1. Персональним комп’ютером може бути домашній комп’ютер, що підключений до інтернету.
2. Велика металева коробка,що є головною частиною комп’ютеру називаеться футляр.
3. Футляр та його складові (пам'ять, системна плата та ін.) називається системний блок.
4. Монітор відображає текстові символи та знаки.
5. Клавіатура використовується для набору команд, символів та знаків.
IV Comprehension.
Ex. 10 Find in the text a passage describing:
1. The main parts of the system.
2. The functions of the keyboard.
3. The definition of the personal computer.
4. The display and the adapter card.
5. The functions of drives.
Ex. 11 Agree or disagree with the following statements.
1. Personal computer is used by many people at the same time.
2. The case and its contents are called the system unit.
3. The mouse works if you hold it in the air.
4. The optical drive can play DVDs, CDs and cassettes.
5. The monitor displays text characters and graphics.
6. The hard disk drive is outside the computer.
7. A display adapter card builds the video images.
Ex. 12 Answer the following questions.
1. What is personal computer?
2. What are the main parts of the system?
3. What is called the case?
4. What functions has the case?
5. Haw does the mouse work?
6. What do the floppy drives provide?
7. What is the difference between floppy drives and hard drives?
8. What can the optical drive play?
VII. Oral Practice.
Ex. 13 speak on the following problems
1. The functions of mouse.
2. The main functions of the case.
3. A display adapter card.
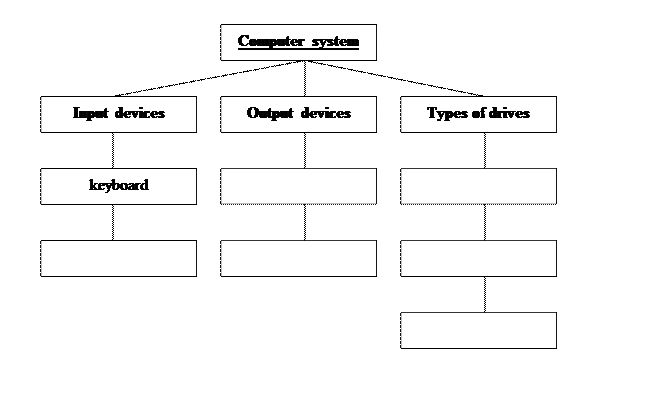
Ex 14. Fill in the chart. Speak on the topic “Computer system”

VI Reading and comprehension.
Ex. 15 Read the text B without a dictionary for 5 minutes and say what problems are mentioned in the text.
Personal computers
Personal computers also called microcomputers or home computer. The most compact are called laptops. They are portable and work on build-in batteries.
Personal computers are designed for use at homes, schools,and offices. At home they can be used for home management (balancing the family finances, for example) and for playing computer games, watching films or listening to music. Schoolchildren can use computers for doing their homework and many schools now have computers for independent learning and computer-literacy studies. In the office personal computers may be used for word processing, bookkeeping, storage and handling of necessary information.
Personal computers were made possible by two technical innovations in the field of microelectronics: the integrated circuit, or IC, which was developed in 1959 and the microprocessor that first appeared in 1971. the IC permitted the miniaturization of computer-memory circuits, and the microprocessor reduced the size of a computer’s CPU to the size of a single silicon chip. Because a CPU calculates, performs logical operations, contains operating instructions, and manages data
flows, a complete microcomputer as a separate system was designed and
developed in 1974.
In 1981, IBM Company offered its own microcomputer model, the IBM PC that became a necessary tool for almost every business. The PC’s use of a 16-bit microprocessor initiated the development of faster and more powerful personal computers, and its use of an operating system that was available to all other computer makers led to a standardization of the industry.
In the mid – 1980s, a number of other developments were especially important for the growth of personal computers. 0ne of these was the introduction of a powerful 32-bit CPU capable of running advanced operating systems at high speeds.
Another innovation was the use of conventional operating systems, such as UNIX, OS/2 an Windows. The Apple Macintosh computers were the first to allow the user to select icons – graphic symbols of computer functions – from a display screen instead of typing commands. New voice-controlled systems are now available, and users are able to use the words and syntax of spoken language to operate their personal computers.
Vocabulary:
Device – устройство
Intelligence – разум
Hardware – оборудование
Software – программы
Processing – обработка
Procedures – процедуры, операции
Perform – выполнять
Manner – манера, способ
Various – различные
Purpose – цель
Ex. 16. Answer the questions:
1. What kinds of personal computers do you know?
2. What technical innovations influenced on the designing of computer?
3. What is differences between early personal computers and today’s computers?
Ex. 17 Read and translate the text with a dictionary:
What is hardware?
What is hardware?
Webster’s dictionary gives us the following definition of the hardware –
the devices composing a computer system. Computer hardware can be divided into four categories:
Input hardware collects data and convert them into a form suitable for computer processing. The most common input device is a keyboard. It looks very much like a typewriter. Processing hardware directs the execution of software instructions in the computer. The most common components of processing hardware are the central processing unit and main memory.
The purpose of storage hardware is to store computer instructions and data and retrieve when needed for processing. Storage hardware stores data as electromagnetic signals. The most common ways of storing data are Hard disk, floppy disk and CD-Rom. The purpose of output hardware is to provided the user with the means to view information produced by the computer system. Information produced by the computer system. Information is in either hardcopy of softcopy form. Hardcopy output can be held in your hand, such as paper with text (word or numbers) or graphics printed on it. Softcopy output is displayed on a monitor.
Unit 5
An operating system
I. Language.
Ex. 1. Remember the following words and word combinations:
device driver – драйвер пристрою
device file – файл пристрою
format (v) - форматувати
format the disk – форматувати диск
integration of dynamic data – інтеграція динамічних даних
keep track of- слідкувати за
kernel (n) - ядро
manage files – керувати файлами
manage information in memory – керувати інформацією в пам’яті
manage the flow (stream) of information – керувати потоком інформації
multimedia extension – розширення мультисередовища
multitasking OS – багатозадачна ОС
operating system - операційна система
portability (n) – рухливість, мобільність
shell – оболонка
single-tasking OS – однозадачна ОС
support application programs- підтримувати прикладні програми
Ex. 2 Make pairs of antonyms:
Similar, secondary, in practice, descendent, advantage, permanent, minor, top, exclude, an extensive number, ancestor, few, internal, specific, major, primary, temporary, external, different, bottom, general, include, in theory, drawback.
Ex. 3 Make pairs of synonyms:
Manage, multiple, involve, significant, interpret, control, numerous, translate, display, need, allocate, purpose, tie, show, require, contain, integration, aim, connect, important, check, hold, combination, goal, share, examine, cooperate, shell, divide, instruction, retrieve, work together, include, nuclear, command.






