1. What kind of shops in this country do you know?
2. What shops are situated not far from your house?
3. What goods can be bought there?
4. What specific features do channels of distribution have in this country?
5. What reforms does this country need to reorganize the channels of distribution?
Exercise 4. Translate into English.
1. Розничная торговля - это продажа товара конечному потребителю.
2. В западных странах есть различные типы торговых учреждений: универмаги, супермаркеты, магазины с низкими ценами, посылторги и т.д.
3. На этот товар можно получить 10% скидку.
4. Розничный торговец может представить покупателю длительный кредит.
5. Эта фирма имеет множество торговых точек по всей стране.
6. Розничный торговец выполняет много важных функций.
7. Я не знаю центр города, мне необходим справочник магазинов.
8. В торговом центре вы найдете все необходимые вам товары.
9. В этом магазине нет бакалейного отдела.
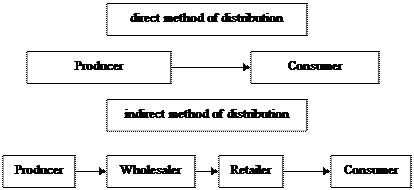
Exercise 5.
a) speak about the differences between the channels of distribution of this country and western countries.
b) look at this chart and say in what industries different methods of distribution are possible.
Grammar Exercises
Exercise 1 Change the sentences according to the model
M o d e l: I should go shopping today.
I should have gone shopping yesterday.
1. The firm should apply for credit very soon.
2. They should see about the new refrigerator today.
3. I should take my wife shopping a bit later.
4. Тhey should get groceries at the supermarket this afternoon.
5. You should order a new car.
6. He should buy a computer today.
7. He should speak with the manager today.
Exercise 2. Change the sentences according to the model.
M о d e l: If there is a shopping center nearby, we will go there together.
If there had been a shopping center nearby, we would have gone there.
1. If she buys too much, she won't be able to carry it herself.
2. If there is ice cream in this store, we will bring the children some.
3. If she tries the new boutique today, she will come very late.
4. If the shop offers home delivery, he will ask them to deliver.
5. If you shop downtown, you will find the shopping center.
80
LESSON 13
PRICING
Теxt
All products and all services have prices. The price depends on different thing such as credit terms, delivery, trade-inallowance, guarantees, quality and other forms of service, which price can produce the biggest profit during a long period of time. It's hardly possible to determine such a price. The price may be too high to produce a large volume or too low to cover costs. No other area of marketing operations has been a subject to bad practice. Many businesses persue unsound price policies for long periods of time and are not aware about it.
Prices can be determined in different ways. For example, the prices of meat, cotton and other agricultural prices can be decided in large central market where forces of supply and demand exist. This is pure price competition. The prices on industrial products (iron; steel, etc.) are usually decided by large companies. As a rule the amount and price of goods sold to large number of buyers is controlled by a few competing sellers. Prices also can be set by the government, usually for different public services - railroads, electricity, manufactured gas, bus services, etc.
If demand increases, prices rise, profits expand and new investment is attracted. But other factors may be involved as well. Prices are related to each other in different ways. Ultimately, everything is related in price, since the consumer can buy and must pay for everything out of a particular, limited amount of money.
Active Vocabulary
credit terms- кредитные условия.
trade-in allowance - сумма денег, отданная за старую вещь и включенная в счет покупки новой
to cover costs - покрывать затраты
to persue unsound price вести неразумную
policies - ценообразовательную политику
supply and demand- предложение и спрос
price competition- конкуренция в ценообразовании
to set prices- устанавливать цены
Comprehension Questions
1. Why is it difficult to determine the right price?
2. Why is the seller interested in the price that produces the highest volume of sales at the lowest unit cost?
3. Why do many businesses follow unsound pricing policies?
4. In what way are agricultural prices decided?
5. How are industrial products usually priced?
6. Why does the government usually set the prices for public utility services?
7. Why is it so important to know the levels of supply and demand when dealing with pricing?
8. Why is everything related by price?
Vocabulary Practice






