The tax system includes a plurality of charged in state taxes, fees and other charges, as well as forms and methods of their control. The tax system plays the role of application: 1) with the help of the government accumulates financial resources necessary for the implementation of its functions, 2) regulates the development of production through the reallocation of money, 3) interferes in the "work" of the market.
Taxes - required cash payments collected by the state from legal entities and individuals. In accordance with the tax laws, use the following classification of taxes:
by the method of withdrawal - direct and indirect,
the nature of charges - progressive, regressive, proportional.
the level of collection - centralized and local.
Direct taxes are levied on all types of income (wages, profits, inheritance). Among this kind of tax is the most well known income tax (for the first time was introduced in England in 1799).
Indirect taxes paid by the end consumer products and are a supplement to the prices of the goods and services. Indirect taxes are the most significant part of the tax revenue to the state budget, they account for almost 80% of the amount of tax payments. There are three main types - excise taxes, fiscal monopoly taxes and customs duties. Customs duty - the amount of money charged for transport of goods across the border, which is regulated by the external economic activity. Fiscal monopoly tax - a tax on those goods whose production is a state monopoly. The most common are the indirect tax excise - supplements to the price of a wide range of consumer products (tobacco, jewelry, furs, as well as communication services, transport, etc.).
Progressive tax increases as income, i.e., increasing the tax rate is set to the growing amount of income.
Regressive tax - a tax that is the same for all payers (excise).
Proportional tax - a tax for which the tax rate does not change depending on the different value of the assets of enterprises and individuals.
Typically, centralized taxes paid into the State budget, where and redistributed as grants (to cover the deficits of local budgets), or subsidies - to finance targeted interventions returning local administration.
Local taxes (land tax, tax on property of the citizens, the local license taxes) are used by local financial authorities to address socio-economic problems in the field.
Taxes, as a major lever of financial policy, the following functions:
a) economic - regulate and control economic processes;
b) social - support the social balance between the incomes of various social groups in order to diminish the inequality between them;
c) fiscal - form the income of the state.
"Laffer Curve", which describes the relationship between tax rates and tax revenues to the budget as follows (Fig. 27). Where: t r-marginal tax rate, and T is the sum of tax revenue.
|



|

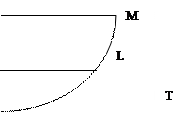 |
Fig. 27. Laffer curve
Based on the graph shows that the increase in the tax rate provides an increasing amount of cash to the state budget, however, reaching the maximum level (say, 50%), government revenues will decline. The tax rate has been withdrawn on all income is confiscatory measure, leading to cuts in legal activity. In practice, the "Laffer curve" is applicable only under the action of the free market mechanism. In conditions of economic transition effect Laffer effect is very limited.
Under the fiscal (tax) policy of the state means a permanent state intervention in economic processes and phenomena in order to regulate their course. This is a set of activities in the field of taxation, aimed at:
- The formation of the state budget - improving the functioning of the national economy, economic growth - employment and the stability of the currency.
The process of formation of fiscal policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan is in a complex of contradictory situation. In the early stages of restructuring the state has lost control over the economic activity, pricing, has not created a legal basis for the tax system. With the increase in tax rates has stopped investment in the sphere of material production, capital focused in the field of trade and mediation, which took criminal. Tax collection amounted to 50-55 per cent of the planned budget amounts. Demonstrated the law of supply: the higher the tax rate the less money goes to the cashier. Internal Revenue Service has become so large that it starts to work on herself. Since the late 90s, a system of the State register of natural persons and begins introducing complete declaration of incomes. However, it is necessary to consider two things: the psychology of people unaccustomed to clear records of their income and expenses, as well as old women and engineers that sell seeds in mass transit and crowds. They left in a public place driven by need and put them around the tax inspector with the state cup would be sacrilege.
The basis of the fiscal policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan is expected to enter the following principles:
- The foundation of the entire tax system should make direct taxes on land, property, capital, income of individuals and legal entities and corporate income;
- Indirect taxes should be applied in the form of excise taxes in order to protect their own producers, limiting the consumption of certain goods, as well as luxury items and income producer monopolist - applications of differential rates of taxation depending on the amount of income received;
- The elimination of unjustified benefits of taxation.
14.6 International relations: the nature, form
The economy of different countries, including Kazakhstan, has a tendency to form a single global economy, to integration, internationalization of economic science and to an increase in international relations. In this case, all the national economy should be closely linked multiple forms of these relationships.
Basic forms of international economic relations.
1) International trade in goods and services;
2) International loan;
3) The international migration of capital;
4) An international labor migration;
5) International scientific links;
6) The formation of free economic zones;
7) International monetary relations;
8) Economic integration.
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between the national economies of the different countries, which is based on the international division of labor (MRI).
MRI are the main factors:
1) Social and geographical factors (geographical location of the country, territory, population, population structure, economic experience and traditions).
2) Natural and climatic conditions (varies by climate, to provide arable land, minerals, water).
3) Technical and economic factors are determined by the fact that countries have different scientific and technical potential of the economy, which makes the production of certain goods cheaper and some more expensive.
Benefits of international specialization and trade can be absolute or relative.
International trade flows are divided into exports and imports. The sum for each country of the foreign trade turnover. Quantitative indicators are included in the balance of trade, reflecting the ratio between cash payments and receipts for all commodities transactions.
Most states actively regulate international economic relations, as in foreign trade have historically two forms of public policy:
1. Protectionism - a policy to protect domestic producers from foreign competition.
The essence of politics: curbing the country's highly competitive foreign products and the protection of the export of goods of national production.
Measures of protectionism: tariffs or tariff barriers, import taxes, raise prices, non-tariff barriers, fiscal policy, import quotas that limit the amount of import licensing, various restrictive rules, regulations and practices.
2. Free trade (liberalism) - is no different product policy barriers.
The benefits of free trade:
1) stimulate competition;
2) limits the monopoly;
3) increases the efficiency of production;
4) reduce the price;
5) improve the quality of products;
6) large selection of products for consumers;
7) ensure the efficient allocation of resources of the world economy.




