Lymphoma Classification
Many classification systems have been used over the years. Presented here is only the current 2008 WHO classification system. Developed in 2008 by the WHO, and adopted by most haematologists/oncologists in 2009 it represents the latest update. There is a link at the bottom of this page to older systems.
WHO classification.
Mature B-cell neoplasms
· Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma
· B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
· Hairy cell leukemia
· Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
 Splenic lymphoma/leukemia, unclassifiable
Splenic lymphoma/leukemia, unclassifiable
 Splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma*
Splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma*
 Hairy cell leukemia-variant*
Hairy cell leukemia-variant*
· Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
 Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Waldenström macroglobulinemia
· Heavy chain diseases
 Alpha heavy chain disease
Alpha heavy chain disease
 Gamma heavy chain disease
Gamma heavy chain disease
 Mu heavy chain disease Plasma cell myeloma
Mu heavy chain disease Plasma cell myeloma
· Solitary plasmacytoma of bone
· Extraosseous plasmacytoma
· Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT lymphoma)
· Nodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (MZL)
 Pediatric type nodal MZL
Pediatric type nodal MZL
· Follicular lymphoma
 Pediatric type follicular lymphoma
Pediatric type follicular lymphoma
· Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma
· Mantle cell lymphoma
· Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), not otherwise specified
 T cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma
T cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma
 DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation
DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation
 Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)+ DLBCL of the elderly
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)+ DLBCL of the elderly
· Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
· Primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma
· Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
· Primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type
· ALK+ large B-cell lymphoma
· Plasmablastic lymphoma
· Primary effusion lymphoma
· Large B-cell lymphoma arising in HHV8-associated multicentric Castleman disease
· Burkitt lymphoma
· B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma
· B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma
· Hodgkin Lymphoma
· Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
· Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
 Nodular sclerosis classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Nodular sclerosis classical Hodgkin lymphoma
 Lymphocyte-rich classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymphocyte-rich classical Hodgkin lymphoma
 Mixed cellularity classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Mixed cellularity classical Hodgkin lymphoma
 Lymphocyte-depleted classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymphocyte-depleted classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Mature T-cell neoplasms
- T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
- T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
- Chronic lymphoproliferative disorder of NK-cells*
- Aggressive NK cell leukemia Systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disease of childhood (associated with chronic active EBV infection)
- Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma
- Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
- Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type
- Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma
- Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
- Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
- Mycosis fungoides Sézary syndrome
- Primary cutaneous CD30+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder
Lymphomatoid papulosis
Primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
- Primary cutaneous aggressive epidermotropic CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma*
- Primary cutaneous gamma-delta T-cell lymphoma
- Primary cutaneous small/medium CD4+ T-cell lymphoma*
- Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
- Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL),
- ALK+ Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), ALK–*
*These represent provisional entities or provisional subtypes of other neoplasms.
Source information from Blood Journal and the 2009 ASH education series
Additional information about the 2008 WHO classification.
The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: evolving concepts and practical applications
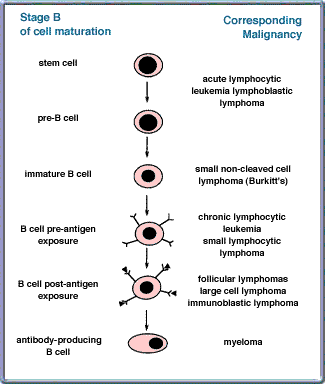
The chart below outlines what types of lymphoma correspond with what stage of B-cell development.
Indolent / Aggressive classification
The following table classifies the lymphoproliferative disorders according to whether they belong to the indolent (slow growing) or aggressive subtype. This includes lymphomas, leukaemias, and myelomas. This is based on the previous REAL/WHO classification system not the current 2008 WHO system.
Indolent lymphoma/leukemia
- A. Follicular lymphoma (follicular small cleaved cell [grade 1], follicular mixed small cleaved and large cell [grade 2], diffuse small cleaved cell)
- B. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma
- C. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia)
- D. Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (MALT lymphoma
- E. Nodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (monocytoid B-cell lymphoma)
- F. Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes)
- G. Hairy cell leukemia
- H. Mycosis fungoides/Sezary syndrome
- I. T-cell granular lymphocytic leukemia
- J. Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma/lymphomatoid papulosis (CD30+)
- K. Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma
Aggressive lymphoma/leukemia
- A. Diffuse large cell lymphoma (includes diffuse mixed cell, diffuse large cell, immunoblastic, T-cell rich large B-cell lymphoma) Distinguish:
1. Mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma
2. Follicular large cell lymphoma (grade 3)
3. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (CD30+)
4. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type
5. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis (angiocentric pulmonary B-cell lymphoma)
6. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
7. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified
8. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
9. Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
10. Enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma
11. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
- B. Burkitt lymphoma/Burkitt cell leukaemia/Burkitt-like lymphoma
- C. Precursor B- or T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukaemia
- D. Primary CNS lymphoma
- E. Adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma (HTLV 1+)
- F. Mantle cell lymphoma
- G. Polymorphic post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD)
- H. AIDS-related lymphoma
- I. True histiocytic lymphoma
- J. Primary effusion lymphoma
- K. Aggressive NK-cell leukemia/blastic NK-cell lymphoma
- L. B- or T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia






