ВАРИАНТ 2
I. Перепишите предложения. Определите по грамматическим признакам, какой частью речи являются слова, оформленные окончанием –s, и какую функцию это окончание выполняет, т.е. служит ли оно: а) показателем 3-го лица единственного числа глагола в Present Indefinite; б) признаком множественного числа имени существительного; в) показателем притяжательного падежа имени существительного (см. образец выполнения 1). Переведите предложения на русский язык.
1. A consultant often works on very small timescales.
2. Qualifications are important but university degrees are useless.
3. Microsoft’s exams you can take are very useful pieces of paper.
II. Перепишите следующие предложения и переведите их, учитывая особенности перевода на русский язык определений, выраженных именем существительным (см. образец выполнения 2).
1. The first key point to realise is that you can’t know everything.
2. Here’s the road map.
3. Differentiate between contract work and consultancy.
III. Перепишите следующие предложения, содержащие разные формы сравнения, и переведите их на русский язык.
1. You may move into one of the larger consultancy companies.
2. The more experience you have, the better.
3. One of the most important things is to be interested in your subject.
IV. Перепишите и переведите на английский язык следующие имена числительные.
1. Количественные: 3 13 5 50 1,000 386 5,007 628,040,009
2. Порядковые: 1 2 3 44 765
3. Даты: 1812, 1904, 1083, 2000
4. Дроби: 

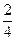
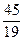 6
6  8.23 0.14 187.23
8.23 0.14 187.23
5. Длина:  километра 1
километра 1  километра
километра
6. Телефонный номер: 638-29-15
V. Перепишите и переведите на русский язык следующие предложения, обращая особое внимание на перевод неопределенных и отрицательных местоимений.
1. No university degrees are useful in this case.
2. Here you can always learn something useful.
3. Any person in that company knows Java and С++.
VI. Перепишите следующие предложения, определите в них видо-временные формы глаголов и укажите их инфинитив; переведите предложения на русский язык (см. образец выполнения 3).
1. Good contractors will move from job to job every few months.
2. Is there anyone who stayed in this company for more than two years?
3. These exams merely prove you can think.
VII. Прочтите и устно переведите на русский язык с1-го по 3-й абзацы текста. Перепишите и письменно переведите 1 и 2-й абзацы.
Пояснения к тексту
1. road map – зд. план действий, ориентиры.
HOW TO BECOME A COMPUTER CONSULTANT
1. The first key point to realise is that you can’t know everything. However you mustn’t become an expert in too narrow a field. The second key point is that you must be interested in your subject. The third key point is to differentiate between contract work and consultancy. Good contractors move from job to job every few months. A consultant is different. A consultant often works on very small timescales – a few days here, a week there, but often for a core collection of companies that keep coming back again and again.
2. There’s a lot of work out there for people who know Visual Basic, С++, and so on. And there are lots of people who know it too, so you have to be better than them. Qualifications are important. Microsoft has a raft of exams you can take, as does Novell, and in my experience these are very useful pieces of paper. University degrees are useless. They merely prove you can think, and will hopefully get you into a job where you can learn something useful. Exams like Microsoft Certified Systems Engineer are well worth doing. The same goes for NetWare Certification. However, this won’t guarantee an understanding of the product, its positioning in the market, how it relates to other products and so on. That’s where the all-important experience comes in.
3. Here’s the road map. After leaving university you get a technical role in a company and spend your evenings and weekends learning the tools of your trade – and getting your current employer to pay for your exams. You don’t stay in one company for more than two years. After a couple of hops like that, you may be in a good position to move into a junior consultancy position in one of the larger consultancy companies. By the age of 30, you’ve run big projects, rolled out major solutions and are well known. Maybe then it’s time to make the leap and run your own life.
VIII. Прочтите 3-й абзац текстаи вопрос к нему. Из приведенных вариантов ответа выберите и полностью перепишите тот вариант, который является ответом на данный вопрос.
What will you do after two years in one company?
1. Stay for a couple of years longer.
2. Make the leap and run your own life.
3. Move into some position in one of the larger consultancy companies.






