Computer network – is a complex of computers, which are linked by data channels, that provides user means of information exchange and the access to users to program, technical, informational and organizational network resources.
The most important characteristic of the computer network is its architecture. Network architecture is a realized network structure of data exchange, which defines its topology, devises' composition and the rules of engagement in network. Within the network architecture, we consider problems of information coding, its addressing and transmission, message flow control, error checking and analysis of network operation in emergency situations and in the deterioration of the characteristics.
Computer networks have different classification signs.
Networks classification by topology..
Network topology is an logical scheme of connection computers by links.
Among the majority of possible configurations there are fully connected and not fully connected. The most common types of network topologies:
Fully connected topology corresponds to network, in which every computer directly connected to others. Despite on logical simplicity, this option is cumbersome and inefficient. Every computer should have large amount of communication ports, necessary for connection to every other network computers.

All other options are based on not fully connected topologies, when for information exchange between two computers may be required transit data transfer via other network nodes.
Cellular topology obtained from fully connected by removing some connections. It allows to connect a large number of computers and is typical for large networks.

The ring topology. A network in which each node is connected to only two branches. All computers are connected coherently to one ring and server functions are distributed among all the machines on the network. The direct exchange of information takes place only between adjacent machines.
Advantage: 1. It provides redundancy links and any pair of nodes connected in two ways - in a clockwise direction and against it.
2. It is convenient to provide feedback – after making a full turn, data goes back to the source node, which can control the data delivery process to the addressee.
Disadvantage: In case of failure of any IBM, network's work may be interrupted. Also the very complicated procedure of expanding network.

The star topology is formed when each computer is connected directly by a separate wire to a single port on a common central unit, which is named concentrator or repeater, or Hub. Its functions are the directing of the computer information transmitted to one or all other computers. направление We use central IBM (server), to which are connected all the other machines on the network. The server provides messaging routes, plugging peripheral devices, and also it is a centralized data storage for the whole network.
Disadvantage: you need a separate machine for Network Management, which is, undesirable for other uses. In addition, server failure leads to the termination of the entire network.

Concentrator is an device, switching multiple communication channels to one.
Repeater is an device, that provides retention of the shape and signal amplitude of the signal in transmitting it to a greater, than it is provided, distance.
Hub is an node, which is connected directly to the network transmission media.
Tree topology. Network with using several concentrators, which are hierarchically interconnected by star-type connections. Any of the machines included in the network can be a server. In addition, it is possible to connect additional machines without significant setting changes. It is resistant to failure of individual nodes and has simple configuration. Nowadays, it is the most common topology in both local and global networks.
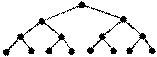
General bus where as a central element is passive cable that connects several computers. At its ends should be terminators. The transmitted information is distributed via cable and is available to all computers connected to this cable. In this topology we build 10 megabit network 10Base-2 and 10Base-5. The coaxial cable is used as a cable.
Advantages: cheapness and ease for the connection of new nodes to the network.
Disadvantages: unreliability and low performance.

Networks with hybrid topology are networks, in which we can distinguish some randomly connected fragments (subnets), that have typical topology. Designed for large networks, which are characterized by arbitrary connections between computers.
Networks by types of transfer media can be wired or wireless.
Wireless networks used when laying cables is difficult, impractical or simply impossible. In these cases network implemented by radio adapters, which are equipped with everywhere directed antennas and they use as a information transmission environment radio waves.
By the speed of the information transfer we have low, medium and high speed.
Distribution of roles between the computers on the network are peer to peer and client-server.
Server is a dedicated high-performance computer, which is equipped with appropriate software, centrally controlling the operation of the network and / or provided by other computers on the network its resources (data files, drives, printer, and so on.).
The client computer is a common network user computer accessing the server resources (servers).
Local and global networks
The network classification by extension can be: local, regional and global.
Local Area Network (LAN) is a network which connects computers in the area bounded by the walls of a room, building or office.
Local networks are for collective use of expensive peripherals - laser printers, plotters, etc., in other words for the collective use of a database or archives; for the transmission of messages between the users-colleagues.
