms decayed in the sedimentary layers. In these layers, there was little or no oxygen present. So microorganisms broke the remains into carbon-rich compounds that formed organic layers. The organic material mixed with the sediments, forming fine-grained shale, or source rock. As new sedimentary layers were deposited, they exerted intense pressure and heat on the source rock. The heat and pressure distilled the organic material into crude oil and natural gas. The oil flowed from the source rock and accumulated in thicker, more porous limestone or sandstone, called reservoir rock. Movements in the Earth trapped the oil and natural gas in the reservoir rocks between layers of impermeable rock, or cap rock, such as granite or marble. These movements of the Earth include:
· Folding – Horizontal movements press inward and move the rock layers upward into a fold or anticline.
· Faulting – The layers of rock crack, and one side shifts upward or downward.
· Pinching out – A layer of impermeable rock is squeezed upward into the reservoir rock.
Ex. 1. Match definitions.
1. Shale
2. To deposite
3. To accumulate
4. Limestone
5. Fine
A. Made of very small grains
B. A type of white stone that contains calcium, used in building and in making cement
C. To gradually get more and more of smth over a period of time
D. (especially of a river or a liquid) To leave a layer of smth on the surface of smth, especially gradually over a period of time
E. A type of soft stone that splits easily into thin flat layers
Ex. 2. Find antonyms to the following words.
1. Thick A. Permeable
2. To decay B. Coarse
3. Fine C. Subtle
4. Affine D. Thin
5. Huge E. Enormous
6. Impermeable F. To rot, to decompose
Grammar
Глаголы в английском языке имеют 4 формы:
Таблица 1.
| Infinitive | Past Simple | Past Participle (II) | Present Participle (I) | |
| I | II | III | IV | |
| regular | to work | worked | worked | working |
| irregular | to speak | spoke | spoken | speaking |
Таблица 2.
| Present Participle (I) | Past Participle (II) | ||
| Indefinite | Active | Passive | changed 1. определение изменяемый, измененный 2. обстоятельство когда изменили Примечание: Причастие II (PII) всегда имеет страдательный характер, т.е. invited – приглашенный, (а не приглашающий) |
| changing 1. определения изменяющий, изменявший 2. обстоятельство изменяя | being changed 1. определения изменяющийся, изменяемый, который изменяется 2. обстоятельство будучи измененным | ||
| Perfect | having changed обстоятельство изменив | having been changed обстоятельство когда изменили, после того как изменили |
Past Participle (II) и Present Participle (I) в предложении выполняют 3 функции:
1. В составе сказуемого: PII a) This task was given to me yesterday.
Это задание дали мне вчера.
Passive voice = to be +PII
b) He has just gone away.
Он только что ушел.
Perfect forms = to have + PII
PI He is working very hard now (Continuous).
Он сейчас много работает
Progressive = to be +PI
2. Определение: PII The text translated is very interesting for all of us.
Переведенный текст интересен всем.
PI The girl listening to you so attentively is my sister.
Девочка, слушающая Вас так внимательно,
моя сестра
3. Обстоятельства:
PII
When asked you should translate. – Когда спрашивают, вам следует отвечать.
PI
While listening to his report they made notes. – Слушая доклад, они делали записи.
Переведите
Образец: The work discussed. – обсуждаемая, обсужденная.
The books translated. – переводимая, переведенная.
1. the matter obtained, the substance applied, the solids determined, the materials included.
2. the students reading, the girl describing, the book including, the teacher speaking, the event occurring, the scientist representing.
3. the workers doing, the work done; the property identified, the man identifying; the country represented, the delegation representing; the sample included, the programme included; a body possessing, the chemist applying.
Информация
Как известно, у правильных глаголов совпадают личная форма – Past Indefinite – и неличная – ed -форма.
Если возникает сомнение при переводе, нужно просмотреть, есть ли дальше в предложении другое сказуемое, если нет, значит эта форма на – ed – личная, ее надо переводить глаголами, если есть сказуемое, то это определение, отвечающее на вопрос какой?
- could not give a correct answer. (за ed -формой следует сказуемое, поэтому перевод – Опрошенный студентом…)
The student asked –
- a question. (Другого сказуемого нет, поэтому перевод – Студент задал вопрос.)
Иногда встречаются 2 ed-формы, в таком случае вторая является сказуемым. Например:
The equipment test ed requir ed some improvement. – Испытанное (или испытываемое) оборудование потребовало некоторого улучшения.
Ex.3. Переведите следующие словосочетания, обращая внимание на второе слово с окончанием ed
Образец: the materials test ed requir ed –испытанные материалы требовали.
1. The work performed showed; 2. The results obtained showed; 3. The equipment tested required; 4. The problem solved proved; 5. The equation obtained resulted; 6. The experiment discussed proved; 7. The results obtained required.
Ex. 4. Определите функции глагольных форм с суффиксом ed и переведите.
1. The equipment test ed requir ed further improvement.
2. The results obtain ed vari ed in some respects.
3. The techniques appli ed increas ed the rate of production.
4. The methods introduc ed receiv ed general recognition.
5. The experiment describ ed attract ed general attention.
6. The materials collect ed serv ed as valuable information.
7. The apparatus install ed show ed good performance.
8. The progress achiev ed result ed in a remarkable technical improvement.
9. The amount of heat generat ed depend ed on the quality of the fuel us ed.
Ex.5. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на различную функцию совпадающих по форме слов.
