1.If I knew her number, I would telephone her. 2. Tom would travel if he had more money. 3. If I were you, I wouldn’t buy that coat. 4. If I were rich, I would buy a castle. 5. We wouldn’t have any money if we didn’t work. 6.If I had known that you were ill, I would have gone to see you. 7. We would have gone out if the weather hadn’t been so bad. In case of fire, please leave the building as quick as possible. 9. In case of emergency, telephone this number. 10. We rang the bell again in case they hadn’t heard the first time. 11.I wish you wouldn’t drive so fast. 12.He is going to take his camera in case he wants to take some pictures.13. Travelling by car is convenient provided (that) you have somewhere to park. 14.Providing (that) she studies hard, she should pass the examination. 15. We’ll be late unless we hurry.
III. Make your own sentences. Use expressions:
If I were you, I …
I wish you wouldn’t …
In case of….
Providing...
Unit IX.
GRAMMAR REVIEW.
I. Read and translate the text.
Remember, not so long ago, when the telephone used to be a simple receiver connected by a wire to the wall? And all you used your phone for was to make a phone call? Today, new technology has changed the telephone and what people use it for.
Computer-based technology has given us instant connections and clearer conversations over the telephone.
But you don’t need to be at home or at the office to use the telephone anymore. Mobile phones (also known as cellular phones) have no wires. You can carry one in your pocket or keep one in your car. A call from a mobile phone travels along radio waves to stations located in different places. From there the radio signal is connected to the regular phone system. With a mobile phone, anyone who can drive and talk can also drive and phone. This means less wasted time: You don’t have to look for a phone booth or use coins to make a call. So remember, next time you are at the beach or riding your bicycle, there might be a call for you!
Answer the questions.
a) How have computers improved telephone services?
b) How many uses of the telephone can you find in the passage?
c) How many uses of a mobile phone can you find?
d) How does a mobile phone call reach a station?
Unit X.
 Degrees of Comparison.
Degrees of Comparison.

1. Read and translate the text:
THE HERMITAGE
The State Hermitage in St. PETERSBURG is one of the largest museum in the world. Fabulous treasures are gathered in the Museum. It contains the better specimens of culture and art.
Within the past few decades the Hermitage has become one of the country’s most important centres of art study. The results of the research work are published in the form of books, articles, periodicals, etc.
Most helpful in the Museum research work in the Hermitage Library which contains about 400 000 books, and is one of the largest among art libraries.
At the present moment the exhibitions of the Hermitage occupy four buildings.
The Winter Palace is the oldest of the buildings occupied by the Museum today. Erected in 1754-1762 to the design of the architect Rastrelli, it ranks among the most wonderful architectural monuments of the city. Later in 1840 it was reconstructed by the architects Stasov and Bryullov.
The most notable rooms of the Winter Palace are the imposing State rooms among them is the Small Throne Room or Peter’s Room, created in the 19-th century in memory of Peter I.
I. Translate the sentences:
The Department of the History of Russian Culture founded in 1941 is the youngest in the Hermitage. 2. The Hermitage collection of works by the great Dutch painter Rembrandt van Rijn is the richest in the world. 3. The building of the Winter Palace is not higher than other ones on the embankment of the Neva. 4. Anything you can do he can do better. 5. Art is much easier to get hold of* these days.
*to get hold of - достичь, получить.
II. Complete the sentences:
1. Mathematics is (difficult) than History. 2. Tom is the (bad) pupil in the class. 3. My mother gets up (early) than all in our family. 4. St. Petersburg is the (beautiful) city in our country. 5. This car is (expensive) than that. 6. It was (hot) this year than last year. 7. Mary is (thin) than Ann. 8. A lion is (dangerous) than an elephant. 9. Dolphins are (intelligent) animals of all after man. 10. Ben is the (good) athlete of all.
ADDITIONAL READING
I. Translate the text, pay attention to the word “IT”.
It is difficult to imagine modern life without a telephone. It is a beautiful instrument of interconnection which enables people to speak to one another over great distances. At present it is as easy to speak across a continent or even overseas as it is to speak to a next door neighbour.
We are usually making long distance calls with the help of an operator, although in some cities it is possible to dial directly.
Telephones are useful and convenient for many reasons. People like to speak with their families and friends, and business organizations can’t carry on their activities without telephones. The telephone really proves its usefulness when there is a fire or when a person is ill. The first thing of which we think then is “where is the nearest telephone or telephone booth?”
as easy as - так же легко... как и...
