1-angle iron (angle), уголкова€ сталь (уголок); 2-leg (flange, полка) 3....T-steel girders, стальные балки; 3-T-iron (tec-iron), таврова€ балка (та€^юва€ сталь), 4-vertical leg, вертикальна€ полка; 5-flaage, полка; 6-H-girder,(H-l>eam), двутаврова€€.балка;
7-E-channel (channel iron), швеллерна€ сталь ќйвелд^^;8-г&и€4№ат, кругла€ сталь;
9-square iron, квадратна€ брускова€^-сталь; 10-flat bar, пейгосоваусталь; tl-strip steel, ленточна€ сталь (штрипс); 12-ironwire, стальна€ проволежа; 13...SO-serewswaSbelts, винты и болты; 13-hexagonat-fepad bolt, болт с шестигранной гол№вкйй; 14-bead, головка; 15-shank, стержень; 16-thread, резьба; 17-washer, шайба (прокладка);
18-hexagonal nut, шестигранна€ гайка; 19-spHt pin, шплинт; 20-rounded'e'ad, скругленный конец; 21-width of head (of flats), размернэд i&HO%;-.32-stud, жвилька;
23-point (end), конец (острие); 24-castlenut (castellated nut), к&рончатадгайка^25-11о1е for the split pin, отверстие под шплинт; 26-cross-head screw, a snect-metal screw (self-tapping screw), винт с полукруглой головкой (самонарезающий винт);
27-hexagonal socket head screw, винт с шестигранной головкой под торцевой ключ;,.
28-countersunk-head bolt, болт с потайной (утопленной) головкой; 29-c^tch, контровка;
30-locknut (locking nut), контргайка; 31-bolt (pin), концевое тело Хшпильки;
32-cotlar-head bolt, болт с гребенчатой головкой; 33-set collar (integral collar), гайка с контргайкой; 34-spring washer (washer);пpyжиннa€ шайба (шайба √ровера); 35-round nut, an adjusting nut, кругла€ гайка, регулировочна€ гайка; 36-cheese-head screw, a slotted screw, винт е цилиндрической головкой, винт под отвертку; 37-tapered pin, конический штифт; 38-screw slot (screw slit, screw groove), шлиц под отвертку;
39-sauare-head bolt, болт с квадратной головкой; 40-grooved pin, a cylindrical pin, желобчатый штифт, цилиндрический штифт; 41-T-headbolt, болте тавровойголовкой;
42-wing nut (fly nut, butterfly nut), гайка-барашек; 43-rag bolt, заершЄнный болт'(ерш);
44-barb, бородка; 45-wood screw, шуруп (винт дл€ дерева); 46-countersunk head, потайна€ головка; 47-wood screw thread, резьба шурупа; 48-grub screw, винт без головки со шлицом под отвертку; 49-pin slot (pin slit, pinХjs^oove),шлиц;, 56-round end, скругленный конец; 51-nail (wire nail),, гвоздь (проволочный гвоздь); 52-head, головка (шл€пка); 53-shank, стержень; 54-point, острие; 55-roofing nail, кровельный гвоздь;
56-riveting (lap riveting), клепка внахлестку; 57.,.60-rivet, заклепка; 57-sel head (swage head, die head), a rivet head, закладочна€ головка; 58-rivet shank, стержень заклепки;
59-closing head, замыкающа€ головка; 60-pitch of rivets, шаг заклепочного шва;
61-shaft, вал; 62-chamfer (bevel), фаска; 63-journal, шейка; 64-neck, цапфа; 65-seat, седло;
66-keyway, шпоночна€ канавка (Ўпоночный паз); 67-conical' seat, коническое седло;
68-thread, резьба; 69-ball bearing, an antifriction bearing, шарикоподшипник, антифрикционный подшипник; 70-steel ball (ball), стальной шарик подшипника;
|
|
|
71 -outer race, наружное кольцо шарикоподшипника; 72-inner race, внутреннее кольцо шарикоподшипника; 73.,.74-keys, шпонки; 73-sunk key (feather), закладна€ шпонка;
74-gib (gib-beaded key), врезна€ шпонка с выступом; 75.,.76-needle roller bearing, игольчатый подшипник; 75-needle cage, сепаратор иглы; 76-needle, игла; 77-castle nut, корончата€ гайка; 78-split pin, шплинт; 79-casing, кожух; 80-casing cover, крышка кожуха; 81-grease nipple (lubricating nipple), ниппель шприца дл€ консистентной смазки; 82...96-gear wheels, cog wheels, шестерни, зубчатые колеса; 82-stepped gear wheel, ступенчатое зубчатое колесо; 83-cog (tooth), зуб шестерни; 84-space between teeth, впадина зуба; 85-keyway (key scat, key slot), шпоночна€ канавка (шпоночный паз); 86-bore, отверстие; 87-herringbone gearwheel, шевронное зубчатое колесо;
88-spokes (arms), спицы; 89-helical gearing (helical spur; wheel), геликоидальна€ (спиральна€) зубчата€ передача; 90-sprocket, цепна€ звездочка; 91-bevel gear wheel (bevel wheel); коническое зубчатое колесо; 92.,.93-spiral toothing, спиральное зубчатое зацепление; 92-pinion, ведущее зубчатое колесо; 93-crown wheel, коронное зубчатое колесо.
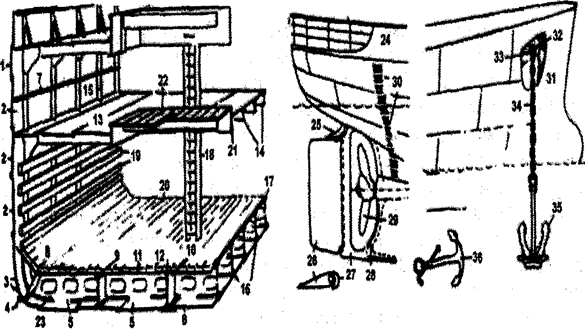
Hull framing
1. Sheer strake
2. Side strake
3. Bilge strake
4. Bilge keel
5. Bottom plating
6. Flat plate keel (keel plate)
7. Stringer (side stringer)
8. Tank margin plate
9. Longitudinal side girder
10. Center plate girder (kelson, keelson, vertical keel)
11. Tank top plating plating (tank top, inner bottomplating)
12. Senter strake
13. Deck plating
14. Deck beam
15. Frame
16. Floor plate
17. Cellular double bottom
18. Hold pillar
19. Side battens (side ceiling, spar ceiling)
20. Selling (flor ceiling)
21. Hatch coaming
22. Hatch cover (hatchboard)
23. Guard reil
24. bulwark
25. Rudder stock
26. Rudder blade
27. Rudder post
28.Propelerpost
29. Propeller
30. Draft marks
31. Bow, stem
32. Hawse
33. Hawse pipe
34. Anchor cable
35. Stockless anchor
36. Stocked anchor

