| 1.Natural ecosystems 2.Pollution 3.Water pollution 4. Air pollution 5.Greenhouse effect 6.Acid rain 7.Ozone hole |
a) "... the direct or indirect introduction, as a result of human activity, of substances or heat into the water or land which may be harmful to human health or the quality of aquatic ecosystems or terrestrial ecosystems directly depending on aquatic ecosystems, which result in damage to material property, or which impair or interfere with amenities and other legitimate uses of the environment."
b) It is another burning ecological problem. It comes from variety of different sources like factories, power plants, cars, buses, trucks, wildfires, etc... It threatens the health of humans, trees and animals and is destroying the ozone layer which protects us from dangerous ultra-violet radiation. Statistically speaking, every day average individual breathes more than 3,000 gallons of air and since many people live in urban areas full of smog this affect their health causing them lot of health problems.
c) There is no limit to its size. It can range from a small puddle to the Pacific Ocean. Planet Earth can be considered as it, as the entire solar system. It has two components: biotic and abiotic. Biotic components are the living entities within the system. They include microorganisms, plants and animals. Abiotic components are made up of air, rocks, water and energy. Populations make up the next scientific section of it.
d) It refers to the presence in aqua substance of harmful and objectionable material —obtained from sewers, industrial wastes and rainwater run—off — in sufficient concentrations to make it unfit for use.
e) The warming of the atmosphere by the trapping of longwave radiation being radiated to space. The most responsible for this effect are water vapor and carbon dioxide. Steady increase in the Earth's average lower atmosphere (near surface) temperature due to heat retention caused by the accumulation of them (including water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs). These substances form a blanket around the earth that lets the incoming sun rays (short wave radiation) to pass through but blocks the reflected heat rays (long wave radiation) from going out into the space.
f) A severe depletion (зменшування) of it in a region of layer, particularly over Antarctica and over the Arctic. The depletion is caused by the destruction of it by CFCs and by other compounds, such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and carbon tetrafluoride (CF4). The amount of it in holes is about 55 to 60 percent of the normal concentration. The amount of ultraviolet radiation the Earth receives is greatly increased by ozone depletion, creating a heightened risk of skin cancers and likely contributing to global warming.
g) Most of them are generally slightly acidic due to the carbonic acid from carbon dioxide in atmosphere. But they are caused when sulfur (sulphur) dioxide and nitrogen oxides (from automobile exhausts and industrial emissions) are washed out from the atmosphere by rain as weak sulfuric (sulphuric) and nitric acid. They can cause serious damage.
Choose one of these pictures and describe the process of greenhouse effect.
A)
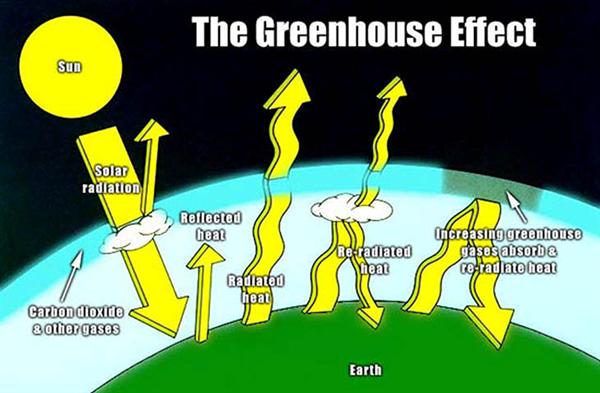
B)
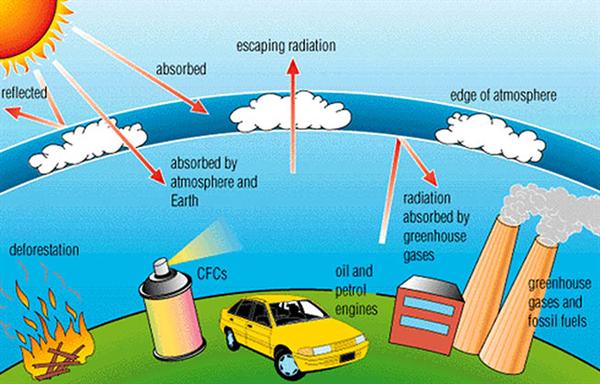 b
b
6. Read the text and name the main factors which influence on people’s health.
Do you think that all these factors are the result of human activity? Why?






