Ex. 7. Compose 2-3- sentences using the words of VOCABULARY.
Ex. 8. What endocrine glands do you know?
Ex. 9. Insert the missing letters:
_drenal; pitu_tary; thyr_id; pancre_s; parathyr_id; o_ary; testi_le; p_neal; t_ymus; ma_mary; la_rimal; swe_t.
Ex. 10. Translate the following words and word-combinations into Ukrainian:
Target organ; response; stimuli; adrenaline; separate glands; enable; secrete the insulin; burst; lacrimal gland; sweat gland; external body surface; bloodstream; produce; glandular; pancreas; adrenal; pituitary; thyroid; parathyroid.
Ex. 11. Read the following words and word-combinations:
Protein; lipid; amino acid; hormone; glycoprotein; polypeptide; breathe [brID]; usual; although; either; affect; mechanism; release; amount of sugar; certain; particular hormone; insulin ['InsjulIn]; to separate; separate glands; via [vaIq].
Ex. 12. Read the following text:
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
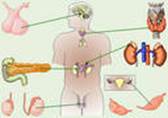 Structure of Endocrine System
Structure of Endocrine System
| The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, and organs that produce hormones or other chemical substances. The organs of endocrine system act together to control body activities and maintain homeostasis. In most people, the pancreas, the adrenal, pituitary, thyroid, and parathyroid glands, and ovaries or testicles work in tandem. The endocrine system regulates various functions of a human organism. It functions as a control system for the human body. Unlike other organs and body parts that enable to move, breathe, eat, |
or sense the world around us, the endocrine system influences the body's processes. Along with nervous system, it coordinates the body's activities and responses to usual and unusual events.
Although both the endocrine system and the nervous system regulate the activities of structures in the body, they do so in different ways. These two systems cannot be separated completely either anatomically or functionally. For example, some hormones secreted by endocrine glands affect the nervous system and markedly influence its activity.
The key mechanism of the endocrine system is the hormone. Different types of endocrine hormones are secreted by different glands (pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads: ovaries and testicles, pineal gland, and thymus gland). Most of these hormones are released into the bloodstream so that they can deliver instructions to various organs and tissues. The pancreas, for example, secretes the insulin hormone, which enables the body to regulate the amount of sugar in the bloodstream. In response to stress or other stimuli, the adrenal glands secrete adrenaline, which produces a sudden and remarkable burst of energy.
Similarly, the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, and gonadal glands influence certain body functions. Glands, which send the chemical substances into ducts leading to external body surfaces, are called exocrine glands. They are mammary, salivary, lacrimal and sweat glands.
|
|
|
A hormone is an organic substance with a special molecular structure secreted by definite cells that has an effect on the function of another cells. Although hormones circulate throughout the body via the bloodstream, each hormone influences on only certain organs (target organs) or tissues. So, several types of chemicals are produced by cells and act as chemical messengers, but not all of them are hormones.
Hormones are proteins, glycoproteins, polypeptides, derivatives of amino acids, or lipids (steroids or derivatives of fatty acids).
As a rule, the greater the amount of a particular hormone in the bloodstream, the greater activity of the target organ. Some hormones (such as several of those produced by the pituitary gland) control other glandular activity, but virtually every system in the body is subject to the influence of the hormones, either directly or indirectly.
Ex. 13. Translate the following words and word-combinations into English:
јдренал≥н, еп≥нефрин; залозовий, такий, що стосуЇтьс€ залози; г≥поф≥з; щитопод≥бна залоза; прищитопод≥бна | залоза; п≥дшлункова залоза; надниркова залоза; зд≥йснювати вплив, впливати; подразники, стимули|стимул-реакц≥њ|; шишкопод≥бна | залоза; загруднинна залоза, тимус|; гормони, що виробл€ютьс€ ендокринними залозами; жирн≥ кислоти.
Ex. 14. Translate the text УEndocrine SystemФ into Ukrainian.
