182 √лава 7__________________________
|
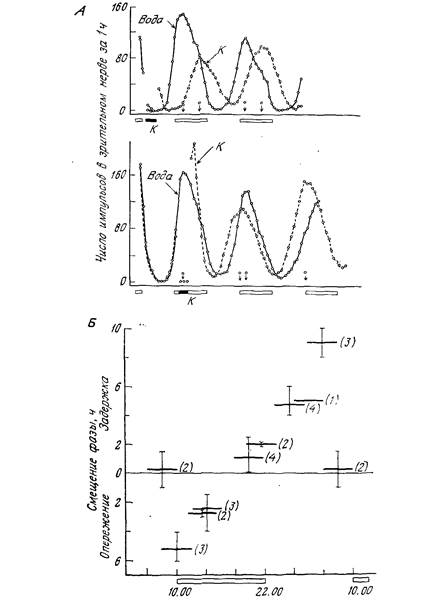
| –ис 8 —мещени€ фазы ритма в глазу Aplysia. вызванные 4-часовым воздействием морской воды с высокой концентрацией кал€€ (106.7 мћ) [26]. ј. ƒва графика соответствуют залепжке (вверху) и опережению (внизу) фазы ритма. —плошные кривые Ч контроль (с профильтрованной морской водой); прерывистые кривые Ч при воздействии высокої концентрации кали€. √лаза находились в посто€нной темноте. Ѕ. ривые смешени€ фазы пол действием высокой концентрации кали€ показывают величину и направление сдвига лазы в зависимости от момента воздействи€. √оризонтальные отрезки Ч врем€ воздействи€ калием вертикальные Ч диапазон, в котором лежит наблюдаемое смещение фазы. ¬ скобках указано число опытов. Ѕелые полоски внизу Ч светлое врем€ —“-цикла. |
Ѕиологические ритмы. ¬ 2-х т. “. 1. ѕер. с англ. Ч ћ.: ћир, 1984.Ч 414 с.
__________ онтроль циркадианных ритмов у беспозвоночных_____________ 183
торецептора (см. выше), либо от контралатерального глазного колебател€. »звестно, что глаз содержит большое количество серотонина, но в каких клетках он образуетс€, не установлено [18].
Ћитература
1. Aréchiga H. Circadian rhythm of sensory input in the crayfish. In: F. O. Schmitt and F. G. Worden (eds,), The Neurosciences: Third Study Program, Cambridge, Mass., MIT Press, 1974, pp. 517Ч523.
2. Aréchiga H., Fuentes Ѕ. Correlative changes between retinal shielding pigments position and electroretinogram in crayfish, The Physiologist, 13, 137,(1970).
3. Aréchiga H., Mena F. Circadian variations of hormonal content in the nervous system of the crayfish, Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 52A, 581Ч584 (1975).
4. Aréchiga H., Wiersma —. A. G. Circadian of responsiveness in crayfish visual units, J. of Neurobiology, 1, 71Ч85,(1969).
5. Aréchiga H., Funetes ¬., Barrera B. Circadian rhythm of responsiveness in the visual system of the crayfish. In: J. Salânki (éd.), Neurobiology of Invertebrates, Budapest, Akadémiai Kiado, 1973, pp. 403Ч427.
6. Aréchiga H., Huberman Α., Naylor Ε. Hormonal modulation of Circadian neural activity in Carcinus maenas (L), Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, B, 187, 299Ч313 (1974).
7. Barlow R. ¬., Jr., Balanowski S. J., Jr., Brachman M. L. Efferent optic nerve fibers mediate Circadian rhythm in the Limulus eye, Science, 197, 86Ч89 (1977).
8. Barrera-Mera B. The effect of cerebroid ganglion lesions on ERG Circadian rhythm in the crayfish, Physiology and Behavior, 17, 59Ч64 (1976).
9. -Bennitt R. Diurnal rhythm in the proximal cells of the crayfish retina, Physiological Zoology, 5, 65Ч69,(1932).
10. Bliss D. E. Neuroendocrine control of locomotor activity in the land crab Cecarcinus lateralis, Memoirs of the Society of Endocrinology, 12, 391 (1962).
11. Block G. D. Evidence for an entrainable circadian oscillator in the abdominal ganglia of crayfish, Neuroscience Abstracts, 2, 315 (1976).
|
|
|
12. Block G. D., Lickey M. E. Extraocular photoreceptors and oscillators can control the circadian rhythm of behavioral activity in Aplysia, J. of Comparative Physiology; 84, 367Ч374 (1973).
13. Block G. D., Page T. L. Circadian pacemakers in the nervous system, Annual Review of Neuroscience, 1, 19Ч34 (1978).
14. Block G. D., Hudson D. J., Lickey M. E. Extraocular photoreceptors can entrain the circadian oscillator in the eye of Aplysia, J. of Comparative Physiology, 89, 237Ч250 (1974).
15. Brady J. Control of circadian rhythm of activity in the cockroach. II. The role of the subesophageal ganglion and ventral nerve cord, J. of Experimental Biology, 47, 165Ч178 (1967).
16. Brady J. The search ïor the insect clock. In: M. Menaker (éd.), Biochronoinetry, Washington, D. C., National Academy of Sciences, 1971, pp. 517Ч 524.
17. Brady J. The physiology of insect circadian rhythms. Advances in Insect Physiology, 10, 1Ч115 (1974).
18. Carrent G., McAdoo D. J., Eskin A. Serotonin phase shifts the circadian rhythm from the Aplysia eye, Science, 202, 977Ч979 (1978).
19. Cymborowski B. Control of the circadian rhythm of locomotor activity in the house cricket, J. of Insect Physiology, 19, 1423Ч1440 (1973).






