Demand. Factors determining the demand. The law of supply
Demand - one of the parties of the multidimensional process of market pricing. Expresses the law of demand: the inverse relationship between price and buys many goods, a gradual decrease in demand for a given product or service.
According to the law of demand, other things being equal, the number of purchased goods or services depends on the level of their prices. In this case, the higher price and a clear tendency to its growth, the lower the amount of goods and services will be purchased by consumers. If the price of a good increases, the volume of sales of the product, according to the fall in demand is reduced.
The law of demand reflects another important process: the gradual decrease in demand. Reducing the number of sales of the product or service is not only due to the increase of their prices, but also due to the saturation of consumer demand. Decrease in demand is because each subsequent purchase of the same product or service brings consumers a relatively smaller benefit, benefit, satisfaction.
The special nature of the relationship between price and quantity of its sales, and the gradual decrease in demand is shown in Figure 3.

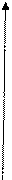 P D
P D

 А
А
В
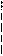
 D
D

Q
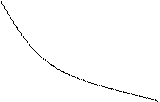
Fig.3. Demand curve
Volume of demand corresponds to a certain value of two variables - prices and sales volume.
If the price of a good rises from point B to point A, the sales decline. Opposite direction of the axes, if the price drops in the direction from point A to point B.
Movement along the demand curve from one point to another shows how a change in one variable, i.e. prices, causing retrogression other, i.e., sales. The demand curve has not changed its shift in one direction or another did not happen. This means that the demand has not changed, it remains the same: price change alters only the volume of sales of goods, but not the demand.
Assume no change relative prices and sales volumes, and so-called non-price factors: income customers, their subjective tastes, fashion, consumer goods, etc. Features what then happens to the demand curve? The answer is simple: change non-price factors and demand causes the configuration change, the slope of the demand curve, expressing the change in the quantity of goods sold for the same price is not changing. Demand is not the case, static, it is constantly changing under the influence of non-price factors, as evidenced by a particular shift the demand curve.
For non-price factors in market demand include:
- Income consumers;
- Consumer expectations;
- Consumer preferences;
- The number of customers;
- The prices of complementary and substitute goods.
In Figure 4. dashed line shows its increase in demand under the influence of non-price factors. Increased demand - shift the entire curve to the right and up, which means an increase in sales of the product for the same, do not change, the price. In Figure 5. shows the decrease in demand: the dotted demand curve shifted to the left and down. This decrease in demand is also due to non-price factors and results in lower sales for not changing the price per unit.


 P D1 Р D
P D1 Р D









 D D1
D D1

 P1 A A1 A1 A
P1 A A1 A1 A
 D1 D
D1 D
D D1
 |
Q1 Q2 Q 0 Q1 Q2 Q
Fig.4. Growth under the Fig.5. Decrease in the demand
influence of non-price factors for non-price factors influence