The most common type of networks. There is also one small subgroup LAN, it is known as HAN (Home Area Network). This term describes networks which are created between home computers. LAN, by definition, is more like a generic term for computer network of offices and homes. Principally, between the LAN and HAN there is absolutely no difference.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) – is a network which is serving the information needs of the big city. It consists of providers - a network suppliers and general users - clients who use any link to connect with the other members of the network. MAN can maintain the transmission of digital data, sound, and even include cable TV.
World Area Networks (WAN) is a network, which connects providers from all over the world into a single computer network, or, in other words, all LANs and MANs connected together. It differs from LAN by the more extensive communications (satellite, cable and etc.).
Local area networks (LANs) may be included as components in the metro network; metro networks - as components of a global network; Finally, the global network can form even larger structures. The largest association of computer networks on the planet Earth today is the "network of networks" - the Internet.
Internet is the most popular global network, which combines many global, regional and local networks. Network name literally translated means "inter net".
Internet is based on the three main principles:
1) the existence of a single center for the coordination of activities and the development of the entire network;
2) the use of a routing system that allows packets to move through the chain of nodes without l human intervention;
3) the use of a single addressing system, making network "transparent" to external networks, and the last - available to any subscriber point system.
The main services provided to the user by advanced global networks: e-mail, newsgroups, access to remote databases.
Internet is a gigantic worldwide computer network, which connects thousands of networks around the world. Its purpose - to provide instant access to any information. The Internet offers almost unlimited information resources, useful information, entertainment, the opportunity to communicate with the competent people, remote access services, file transfer, e-mail and more. Internet provides a fundamentally new way of communication between people, which has no analogues in the world.
The most common and inexpensive way to communicate with the Internet - via modem and telephone line. It has three types of connection that differ from each other in the type of services and price:
1. Mail - allows only exchange emails with any Internet user, the cheapest;
2. On-line - usage in interactive mode - all the network opportunities at the time of the session;
3. Direct (private),the most expensive, but all opportunities at any time.
Modem is a device for converting digital signals to analog (and vice versa) for transferring it on the telephone line (a device that performs modulation and demodulation of information signals from their IBM to the communication channel and receiving in the IBM from the communication channel).
When working in on-line mode, the access to the Internet usually purchased from providers. In other words, organizations that provides access to network resources.
Lecture 8
Lecture's topic: Cyber security
Cyber security is a set of tools, policies, security concepts, security guarantees, guidelines, risk management approaches, actions, training, experience, insurance and technology that can be used for protection of cyber environment, resources of the organization and the user. The organization and user resources include connected computing devices, staff, infrastructure, applications, services, telecommunication systems, and the complex of transmitted and / or stored information in the cyber environment. Cyber security is focusing in achieving and maintaining the security properties of the organization's or user's resources against relevant security risks in the cyber environment. The main safety goals include:
- Availability;
- integrity, which may include authenticity and non-repudiation;
- confidentiality.
The world cannot be imagined without a computer. It involves every sphere of daily life. Consequently, cyber security concerns everyone, even if not everyone is aware of this. Cyber security covers concepts such as the protection of personal data, to be precise - the detection, avoidance, or a reaction to the attack.
Risks
There are a variety of risks. From the malicious software that can permanently delete your entire system, as well as interference in the computer system, where can be not authorized data manipulation for destructing other systems, or even stealing personal files. Despite the fact that 100% protection is not possible, you can get closer to the ideal, resorting to the usual precautions, and reducing the risk. First of all, we will try to identify and explain the risks and associated key concepts.
Hackers and attackers
Hackers / attackers - this uninvited guests, who have nothing to do with your system. They illegally use security gaps and weaknesses of the computer system locations to conduct their own machinations.
Malvars
Malvars - it is a generalized term for software that performs undesirable function on the damaged computer invisibly to the user. The concept of Malvar is divided into the following categories.
Trojans
Trojans differs from worms and viruses in the inability to be reproduced independently. Trojans contain a hidden program part, which opens the black entrance to the damaged computer and thus provides almost full access to the damaged system invisibly to the user. These insidious programs can be sent by mail as well as screensavers or games. It is enough to run once and the whole system will be infected.
Worms
The worm, as opposed to the virus, not attached to the work files. It is distributed over the network or other related PC.