Ex. 15. Answer the following questions:
1. What does the endocrine system consist of? 2. What is the function of endocrine system? 3. What glands of external secretion do you know? 4. What glands are the glands of internal secretion? 5. What is a hormone? 6. Where do the hormones circulate?
Ex. 16. Read the following abstract and say what it deals with:
Pituitary gland is at the base of the brain. Thyroid gland is located on either side of the trachea below the thyroid cartilage. Parathyroid glands are located on the dorsal side of the thyroid gland. Pancreas is behind the stomach. The adrenal glands are situated one on top of each kidney.
Ex. 17. Choose the correct terms (parathyroid gland; thyroid gland; adrenal glands; endocrine gland; pancreas; exocrine gland; pituitary gland) for the following definitions:
1. Gland that releases its secretion internally into a body fluid. 2. A gland that releases its secretion to the outside through a duct. 3. A set of glands located near the surface of the thyroid gland. 4. This is a largest gland of the human body. 5. This gland is located in the neck and consists of two lobes. Its hormones are thyroxine and calcitonin. 6. These glands are located atop the kidneys. Each gland consists of a medulla and a cortex. 7. This gland is attached to the base of the brain, has an anterior lobe and a posterior lobe. Most its secretion are controlled by the hypothalamus. Its hormones are growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormones, and some others.
Ex. 18. Choose the correct answer:
A mother consulted the doctor about her son who had grown up in height about 18 cm during the summer. On examination: height Ц 190 cm, weight Ц 68 kg. What endocrine glandТs hypersecretion may cause this condition? (thyroid gland, epiphysis, adrenal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas)
Ex. 19. Write out key words of the text УEndocrine SystemФ.
Ex. 20. Make up a plan of the text УEndocrine SystemФ.
|
|
|
Ex. 21. Give a summary of the text УEndocrine SystemФ.
Ex. 22. Pronounce and memorize the words to the theme studied:
Secretory [sI'krI:tqrI] activity секреторна д≥€льн≥сть; extension подовженн€; band смуга, зона; зв'€зка; vascular судинний; triiodothyronine ["traIaI'OdqTaI'ronIn] трийодтирон≥н; tetraiodothyronine тетрайодтирон≥н; thyroxine [TaI'rOksIn] тироксин (гормон щитопод≥бноњ залози); parietal [pq'raIItl] пар≥Їтальний, прист≥нковий; peritoneum ["perItqu'nI:qm] очеревина; adrenal cortex ['kO:teks] кора наднирковоњ залози; adrenal medulla [me'dAlq] мозкова речовина наднирковоњ залози; pancreatic islet (Langerhans islet) ['la:Ngqha:ns 'aIlIt] остр≥вець Ћангерганса, панкреатичний остр≥вець; norepinephrine ['nourepI'nefrIn] нореп≥нефрин, норадренал≥н; circulatory system система кровооб≥гу, кровотворна система; glucagon ['glu:kqgOn] г≥пергл≥кем≥чний гормон п≥дшлунковоњ залози, глюкагон; immature ["Imq'tjuq] cell незр≥ла кл≥тина.
Ex. 23. Read the following words and word-combinations:
Hypophysis; antidiuretic; hypothalamus; molecule; initiate protein synthesis; embryonic; capsule; mesoderm; elongate; enzyme.
Ex. 24. Read the following text:
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is known to secrete some major hormones (e. g. antidiuretic hormone, growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, lipotropins, prolactin) that directly regulate numerous body functions and the secretory activity of several other endocrine glands. The hypothalamus of the brain regulates the secretory activity of the pituitary gland, and, in turn, the activity of the hypothalamus is influenced by the central nervous system, and by the emotional state of the individual. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are the major sites in which the two regulatory systems of the body (the nervous and endocrine systems) interact. Indeed, a major portion of the pituitary gland (the posterior pituitary) is an extension of the hypothalamus. As for pituitary gland, it is roughly 1 cm in diameter and weighs 0.5 to 1 g. The pituitary gland is located inferior to the hypothalamus. It is divided functionally into two parts (posterior pituitary gland and anterior pituitary gland).