II. Read and translate the text. Speak about your own city.
HELSINKI - DAUGHTER OF THE BALTIC
Helsinki is a modern city. Here is tourist does not come face to face with the past as he does in many old European capitals. Yet there are areas in Helsinki which give a genuine and comprehensive picture of the atmosphere and architecture of the past.
HISTORY. Great fires destroyed the old wooden Helsinki many times, but it was always rebuilt. The only remains of the trade and seafaring town that Swedish King Gustav Vasa founded in 1550 at the mouth of River Vantaa are the foundations of a church. The massive walls of the Suomenlinna fortress date from 18-th century. Helsinki became Finland’s capital in 1812. Many the city’s historically interesting sights date from the beginning of the 19-th century, when the administrative centre was built around the Senate Square. Helsinki had a population of 4000 in 1812. At the turn of the century the figure was 79000 and it is just over a million at present.
III. Read and translate the text. Pay attention to the word “ONE”.
TRAVELLING IN BRITAIN
Once you have arrived in Britain, you will have no difficulty in travelling around the country. A network of rail services links all principal towns and cities, only in remote or sparsely populated areas can you be more than a few miles from a railway station. In addition, there are express coach services available between many towns.
Each town or district also has its local bus routes serving even the more remote villages. There are regular air services between the major cities operated by British Airways and several independent air lines. If you bring your own car, you will find that even the smaller country roads are well surfaced and in good condition. And you can take advantage of the scenery and picturesque villages on the way. Considerable lengths of motorways are now in use, others are being built and will be open soon. Most of these motorways are long-distance roads, like the one connecting London and Birmingham1), but some are just short stretches by-passing heavily congested towns or industrial areas.
 |
like the one connecting London and Birmingham -
подобно дороге, соединяющей Лондон и Бирмингем.
Слово “one” здесь употребляется как заменитель существительного.
Обратите внимание на перевод “one” перед сказуемым.
В сочетании с модальными глаголами “one” переводится:
one can - можно, one must - нужно, one should - следует.
Замените в подчеркнутых предложениях подлежащее “you“ на “one”. Переведите полученные предложения. Сравните перевод.
1. Найдите в тексте предложение в Present Continuous Passive.
REVISION EXERCISES.
I. Make sentences interrogative and negative.
1. He is my friend. 2. He is a doctor. 3. He has a wife. 4. You are a doctor. 5. They are students. 6. We are in my room now. 7. There are many things in my room. 8. There is a TV set in my room. 9. The flowers are in the vase.
II. Put the above sentences into The Past and Future Indefinite.
III. Insert prepositions.
1. My father works... a plant. 2. My mother is a telephone-operator... an Institute 3. I was... the Army... two years. 4. My sister teaches... school. 5. I live together... my parents... a four-room flat. 6. We have a flat... all modern conveniences. 7. My friend lives far... our plant. 8. He gets... the plant... the Metro. 9. Our working day begins... half past eight. 10. She goes... the Institute... Monday, Wednesday and Friday.
IV. Answer the questions.
1. What is your name? 2. How old are you? 3. Do you work? 4. Where do you work? 5. What are you? 6. When did you leave school?7. Where you in the Army? 8.When did you begin to work? 9. Do you like your job? 10.Are you married? 11. Do you study? 12. What institute do you go to? 13. Have you a family? 14. How many are you in the family? 15. What is your father (mother)? 16. Have you any sisters or brothers? 17. What is your sister (brother)? 18. How old is your mother (father, sister, brother)? 19. Where do you work? 20. Do you live with your parents? 21. Do you live in a new or an old house? 22. Have you got (=have you) a good flat? 23. How many rooms are there in your flat? 24. Do you like it or not?
VIII. У Р О В Е Н Ь 1
ТЕСТ 1
1. В каком из следующих слов звук, передаваемый буквой “ о “ отличается от остальных?
1) phone, 2) know, 3) sorry, 4) zero 5) no, 6) bone, 7) role.
2.Выберите правильную форму глагола “ to be “:
1) I... in the 10th grade.
a) is
b) are
c) am
d) were
2) He... at the theatre yesterday.
a) is
b) was
c) will be
d) were
3.Укажите предложение, в котором глагол “to be“ является вспомогательным:
a) She was sixteen last year.
b) The delegation is to come on Monday.
c) Mother is at home.
d) What are you going?