Email worms
While you distribute e-mail, worm can use the e-mail programs (e.g. Outlook, Outlook-Express) or its own SMTP. In addition to network traffic and the increased consumption of system resources, worms may contain other harmful functions. Significant representatives of this group are the "Beagle" and "Sober".
Peer-to-Peer-worms
P2P worms copies to the shared from the Pier-to-Pier file sharing folder like "Emule", "Kazaa", etc. There they wait for a victim under attractive names of actual software or a reputable person.
Viruses
Viruses also tend to own reproduction and spreading to other computers. In addition, they attach themselves to other files or embedded in the boot sector of data carriers. Often, they are quietly infiltrate from removable storage media (such as a floppy disk), through network (also P2P networks), by e-mail or from the Internet.
Viruses can be installed in various places of the operating system and act through different channels. There are several groups of viruses:
Master Boot Record Viruses
MBR Viruses set before the boot sector of data carrier and ensure that the boot process through the storage is first read by the virus code, and then the original boot sector. Thus, the virus is seamlessly incorporated into the system and from that moment acts when the hard drive is booting. Often the virus code is stored in the memory after infection. Such viruses are called "memory resident". When you format a floppy disk the virus is passed on and can spread to other computers. But the download area can remain active for all the formatting process. So DOS-command «DIR» can trigger transmission of the virus from an infected floppy disk. Depending on the type of malware viruses, loading areas can be very dangerous or just cause interference. The oldest and widespread virus of this type is called the «Form».
File viruses
Many viruses use the opportunity to hide in the working files. At the same moment. host file can be deleted or overwritten, as well as the virus itself is attached to the file. In the latter case, the file code remains functional. If a working file is requested, in the assembler program, so first starts virus code and only then the original program (if it is not removed).
Multicomponent viruses
This group of viruses is especially dangerous, as its representatives not only infect the boot sector (or disk partition table), but the executable files
Companion viruses
In DOS COM files runs of the same name EXE files. At a time when computers were controlled through the command line, this effective mechanism has worked to run malicious code on your computer.
Macro viruses.
Macro viruses attach themselves to files. But they are not executable. Macro viruses are written not only on assembler, but also at the macro language such as Visual Basic. In order to execute the viruses, you need a macro language interpreter commands, which is integrated into Word, Excel, Access and PowerPoint. Otherwise, the macro can be run with the same mechanisms as the file viruses. They can be coded, even infect the boot sector or install companion viruses.
Hidden viruses and root kits
Hidden viruses or viruses stealth have protective mechanisms in order to avoid detection by virus search programs. At the same time they take control of various system functions. If this mode is set for the first time, the viruses from normal access to files or system areas cannot be set. They imitate the status of not infected files for the virus scan program or make the file invisible to anti-virus protection. The mechanism of stealth viruses takes effect after the virus becomes resident in memory module.
Polymorphic viruses
Polymorphic viruses contain mechanisms to modify them in each infection. For this, the parts of the virus are coding. The information contained in the virus, encoding the program creates for each copy the new key, and sometimes even new encoding software. The command sequence can be modified or randomly mixed, if it is not critical for the existence of the virus. Thus, there are billions easily virus variants. In order to recognize and destroy the encoded and polymorphic viruses to install the classic anti-virus signatures are not enough. The special programs must be written.
It is difficult to analyze and provide appropriate countermeasures. Thus, polymorphic viruses without exaggeration can be referred as the royal class of viruses.
Intended вирусы
Under Intended viruses we understand partially defective virus that produces a primary infection and can no longer reproduce.
Many of these attacks affect a wide range of private, corporate and public interests.
The main trends of the threats are following:
- increase in the number of attacks, many of which lead to large losses;
- increase in the complexity of attacks, which may include several stages and apply special methods of protection against possible counter methods;
- impact on almost all the electronic (digital) devices, including the recently acquired increasing importance of mobile devices, as they are most exposed to risks in the field of information security;
- increasingly frequent attacks against the information infrastructure of large corporations, major industrial facilities and even government agencies;
This is confirmed by daily news, which reports new attacks of the criminals on the information world.