|
Floating dock
1. Side tank (wall)
2. Bottom tank
3. Keel block
4. Bilge block (side support)
5. Flooded floating dock
6. Tug towing the ship
7. Emptied (pumped out) dock
GENERAL ARRANGEMENT API

lignum vnae
pintle
бакьут
штыри
CAST STEEL STERN FRAMES


STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
Stresses
TENSION
| STRESSES |
| √-L |
| COMPRESSION SHEAR |

TORSION

|
My - torsion moment <p - angle of torsion
Stress is load or force acting per unit area and is usually expressed in kilogrammes per square millimetre or Pa (ѕаскаль).
Strain is the distortion (деформаци€) in a material due to stress. Stresses are of three main types:
Sensile - forces acting m such a direction as to increase the lengu. Coi^pressive - forces acting in such a direction as to decrease the leflgth. Shear ' the effect of two forces acting in opposite directions and along parallel lines. The forces act in such a direction so as to cause the various parts of a section to slide one on the other. Stress is proportional to the distance from neutral axis passes through. centroid of the section.
|
|
|
Strength of materials.
When a force, or a load, is appUed to a solid body it tends to change the shape of the body. When the applied force is removed the body wiUrestQrei^.ori^ria shape. This property of returning to their original shape is termed 'e^Mlate'.
Should the applied force be large enough, the resistance offeredbythematerial will be overcome and when the force is removed the body will no longer return to its original shape and will become permanently distorted.
The point at which the body ceases to be elastic and becomes рей^эде^у distorted is termed 'yield point' and the load which is applied to eausethis istffr 'Х 'yield point load*. The load is then said to have undergone 'plastic deformation or now*.
Whenever a change of dimensions of a body occurs a state of strain is set up in that body.
allowable stress bending
bending moment v elasticity
elastic deformation elastic limit elongation fatigue
fatigue stress fracture.rupture ductile fracture hardness loading "plasticity
rigidity, stiffness safety factor shear strength stress
stress concentrator tensile strength torsion yield point
допускаемое напр€жение изгиб
'изгибающий момент упругость ^Дзд,, упруга€ деформаци€ предел упругости удлинение
усталость - я сопротивление усталости разрушение в€зкое разрушение твердость нагружение пластичность жесткость запас прочности сдвиг
прочность напр€жение
концентратор напр€жени€ предел прочности (раст€ж.) кручение предел текучести


с)


Spanners and pliers
a - diagonal cutting nipper and "alligator", pipe grip and spanner in one; b - combination pliers;
с - screwdrivers; d - spanners and ajustable wrenches
| b) |

|

|

Hammers and chisels a - hammers; b - flat cold chisel and crosscut shisel

1 ________ 6


3 8

|

|

|

5__________
1. Combination Wrench 6. Ratchet Handle
2. Box End 7. Socket Extension
3. Ratchet Box End 8. Standard Socket
4. Hinged Offset Socket Handle (Breaker Bar) 9. Impact Socket
5. Speeder Handle 10. Universal Socket
SOCET EXTENSIONS


|

|

UNIVERSAL JOINT
' Allows access to a bolt from an angle. Ideal for use in confined areas where direct access is impossible.
SOCKET EXTENSION.
Allows the tightening of a bolt in a recessed area. Extensions are available in any of the various drive sizes (1/4", 3/8", etc).

Wrench to provide required mechanical leverage to hold, twist or turn an object such as a nut or bolt

|

Sockets and key sets

Clamp and pressure gauge Multy-meter