4.Выберите правильную форму глагола “to have”:
Mr. Smith stayed at his office very late because he... a lot of work.
a) has
b) have
c) will have
d) had
5. Укажите предложение, в котором глагол “to have” является модальным:
a)We shall have a party tomorrow.
b)We have invited our friends.
c)We’ll have to prepare for the party.
d)I hope we’ll have a good time.
6. Укажите правильные варианты перевода:
1) The flowers are in the vase.
а) Цветы в вазе.
b) В вазе цветы.
2) There is no telephone in the room.
а) Телефона нет в комнате.
b) В комнате нет телефона.
7. Подберите эквиваленты в английском, соответствующие русскому:
1) Дверь открылась и вошла девочка.
2) Дверь открылась и девочка вошла.
a) The door opened and a girl came in.
b) The door opened and the girl came in.
8. Выберите нужное местоимение:
1) I invited my friend to... place.
a) me
b) his
c) my
d) mine
2) It’s easy, you can do it....
a) you
b) your
c) yours
d) yourself
9. Выберите правильную форму существительного:
1) The... comes every morning.
a) postman
b) postmen
2) How many... high is this house?
a) feet
b) foot
10. Укажите, какое слово можно употребить вместо подчеркнутого так, чтобы смысл предложения не изменился:
1)We usually drink much water in hot weather.
a) few
b) a lot of
c) many
d) little
2)This text is easy, there are not many new words in it.
a) little
b) not much
c) a lot of
d) few
11. Выберите нужное по смыслу слово:
1) We have... bread, please, go and buy some.
a) much
b) many
c) little
d) few
2) I have... time, I can wait.
a) little
b) a plenty of
c) many
d) few
12. Выберите правильное местоимение:
1) She wanted to tell me... interesting.
a) somebody
b) something
c) some
d) somewhere
2) I think we have met her....
a) somebody
b) something
c) some
d) somewhere
13. Укажите, в каком из предложений можно употребить все указанные слова: many, few, a lot of, some.
a) He likes to spend much time watching TV.
b) They have red 10 English books in the original.
c) There is no news today.
14. Укажите предложение, в котором числительное является порядковым:
1) There are 300 pages in the book.
2) He was born in 1980.
3) School year begins on the first of September.
4) Room 5 is empty.
15. Подберите слово, близкое по значению к подчеркнутому:
1) We do English at school.
a) work
b) learn
c) teach
d) know
2) She spoke to her English teacher after classes.
a) talked
b) said
c) told
d) discussed
16. Из следующей группы слов отметьте то, которое не имеет к остальным никакого отношения:
1) weather, season, rain, cloudy, expensive, forecast, hot, cold.
2) London, sights, monument, tourist, art gallery, to found, to build, to design, guide, the president.
17. Определите, какое из слов не является продуктом питания:
butter, cream, flour, tea, orange, cucumber, fish, sausage, beans, chicken, ham, hot dogs, chips, butter-fly, berries, jam, pine-apple.
18. Какое из утверждений является верным?
1)
a) English is impossible to learn.
b) English is the most difficult language in the world.
c) English is the most popular foreign language in our country.
2)
a) After Friday comes Monday.
b) The sun rises in the West.
c) The first of April is ’’All Fools’ Day’’ in Britain.
19. Укажите, какое из утверждений верно:
1) People don’t usually work hard on their days off.
2) All schools have classes on Sundays.
3) Few people leave school at the age of 16.
20. Скажите, в какой день Джон должен сдавать экзамен?
John came late. The party was very interesting. He didn’t want to leave earlier than others. He liked the parties that the Browns sometimes had on Saturdays. He was happy. But suddenly he remembered that he must take his exam in History and there was no time left. He had only one day to prepare for it. The party was forgotten at once.
21. Прочитайте текст и ответьте на вопрос:
The police stop the car. There are three people in the car: John, Ann and Mary. On the back seat there is a revolver. John says: ’’It’s mine’’. Ann says:
’’It’s hers’’. Mary says:’’It’s his’’. Nobody is telling the truth.
Whose revolver is it?
22. Заполните пропуски:
I. Great Britain..... rich in minerals.
A) is B) has C)are
2. …. he many good ideas?