Without the system analysis and evaluation of the receipt of the application or other measures it is impossible to build an effective cyber security system. It seems appropriate that complex cyber security research should include the following areas:
1. Developing a common terminology of cyberspace and cyber security, harmonized with the existing terminology in the field of information security.
2. Development of an integrated system of indicators covering all aspects of the functioning of cyberspace and to ensure its protection against possible threats.
3. The creation of special methods to ensure the stability of cyberspace or its threats. Here are a few possible topics:
• analysis of the topological structure and make recommendations for its amendment, methods and specific algorithms for their implementation;
• New methods of cryptographic protection, based not only on a purely computational implementation mechanisms of resistance, but also to take advantage of multiply architecture links and a large number of law-abiding users;
• information security techniques based social services to deal with cyber-attacks, with special group behavior analysis procedures.
4. Intelligent methods to ensure cyber security:
• intelligent user identification methods;
• intelligent methods of preventing viral and other attacks;
• intelligent methods of attack and intrusion detection;
• methods of situational analysis of information security status;
• New methods of cryptographic protection, based on neural network technology.
Lecture №9
Lecture’s topic: Internet technologies
Lecture’s goal: to tell students about the search and identification of a computer in the Internet using the IP-address and a domain name; introduce Internet protocols, providing transmission and delivery of information; to introduce to the students with the Internet services
1) Addressing in the internet.
2) Data transmission protocols.
3) Internet services:
· WWW technology
· File archives
· Internet telephonie
· E-commerce.
1) Every computer connected to the Internet has a unique 32-bit (in binary) IP-address. IP-address contains the network address and the address of the computer in this network.
Depending on the number of computers in the network, addresses are divided into three classes A, B and C. The first bits of the address are assigned to identify the class and the rest is divided into a network address and address of the computer (see the table).
| Class А | Network address (7-bit) | Computer address (24-bit) | |||||
| Class В | Network address (14-bit) | Computer address (16-bit) | |||||
| Network address (21-bit) | Computer address (8-bit) | ||||||
For example, the network address class A has only 7 bits for the network address and a 24 bit address for the computer, i.e. may exist only 27 = 128 networks of this class, but each network may contain 224 = 16 777 216 number of computers.
In the decimal system, IP-address consists of four numbers separated by dots, each of which lies in the range from 0 to 255 (e.g., 195.34.32.11). On the first of these numbers is possible to determine a computer belonging to the network of a particular class:
· Address of class А – the number from 0 to 127;
· Address of class В – the number from 128 to 191;
· Address of class С – the number from 192 to 223.
Providers often provide users with Internet access without constant, but with a dynamic IP-address, which can change every time you connect to the network.
Since the numeric IP-address is not easy to remember, for convenience, the Domain Name System (DNS) was introduced. This system assigns to a numeric IP-address a unique domain name.
Domain names and IP-addresses are allocated by international coordination center of domain names and IP-addresses (ICANN), which includes five representatives from each continent.
DNS has hierarchical structure:
 top level domains
top level domains
second level domains
 |
and so on …
Top-level domains are of two types: geographical (two-letter, that is, each country has the two-letter code) and administrative (three-letter).
Let’s consider some of the names of top-level domains:
| Administrative | Type of organization | Geographical | Country | |
| Commercial | ca | Canada | ||
| edu | Educational | de | Germany | |
| gov | Governmental | jp | Japan | |
| int | International | ru | Russia | |
| mil | Military | su | Former USSR | |
| net | Computer network | uk | England/Ireland | |
| org | Not commercial | us | USA |
For example, Microsoft has registered a second level domain Microsoft in administrative top-level domain com. Names of computers, which are web servers, include the full domain name and the actual name of the computer. For example, the company's main server name www.microsoft.com.
2) Communication protocol TCP / IP.
The development of the Internet is possible because the use of a common data transfer protocol TCP / IP. The term TCP / IP includes the name of two protocols:
· Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) – transport protocol;
· Internet Protocol (IP) – routing protocol.
Let’s consider each of them in detail.
IP protocol.
