In Russia (and CIS), including Kazakhstan, the following options for laying fiber optic link:
- Laying in wOC primer in protective polyethylene pipes (I);
- Laying FOC in protective plastic conduits and symmetrical copper cable to solve the distillation, interoffice communication and signaling circuits in liquidation communication overhead line (II);
- Suspension FOC transmission line supports up to 10 kV, and supports high-voltage lines of automatic block system (III);
- Suspension FOC on the contact rail network supports (IV). Below is a table that compares key indicators.
The following table 1.4 compared methods of laying OC on the basic parameters.
Table 1.4-A comparison of methods for laying OC key indicators
| Variants | Main factors | ||||||||
| The cost of material resources | Reliability | Speed of construction | Repairability | Durability | Operating costs | The ability to replace the cable at reconstruction | Workability | A place | |
| I | + | I | |||||||
| II | + | II | |||||||
| III | + | III | |||||||
| IV | + | IV |
The method directly into the ground along the railways and roads unprotected against mechanical damage and rodents. However, the method is facilitated by direct burial cable service link. In addition, reduced capital and operating costs. The service life of 20-25 years.
A method of laying cable in the ground in a plastic pipe protects against mechanical damage and rodents. The service life of fiber-optic cable in this case is 40-45 years. Capital and operating costs are greater than the method for directly into the ground.
If the suspension on catenary poles electrified railways, as well as supports high-line power companies will need to pay for their rent and electricity grids corresponding fee optic cable embedded in the ground wire is more expensive than conventional optical cable. This increases the capital costs and operating costs. Term of suspension cable service is 12-15 years, and difficult maintenance of cable lines.
Of the above methods choose II method of laying cable in the ground in a plastic pipe along the road, as in this case, easier maintenance of the cable lines and repair compared with overhead cables, protected from mechanical damage and rodents lifetime longer than that of both methods. This provided access roads maintenance personnel to places of cable laying and the CHP, and in case of damage to the surgical removal of a fault on the line.
The presence of settlements in the path of the track makes it possible to accommodate unserved regeneration areas and the use of existing facilities available telecommunications nodes, which significantly reduces the amount of construction work, and helps to reduce the cost of construction of the road in general.
Depth of the underground installation of optical as well as electrical and 1.2 m. Cable water crossings can be performed by laying under water, on the bridge or by the suspension on the supports. The most reliable is the laying of submarine.
To develop the plan of construction and financial estimates specify the path of receipt of goods for construction, the possibility of using the existing warehouses and handling areas, the deployment of new sites and warehouses, distance methods of delivery of materials to the warehouses, the prices of local materials, etc.
Referring to the map area (Figure 1) we see that the only viable option is obvious route. This option cabling along the highway connecting the city of Stepnogorsk - KOCshetau. [PA].
The total line length is 251 km, the length of the areas: Stepnogorsk - Makinsk - 141 km; Makinsk - KOCshetau - 110 km.
Railway track laid at a distance of 30-60 meters (depending on the specific local conditions) from road axis.
In Akmola region is dominated by flat terrain, it allows you to lay the cable in the main mechanized way. In more detail the organization of railway crossings, as well as mechanized methods cabling discussed in the relevant chapter of the diploma project.
Primary BCC network
To construct a communication network are required so-called transmission system, ie apparatus through which connection lines for creating channels and group paths. And then arrange of lines and nodes and terminal stations, primary and secondary telecommunications network.
Primary networks consist only of lines, regeneration (amplification) and channeling equipment at the stations. Secondary network comprise further switching nodes allowing to switch communication channels to multiple destinations. But already on the basis of secondary networks are numerous communication services, providing a variety of services. Communication lines laid between the cities and in the major cities, intermediate regeneration (amplifier) Items endpoints - all primary network, serving for standard analog and digital channels and paths.
Primary BCC network (interconnected network) is divided into the trunk, zonal and local area network (Figure 1.2).
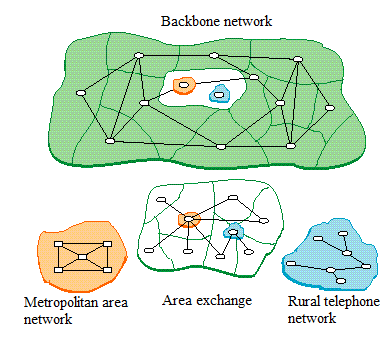
Figure 1.2 - Backbone, zonal and local primary network
Typical telecommunication channels have the same characteristics, regardless of at what portion of the primary network are formed: these characteristics are strictly standardized and accurately performed. Standardized telecommunication channels a lot, but we are referring only two: the analog channel voice frequency (VF channel) with a bandwidth of 0,3-3,4 kHz and the main digital channel, the bandwidth is 64 kbit / s. Along the lines of the primary network connection is formed such channels. You can create and broadband analog channels, digital channels and with greater bandwidth, but the vast majority of available channels is as follows.
the secondary network is organized on the basis of the above-mentioned basic channels: telephone, telegraph, data transmission, faxes. The number of telecommunication services is growing right before our eyes, and now their number was thirty. To name just a few: city, intercity and international telephone, telegraph subscriber (so-called "TTY"), telex, teletex, telefax, bureaufax, videotex, etc.
Of course, the biggest secondary network and the most numerous services - telephone. Most of the PM and digital channels in the country (it is necessary to think and abroad) are used for the formation of telephone networks. Moreover, often thought (evidenced by many publications) that the telephone network - the only secondary network, the other is not there. In fact this is not true: there are telegraph network - work on them telex (subscriber telegraph) and telegraph service in all offices. Any data transmission network, and not only with the rate of 64 kbit / s, but higher speed, e.g. 2048 kbit / s (E1 channel).