A) Have B) Has C) Are
3. That's..... good idea!
A) the B) a C) an
4. I heard.... news on..... radio.
A) a...a B) the... the C)the... a
5. A boat is.... than a ship.
A) as small B) small C) smaller
6. We were so tired that we would have slept...
A) anywhere B) somewhere C) however
7. Every old palace has... strange stories.
A) his B) its C) a
8. The students had to... several dictations.
A) write B) wrote C) written
9. This seems..... an interesting book.
A) is B) is being C) to be
10. This room can.... as a classroom.
A) use B) be used C) have used
II. There is a long table... the corner.
A) in B) with C) of
12. Do you usually have a large party...your birthday?
A) a B)with C)on
13............. Why you writing with a pencil?
A) do B)have C) are
14. These new houses... two years ago.
A) were built B) have built C) build
15. But the new school... next year.
A) will build B) will be built C) has built
ARGUING:
IS TV GOOD OR BAD?
TODAY, THERE IS A TV SET IN NEARLY EVERY HOME.
PEOPLE WATCH TV EVERY DAY, AND SOME PEOPLE WATCH IT FROM MORNING UNTIL NIGHT.
AMERICANS WATCH TV ABOUT 35 HOURS A WEEK BUT IS TV GOOD OR BAD FOR YOU?
PEOPLE HAVE DIFFERENT OPINIONS.
READ WHAT SOME AMERICANS COLLEGE STUDENTS SAY.
a)..... People don’t get any exercise. They just sit and watch TV.
b)..... It brings news from around the world into peoples homes.
c)..... People just want entertainment today. They don’t want to think.
d)..... There is a lot of crime and violence on TV today. The programs are terrible!
e)..... Children learn many useful things from programs like sesame screen. It teaches them to read.
f)..... It helps me relax after along day.
g)..... Programs on the radio are better. They make you think.
h)..... It’s all commercials. I hate it!
i)..... People learn about life in other countries.
j)..... People don’t read anymore. It’s easier to watch TV.
1. Do the students think TV is good or bad? Write G for good and B for bad. Then compare with a partner.
2. Do you agree with the opinions above? Write YES or NO next to each opinion.
Table 1
Спряжение глагола to be (быть, находиться, являться)
в PRESENT INDEFINITE:
Утвердительная Отрицательная Вопросительная форма форма форма и краткие ответы
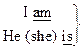 a student
It is a book a student
It is a book
| 
|  No, I’ m not. = I am not.
No, he isn’t. = He is not.
No, I’ m not. = I am not.
No, he isn’t. = He is not.
|
| We (you, they) are Students. | We are not students. | Are you students? Yes, we are. No, we aren’t. = We are not. |
Спряжение глагола to have (иметь) в Present Indefinite:
| I (we, you, they) have a brother. | I have no brother. | Have you a brother? Yes, I have. No, I haven’t. = I have not. |
| He (she) has a brother. | He has no brother. | Has he a brother? Yes, he has. No, he hasn’t = He has not. |
Table 2
Времена группы Indefinite (Active):
PRESENT INDEFINITE:
I test the devices regularly.
Я испытываю эти приборы регулярно.
(Do you test the devices? I do not test the devices.)
PAST INDEFINITE:
I tested the device yesterday.
Я испытал этот прибор вчера.
(Did you test the device yesterday? I did not test the device yesterday.)
FUTURE INDEFINITE:
I shall test the device tomorrow.
Я испытаю прибор завтра.
(Shall I test the device tomorrow? I shall not test the device tomorrow.)
Table 3
Времена группы Indefinite (Passive)
Present Indefinite Passive:
The devices are tested regularly.
Эти приборы испытываются регулярно.
Past Indefinite Passive:
The device was tested yesterday.
Этот прибор был испытан вчера.
Future Indefinite Passive:
The device will be tested tomorrow.
Прибор будет испытан завтра.
Table 4
Времена группы Continuous (Active):
Present Continuous Active:
I am testing the device. Я испытываю этот прибор (сейчас).
Past Continuous Active:
I was testing the device when you came.
Я испытывал этот прибор когда вы пришли.
Future Continuous Active:
I shall be testing the device when you come.
Я буду испытывать прибор, когда вы придете.


Времена группы Continuous (Passive):
Present Continuous Passive:
The device is being tested.
Этот прибор испытывается (сейчас).