1. The war ruined many cities. There are no ruined houses in our cities.
2. Planned work gives good results. The professor planned all his lectures.
3. The institute admitted 150 students. Peter was one of the admitted students.
4. The candidate submitted his documents. All the submitted documents are in the office.
5. The schoolchildren made a fine model of a rocket. It was the first model made by children.
Ex.6. Выберите правильную форму.
1. At our Institute there are several subjects…(studied, studying).
2. Students…(taking, taken) exams next week should come to the dean’s office.
3. The engineer…(represented, deriving) this factory is a good specialist.
4. The matter …(derived, deriving) in this reaction will possess these properties.
5. Scientists …(applied, applying) such methods obtain interesting results.
Ex.7. Найдите эквиваленты.
1. the energy possessed; a) сила тяжести;
2. a lifted weight; b) по отношению;
3. an isolated system; c) энергия, присущая;
4. will respect to; d) данное тело;
5. the given body; e) поднятый груз;
6. uniformly accelerated motion; f) равномерноускоренное движение;
7. the velocity acquired; g) изолированная система;
8. the forces of gravity. h) приобретенная скорость.
Lesson 3
| How Oil Drilling Works |
 Searching for oil over water using seismology
Searching for oil over water using seismology
|
Locating Oil
The task of finding oil is assigned to geologists, whether employed directly by an oil company or under contract from a private firm. Their task is to find the right conditions for an oil trap – the right source rock and reservoir rock. Many years ago, geologists interpreted surface features, surface rock and soil types, and perhaps some small core samples obtained by shallow drilling. Modern oil geologists also examine surface rocks and terrain, with the additional help of satellite images. However, they also use a variety of other methods to find oil. They can use sensitive gravity meters to measure tiny changes in the Earth's gravitational field that could indicate flowing oil, as well as sensitive magnetometers to measure tiny changes in the Earth's magnetic field caused by flowing oil. They can detect the smell of hydrocarbons using sensitive electronic noses called sniffers. Finally, and most commonly, they use seismology, creating shock waves that pass through hidden rock layers and interpreting the waves that are reflected back to the surface.
The shock waves travel beneath the surface of the Earth and are reflected back by the various rock layers. The reflections travel at different speeds depending upon the type or density of rock layers through which they must pass. The reflections of the shock waves are detected by sensitive microphones or vibration detectors – hydrophones over water, seismometers over land. The readings are interpreted by seismologists for signs of oil and gas traps. Although modern oil-exploration methods are better than previous ones, they still may have only a
10-percent success rate for finding new oil fields. Once a prospective oil strike is found, the location is marked by GPS coordinates on land or by marker buoys on water.
Vocabulary
| beneath под, ниже; boundary граница, межа; conductor pipe направляющая труба; core сердцевина, центр; crew бригада; cuttings выбуренная порода; density плотность; to dig копать, рыть; drilling mud буровой раствор; drilling rig буровая установка; | featureособенность, признак; hole скважина; hydrocarbon углеводород; hydrophone сонар, гидролокатор; inland внутриматериковый; to level разравнивать; to line здесь облицовывать; marsh болото, топь; offshore морской; pit котлован; | remoteness удалённость; satellite спутник (Земли); shallow поверхностный; soil грунт, почва; strike идиом. месторождение; success rate вероятность успеха; to survey исследовать; temporarily временно; trap моноклиналь; wilderness пустыня. |
Warm up
1. Do you know how oil is found?
2. Do you know any ways of finding oil? (if you do not know find the answers in the text when reading)
Ex. 1.
1) to assign – assignation, assignment
2) to employ – am employ, employable, employee, employer, employment
3) to measure – measure, measured, measureless, measurement, measuring cup (jug, tape)
4) to help – help, helper, helpful, helping, helpless, help-line, help-mate
5) to create – creation, creationism, creative, creator, creature
6) to reflect – reflectance, reflection, reflective, reflectivity, reflector
7) to depend – dependable, dependant, dependence, dependency, dependent
Ex. 2. Glossary
1. to assign – 1) to give sb. sth. That they can use, or some work or responsibility
2) to provide a person for a particular task or position
2. to measure - to find the size, quantity, etc. of smth. in standard units
3. to cause – to make smth happen, especially smth bad or unpleasant
4. density – the thichness of a solid, liquid or gas measured by its mass per unit of volume
5. exploration – 1) the act of travelling through a place in order to find out it or look for smth in it
6. surface – the top layer of an area of water or land
Ex. 3. Find definitions
1. to employ – to give smb a job to do for payment
2. soil – the top layer of the earth in which plants, trees etc. grow
3. terrain – used to refer to an area of land when you are mentioning its natural features, for example, if it is rough, flat, etc (difficult/ rough/ mountainous, etc. terrain)
4. to create – to make smth happen or exist
5. to hide – to put or keep smb or smth in a place where they/ it cannot be seen or defend
6. to reflect (us. passive) – to throw back light, heat, sound etc. from a surface
7. speed – rate of movement/ action, the rate at which smb/ smth moves or travels
Ex. 4 Find synonyms
1. soil – clay – land – earth – dirt – ground
2. to measure – to match up, to access, to sniff – to smell
3. to help – to assist
4. to hide – to cancel – cover – disguise – mask - camouflage
5. speed – rate – pace - step
6. to obtain – to get smth
Forming oil
Ex. 1 Warm-up
1) What is oil? What kind of oil do you know? When was it formed?
2) Do you know how oil is formed?
3) Have you ever seen or smell oil?
Possible answer: oil is a fossil fuel that can be found in many countries around the world. If you do not know, find the answers in the text.
What information was new for you? Share your opinion if oil and gas can be formed nowadays?
Ex. 2 Give definitions






