 Granular (rough) ER is composed of the flattened membrane cisterns and tubules. Ribosomes and polysomes on the outer surface of them. 1
Granular (rough) ER is composed of the flattened membrane cisterns and tubules. Ribosomes and polysomes on the outer surface of them. 1

 3
3  2
2
 1) tubules
1) tubules
2) cistern
3) ribosomes.
Function: synthesis of the proteins for the cell (proteins of the plasmalemma, proteins-enzymes) and proteins for the export.
Agranular (smooth) ER has not ribosomes on its surface. Functions:
1) metabolism of the lipids;
2) metabolism of the carbohydrates;
3) accumulation of the calcium ions;
4) detoxication of the harmful substances.
Ribosomes.
They are not enclosed by a membrane. The function is the synthesis of the proteins. They connect aminoacids and form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two units: small and large. Ribosomes are composed by ribosomal RNA (ribosomal ribonucleic acid) and proteins. Several ribosomes, when they are on the common messenger RNA, form polysomes.
Golgi Bodies.
It is membranous organelle. It is composed by stacks of cisterns with membranous sacs at the ends. The complex of this elements is called dictyosome.

1. Sacs.
2. Tubules.
3. Cisterns dictyosome.

Functions:
1) accumulation and ripening of the products of the synthetic activity of a cell.
2) synthesis of the polysaccharides and connecting with the proteins (glycosylation).
3) removing of the secretion substances for a cell limits.
Microfilaments.
They are not membranous organelles; they enter into structure of the cytoskeleton of the cell. Microfilaments are composed of proteins: actin, myosin, tropomyosin.
Functions:
1) shortening of the muscle cells;
2) they compose cortical layer of the plasmalemma;
3) moving of the organelle inside the cell.
Microtubules.
They look like hollow cylinder with diameter 25 nm (nanometer), and thickness of the wall - 5 nm. A wall is composed of thirteen strings, which are composed of tubulin protein molecules.

Functions:
1) providing of the transport inside the cell;
2) they form a cytoskeleton of the cell (maintain the shape of the сеll);
3) they construct other organelles such as: centrioles,cilia;
4) providing of the locomotion of other organelles.
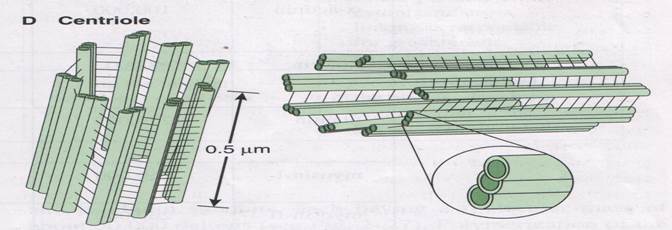
9. Cytocentrum (centrosome).
Function - providing the divergence of the chromosome during the cell division. It consists of two centrioles. Two centrioles form the diplosome. Centrosphere is situated near centrioles. Centrioles contain nine triplets of parallel microtubules. The triplets are connected by protein dinein. During the preparing of a cell to division, the doubling of centrioles and their divergence to a poles take place.
Cilia and Flagella.
They are organelles of the special importance. They take part in the processes of locomotion. They are sprouts of cytoplasm; the base of which are microtubules. They are called axial string or axoneme. The length of cilia are 2-10 mc (micrometer), the length of flagella is 50-70 mc. Axonema contains nine pairs of peripheral microtubules and one more pair is situated in the centre. It can be described with a formula (9*2) +2.
The basal body is situated at the base of cilia, in a place where it passes to a cytoplasm. It contains nine triplets of microtubules. Basal body and axonema are connected between themselves: two microtubules of each triplet of basal body enter a duplet of axonema microtubels.
Cells, which have cilia and flagella, can move in a space or transport substances.
Inclusions – temporary components of the cytoplasm, formed as a result of a cell vital activity.
Inclusions can be:
1) trophic - a) lipid inclusions
- b) carbohydrate (granules of glycogen).
2) secretory - membranous vesicles with a cell secretory products.
3) excretory – contain harmful products of metabolism, be removed
from the cell.
4) pigmentary – congestion of endogenous or exogenous pigments.
Endogenous: hemoglobin, melanin (secretion in the pigmentary cells), aging pigment.
Exogenous: dyes, particle of dust.
Theme: Introduction to a course of Histology, Cytology and