The information transmitted on the network, is "packed in an envelope" on which is "written" the IP-address of the recipient and the sender's computer. The contents of this envelope is called the IP-packet and it is like the set of bytes. The IP-packets on their way to the recipient computer pass through many intermediate servers of the Internet, where there is a routing operation. As a result of routing, IP-packets are routed from one web server to another, gradually approaching to the recipient computer. This routing provides the IP protocol.
The speed of receiving information depends on the route.
TCP protocol.
Often, computers on the Internet need to share large files. If you send a file as a whole, it may "clog" the communication channel for a long time, making it unavailable for other messaging. To avoid this, the sender computer need to split a large file into smaller pieces, number them, and transport in the IP-specific packages. The receiving computer must gather these packets into the original file in the correct sequence. Such fragmentation of files on IP-packets during transmission, and the assembly process during obtaining files provides TCP transport protocol.
For the IP-protocol specific parts of the file are not connected to each other, so the last IP-packet can overtake the first, and even delivery routes of these packets can be completely different. However, the TCP will wait for the first IP-packet and gather the source file in the correct order.
Internet services
· WWW technology.
WWW (World Wide Web) is an Internet technology which is based on creating hyperlinks. Such links implement transitions within the source document to any other document located on computer, and on any document of any computer currently connected to the Internet. As we already know, the hyperlink consists of two parts:
· reference pointer - object (a piece of text or a picture), the activation of which causes the transition.
· The address of the link - the path to the object to which the transition will be carried out.
The text containing control characters (tags) that are displayed in a special program (browser) as the form of web-pages, called hypertext. With tags, you can change the size, style and color of the characters, background, define the position of the text on the page, insert hyperlinks, etc. You can create web-pages by HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language.
Nowadays, we have following types of web pages.
· Multimedia - contain links to media objects: graphics, animation, sound, and video.
· Interactive - contain forms that could be filled by users.
· Dynamic - may be changed after loading in the browser (i.e., web-pages are considered as a set of objects which properties can be changed). For example, moving the title or changing its color.
Now, let’s consider a universal resource locator (URL), which allows to find in the Internet any web-page or file.URL includes protocol access to the document, the domain name or IP-address, which contain a document, and also the path and own name the file: protocol://domain_name/path/file_name.
Access protocol to the document defines a way of transferring information. To get access the web-page we use HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol). Let’s consider this URL as an example:
http://schools.keldysh.ru/info2000/index.htm
It consists of three parts:
http:// – access protocol;
schools.keldysh.ru – server’s domain name;
/info2000/index.htm – the path to the file and the name of the page.
Browsers
Browser - a special program, which helps in browsing web-pages. Today, the most common browsers are Google Chrome and Internet Explorer. Browser settings allows you to change the browsing options of web-pages.
· File archives
The hundreds millions of various files stores in Internet (software, device drivers, images and sound files, and so on). These files are located on a special Internet servers (file archives). With these servers, users can "download" the various required files.
Many companies support file servers. Like software developers, computer manufacturers of hardware components and peripherals. The software that hosted on the servers is freely available (freeware) or shareware, and therefore, "downloading" some file, the user does not violate copyright law on software.
Many file servers can be operated using a browser, as they support the web-interface.
Access to files on the file archive servers is possible via HTTP and FTP (File Transfer Protocol). The FTP protocol allows you to download files from a remote file archives server on the local computer and upload files from the computer to a server, for example, in the process of publishing a web-site.
You can download the file to your local computer by using:
· Browsers;
· Special software (for example Go!Zilla, ReGet and etc.).
Мобильный Интернет.
WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) - it enables wireless access to the Internet from a mobile phone resources (which is supported by WAP).
WAP-pages are located on web-servers and presented in a special WML format. This markup language specifically adapted to the mobile phone features - two-color graphics, small screen and small memory.
WAP-pages contain a variety of political, economic and sports news, weather forecast, exchange rates and so on. You can also send e-mail and participate in a WAP-chat.
In addition, the technology GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) allows full high-speed Internet access.
E-commerce in Internet
E-commerce is a – it is a commercial activity in the field of advertising and distribution of goods and services through the Internet.
Let’s consider main areas if e-commerce.
Hosting – hosting services on the Internet, that is, the assignment of disk space for a web-site on the web-server, providing access to this site through the communication channel with a specific bandwidth and site administration rights.