The thyroid gland is composed of two lobes connected by a narrow band of thyroid tissue. The lobes are lateral to the upper portion of the trachea just inferior to the larynx. The thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands with a weight of approximately 20 g. It is highly vascular and appears redder than its surrounding tissues. The thyroid hormones include both triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4); T4 is also called thyroxine. These substances constitute the major secretory products of the thyroid gland, with 10% T3 and 90% T4. Thyroid hormones bind with intracellular receptor molecules and initiate new protein synthesis.
The adrenal glands are near the top of each kidney. Like kidneys, they lie posterior to the parietal peritoneum and are surrounded by adipose tissue. They are enclosed by a connective tissue capsule and receive a well-developed blood supply. The adrenal glands are composed of an inner medulla and an outer cortex, which are derived from two separate embryonic tissues. Unlike most glands of the body, which develop from epithelial tissue, the adrenal cortex is derived from mesoderm. The adrenal medulla is a component of the autonomic nervous system and secretes two types of hormones: epinephrine (adrenaline), 80%, and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), 20%. The adrenal cortex secretes three hormone types: mineralocorticosteroids, glucocorticoids, and sex hormones. All are similar in structure in that they are steroids, highly specialized lipids that are derived from cholesterol.
The pancreas lies behind the peritoneum between stomach and the duodenum. It is elongated structure approximately 15 cm long. It weighs 85 to 100 g. The head of the pancreas lies near the duodenum, and its body and tail extend toward the spleen. The pancreas plays a key part in the digestive process, producing enzymes essential to the digestion of food. The pancreas is both an exocrine gland and endocrine gland. The endocrine portion, consisting of pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans), produces hormones that enter the circulatory system. Each islet is composed of alpha cells (20%), which secrete glucagons, beta cells (75%), which secrete insulin, and other cell types (5%). The remaining cells are either immature cells of questionable function or delta cells, which secrete somatostatin.
|
|
|
Ex. 25. Insert the missing words from the box:
1. The _ secretes at least nine hormones that regulate numerous body functions and other endocrine glands. 2. The hypothalamus _ pituitary gland activity through neurohormones. 3. The _ is just inferior to the larynx. 4. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of glucose, fat, and protein metabolism in many tissues, thus increasing body _. 5. Normal growth of many tissues is dependent on _ hormones. 6. The adrenal glands are near the superior pole of each_. 7. The adrenal cortex is derived from _. 8. Norepinephrine stimulates cardiac muscle and causes constriction of most peripheral _ vessels. 9. The adrenal _ hormones prepare the body for physical activity. 10. The pancreas is located along the small _ and the stomach. 11. It is both an _ and endocrine gland. 12. The endocrine portion of pancreas _ the pancreatic islets.
| thyroid gland; exocrine; regulates; consists of; thyroid; mesoderm; blood; medulla; temperature; pituitary gland; kidney; intestine. |
Ex. 26. Answer the following questions:
1. What hormones of the pituitary gland do you know? 2. What is the major function of the pituitary gland? 3. Where is the pituitary gland located? 4. What is the thyroid gland composed of? 5. What thyroid hormones do you know? 6. What do thyroid hormones initiate? 7. Where are the adrenal glands located? 8. What are the adrenal glands composed of? 9. What hormones does the adrenal cortex secrete? 10. What does the pancreas consist of? 11. What is the major function of the pancreas?
Ex. 27. Pick up correct statements (true or false choice):
1. As a group, endocrine glands are concerned with the regulation of metabolic processes. 2. Exocrine glands secrete hormones. 3. Hormone is carried to its target cells by body fluid. 4. Endocrine glands do not secrete hormones that affect target cells possessing specific receptors.
Ex. 28. Retell the text УEndocrine GlandsФ.
«аключний етап.