Past Continuous Passive:
The device was being tested when you came.
Прибор испытывали, когда вы пришли.
Future Continuous Passive Не существует.
Table 5
В английском языке следующие глаголы выражают
ДОЛЖЕНСТВОВАНИЕ:
MUST - должен, нужно, необходимо
TO HAVE TO - должен, вынужден, придется
TO BE TO - должен, нужно

present past future эквиваленты
| Can могу, умею | Could | - | to be able to...(am, is, are, was, were, shall, will be able to) |
| May могу в смысле “разрешено”, возможно | Might | - | to de allowed to... |
Table 6
Многофункциональность глагола to be
|
 |  |  |  | ||||
|
|
|
|
1А. Смысловой - со значением БЫТЬ, НАХОДИТЬСЯ;
The rules were on the desk. Линейки были на парте.
1B. СВЯЗКА – со значением БЫТЬ, ЯВЛЯТЬСЯ, СОСТОЯТЬ,
ЗАКЛЮЧАТЬСЯ.
He was a worker before, now he is a - Раньше он был рабочим, designer; теперь он конструктор.
2.МОДАЛЬНЫЙ – со значением – «должен»
We are to prepare everything - Мы должны все подготовить
for the experiment. к опыту.
3.ВСПОМОГАТЕЛЬНЫЙ
а) в группах Continuous и Perfect Continuous:
She is working now. - Она работает сейчас.
She has been working since - Она работает с раннего утра.
early morning.
b) в страдательном залоге с Participle 2:
He is (was, will be) asked to - Его просят (просили, попросят)
make a report. сделать доклад.
Table 7
Степени сравнения прилагательных
(Degrees of Comparison)
| Исходная форма | Сравнительная степень | Превосходная степень | ||||||
| Односложные и некоторые двусложные прилагательные | short короткий big easy | shorter короче bigger easier | (the) shortest самый короткий (the) biggest (the) easiest | |||||
| Двусложные и многосложные прилагательные | important важный | more важнее более важный | (the) most самый важный | |||||
| VIII. Прилагательные и наречия образующие степени сравнения не по правилу | good well bad badly much many little far | better worse more less farther further | best (the) worst (the) most (the) least (the) farthest (the) furthest | |||||
Table 8
Многофункциональное местоимение it.
 |
 |  |  |  |
1. Личное (подлежащее, дополнение).
It is very important. Он (она, оно) очень важен.
Explain it? Please. Обьясните его, пожалуйста.
2. Указательное (в функции подлежащего):
It is a new device. Это новый прибор.
3. Безличное (в функции подлежащего):
It is cold in the class room. В аудитории холодно.
It is said that he is an Говорят, что он опытный experienced engineer. инженер.
4.Усилительное (для выделения отдельных членов предложения):
It is Popov who invented the radio Радио изобрел не кто иной, как Попов.
It is at these benches that Именно на этих столах
experiments are usually done. обычно проводятся
опыты.
Ф О Н Е Т И Ч Е С К И Й С П Р А В О Ч Н И К
I тип чтения гласных
a [ei] - c a ke, J a ne, Gr a ce
o [ou]- g o, n o, R o man
u [ju:]- t u be
e [i:] - b e, m e, h e, sh e, w e, P e te
i [ai] - l i ke, n i ce, five
y [ai] - m y
II тип чтения гласных
a [ae] - th a t, bl a ck, b a g, c a n
o [ ] - h o bby, fr o m, n o t, s o ng
e [e] - h e lp, y e s, qu e stion
u [ ] - l u ck, m u ch, u s, h u rry u p
i,y [i] - th i s, g y m, w i sh, qu i ck
III тип чтения гласных
-ar [:] - D ar cy, p ar ty, ar mchair, l ar ge, d ar k, Ch ar les, f ar, c ar pet
-or [:] - sh or t, N or man, New Y or k, p or t
-ir [:] - g ir l, Sh ir ley, b ir thday, sh ir t
-ur [:] - s ur name, f ur niture, c ur tains, f ur, T ur ner
IV тип чтения гласных
-ar+гласн. [:] - M ary, nightm are, prep are
-er+гласн. [:] - h ere
-ir+гласн. [:] - f ire, t ire d
-ur+гласн. [:] - d uri ng, p ur -or+гласн. [:] - m ore, bef ore
-or+ [:] - m ore, bef or
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ






