The _________ has existed for about 3.5 billion years. The biosphere’s earliest life-forms, called prokaryotes, survived without ______. Ancient prokaryotes included single-celled ___________ such as bacteria and archaea.
Some ___________ developed a unique chemical process. They were able to use sunlight to make simple sugars and oxygen out of _________ and carbon dioxide, a process called photosynthesis. These photosynthetic organisms were so plentiful that they changed the biosphere. Over a long period of time, the atmosphere developed a mix of oxygen and other __________ that could sustain new forms of life.
The addition of _________ to the biosphere allowed more complex life-forms to evolve. Millions of different ___________ and other photosynthetic species developed. _________, which consume plants (and other animals) evolved. ___________ and other organisms evolved to decompose, or break down, dead animals and plants.
The biosphere benefits from this ________ web. The remains of dead plants and animals release nutrients into the _________ and ocean. These nutrients are re-absorbed by growing _________. This exchange of food and energy makes the biosphere a self-supporting and self-regulating __________________.
The biosphere is sometimes thought of as one large ecosystem—a complex community of living and nonliving things functioning as a single __________. More often, however, the biosphere is described as having many ___________.
Task 10. Translate the text and retell it in English:
Biosphere 2.
In 1991, a team of eight scientists moved into a huge, self-contained research facility called Biosphere 2 in Oracle, Arizona. Inside an enormous, greenhouse-like structure, Biosphere 2 created five distinct biomes and a working agricultural facility. Scientists planned to live in Biosphere 2 with little contact with the outside world. The experiments carried out in Biosphere 2 were designed to study the relationship between living things and their environment and to see whether humans might be able to live in space one day.
The mission was supposed to last 100 years, with two teams of scientists spending 50 years each in the facility. Instead, two teams made it just four years, and the scientists moved out in 1994. Though the live-in phase is over, research is still taking place in Biosphere 2, with a main focus on global warming.
The biosphere is made up of the parts of Earth where life exists. The biosphere extends from the deepest root systems of trees, to the dark environment of ocean trenches, to lush rain forests and high mountaintops.
Scientists describe the Earth in terms of spheres. The solid surface layer of the Earth is the lithosphere. The atmosphere is the layer of air that stretches above the lithosphere. The Earth’s water—on the surface, in the ground, and in the air—makes up the hydrosphere.
Since life exists on the ground, in the air, and in the water, the biosphere overlaps all these spheres. Although the biosphere measures about 20 kilometers (12 miles) from top to bottom, almost all life exists between about 500 meters (1,640 feet) below the ocean’s surface to about 6 kilometers (3.75 miles) above sea level.
Task 11. Render this text in English:
Крупнейшим обобщением в комплексе наук о Земле (геология, география, геохимия, биология) стало учение о биосфере, созданное русским ученым В. И. Вернадским. Начав свою научную деятельность (как геолог) с изучения осадочных пород земной коры, В. И. Вернадский выявил огромную роль живых организмов в сложных геохимических процессах нашей планеты. В 1926 г. вышла его книга «Биосфера». В этом произведении глубоко анализируются сложные взаимоотношения живых организмов и неживой природы Земли. Его работа несколько опередила время. Лишь во второй половине ХХ в., на фоне обострения экологических проблем, его учение о биосфере получило широкое распространение.
Важным элементом учения В. И. Вернадского о биосфере является идея тесной зависимости биосферы от деятельности человека и сохранности ее в результате разумного отношения человека к природе. Ученый писал: Человечество, взятое в целом, становится мощной геологической силой. Перед ним, перед его мыслью и трудом становится вопрос о перестройке биосферы в интересах свободно мыслящего человечества как единого целого. «Это новое состояние биосферы, к которому мы, не замечая этого, приближаемся, и есть ноосфера» (В. И. Вернадский).
В настоящее время учение о биосфере представляет собой важнейшую часть экологии, непосредственно связанную с проблемами регулирования взаимодействия человека и природы.
Впервые термин «биосфера» был употреблен Ж. Б. Ламарком в начале XIX в. Позднее он был упомянут в работе австрийского геолога Э. Зюсса в 1875 г. Однако это понятие не было детально разработано названными учеными, а использовано вскользь для обозначения области жизни на Земле. Лишь в работах В. И. Вернадского оно анализируется детально и тщательно и под ним понимается «оболочка жизни» на нашей планете.
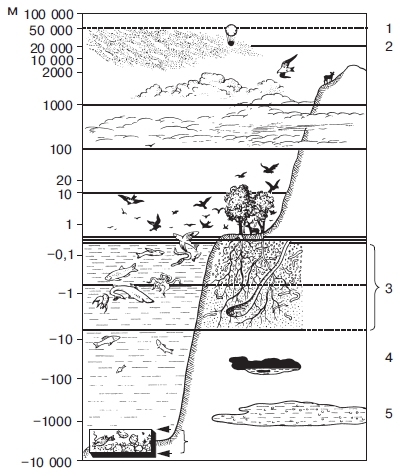
Биосферой называют совокупность всех живых организмов нашей планеты и те области геологических оболочек Земли, которые заселены живыми существами и подвергались в течение геологической истории их воздействию.
Границы биосферы. Живые организмы неравномерно распространены в геологических оболочках Земли: литосфере, гидросфере и атмосфере (рис. 1). Поэтому биосфера сейчас включает верхнюю часть литосферы, всю гидросферу и нижнюю часть атмосферы.