ќц≥нюванн€ поточноњ д≥€льност≥ кожного студента упродовж зан€тт€, проведенн€ стандартизованого к≥нцевого контролю та анал≥зу усп≥шност≥ студента. ¬иставленн€ оц≥нок та бал≥в у журнал обл≥ку в≥дв≥дувань ≥ усп≥шност≥ студент≥в. ≤нформац≥€ про тему наступного зан€тт€ та домашнЇ завданн€.
6. ƒодатки. «асоби дл€ контролю:
“естов≥ завданн€:
“естуванн€ початкового р≥вн€:
Test No 1: Insert the missing letters:
1 _drenal;
2 pitu_tary;
3 thyr_id;
4 pancre_s;
5 parathyr_id;
6 o_ary;
7 testi_le;
8 p_neal;
9 t_ymus;
10 ma_mary;
11 la_rimal;
12 swe_t.
a) a
b) i
с) o
d) v
e) c
f) e
g) h
h) m
“естуванн€ п≥д час основного етапу:
Test No 2:Match the following words with their translation:
| 1 lacrimal gland 2 sweat gland 3 target 4 protein 5 glycoprotein 6 polypeptide 7 amino acid 8 lipid 9 glandular | a. м≥шень b. б≥лок, протењн c. гл≥копротењн d. ам≥нокислота e. гландул€рний, залозовий, такий, що стосуЇтьс€ залози f. л≥п≥д g. сльозна залоза h. пол≥пептид, пол≥пептидний |
“естуванн€ к≥нцевого р≥вн€ знань:
|
|
|
Test No 3: Insert the missing words from the box:
1. The _ secretes at least nine hormones that regulate numerous body functions and other endocrine glands. 2. The hypothalamus _ pituitary gland activity through neurohormones. 3. The _ is just inferior to the larynx. 4. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of glucose, fat, and protein metabolism in many tissues, thus increasing body _. 5. Normal growth of many tissues is dependent on _ hormones. 6. The adrenal glands are near the superior pole of each_. 7. The adrenal cortex is derived from _.
| a) thyroid gland; b) exocrine; c) regulates; d) consists of; e) thyroid; f) mesoderm; g) blood; h) medulla; i) temperature; j) pituitary gland; k) kidney; l) intestine. |
—итуац≥йн≥ завданн€.
1. Tell your fellow-student about structure of endocrine system.
2. Describe the functions of endocrine system.
онтрольн≥ питанн€:
1. What does the endocrine system consist of? 2. What is the function of endocrine system? 3. What glands of external secretion do you know? 4. What glands are the glands of internal secretion? 5. What is a hormone? 6. Where do the hormones circulate?
ѕрактичн≥ завданн€:
Choose the correct answer:
A mother consulted the doctor about her son who had grown up in height about 18 cm during the summer. On examination: height Ц 190 cm, weight Ц 68 kg. What endocrine glandТs hypersecretion may cause this condition?
(thyroid gland, epiphysis, adrenal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas)
7. –екомендована л≥тература.
1. Ѕердический ј.Ћ. ќптимизаци€ системы обучени€ иностранному €зыку. - ћ.: ¬ысша€ школа. Ц 1989. - 101 с.
2. ‘оломкина —. . ќбучение чтению на иностранном €зыке в не€зыковом вузе. - ћ.: ¬ысша€ школа. Ц 1987. - 206 с.
3. ™н≥кеЇва ј.Ѕ., орнейко ≤.¬. Ц јнгл≥йська мова дл€ медик≥в. Ц ’арк≥в, ’ƒћ”, 2000 Ц 64 с.
4. Ogarkova A. Modern Medical Potential. Ц ињв: Ќ” ≥м. “.Ўевченка. Ц 2004. Ц 111 с.
5. Ritchel ¬. Tests in English. Ц WsiP, 2002. Ц 345 p.
6. DorlandТs Ilusrated Medical Dictionary. Ц W.B. Saunders Company, 1994. Ц 1338 p.
ћетодична рекомендац≥€ складена к. ф≥лол. н., доц. «наменською ≤.¬.






