A) moisture content
B) temperature
C) pressure gradient
D) weather conditions
5. Which of the following is NOT considered a "Greenhouse Gas?"
A) water vapors
B) nitrous oxide
C) carbon dioxide
D) hydrogen
6. Lead compounds are added to the gasoline in order to
A) enhance fuel efficiency.
B) increase octane number of the fuel
C) reduce emissions of green house gases
D) all of the above
7. _____________________________ emphasizes the idea that all creatures have equal rights and
values, being centred on nature rather than humans.
A) anthropocentrism
B) biocentrism
C) conservation
D) environmentalism
8. Replacement of incandescent bulbs by fluorescent lights saves ________of electricity consumed.
A) 80%
B) 60%
C) 40%
D) 20%
E) None
9. Rivers and lakes represent only ______ of the total water resources on the Earth.
A) ~3%
B) 0.02%
C) 0.82%
D) 0.50%
10. Which country in Central Asia is rich in water resources and has more control over these resources:
A) Kyrgyzstan
B) Uzbekistan
C) Kazakhstan
D) Turkmenistan
11. Excessive amounts of fertilizers runoff into surround water reservoir and cause eutrophication.
A) True
B) False
12. Domestic water is mostly used for the following purpose:
A) taking a bath/ a shower
B) toilet flashing
C) drinking and cooking
D) washing dishes
13. Hydrogen represents
A) renewable energy source
B) primary energy source
C) secondary energy source
D) none of the above.
14. What should be on top of your list of energy saving measures?
A) turning off lights
B) insulation
C) closing windows
D) turning off electric appliances
15. Which of the following types of radiation is characterized by the highest energy?
A) ultra-violet radiation
B) infra-red radiation
C) visible light
D) microwaves
E) X-rays
16. Idea of recycling the matter is a distinctive feature of
A) classical economics
B) neoclassical economics
C) ecological economics
D) none of the above
17. Internal costs are expenses borne by
A) those who are using a natural resource.
B) by someone other than the individual/company who uses a natural resource
C) by the owner of the land, on which a natural resource is located
D) none of the above
18. Resources in Neoclassical Economics are considered as:
A) Resources exist in fixed (finite) amounts.
B) Expanded idea of resources: labor, knowledge, and capital.
C) Renewable and nonrenewable resources.
D) None of the above
19. All the following are the ways to achieve Urban Sustainability EXCEPT for:
A) Maintain greenbelts in and around cities.
B) Encourage walking and low-speed vehicles.
C) Recycling wastes and water.
D) Unlimited city size, unlimited population growth
20. The largest gas deposit in Kazakhstan is
A) Tengis
B) Kashagan
C) Karachaganak
D) Kalamkas
21. The major problem associated with the use of natural gas as fossil fuel is:
|
|
|
A) Low heating capacity
B) High level of pollution produced when burning gas
C) Transportation problems
D) None of the above
22. Fuel efficiency of 5 L gasoline per 100 km is equivalent to
A) 0.05 km/L
B) 20 km/L
C) 5 mpg
D) none of the above
23. At the present consumption rate, it is likely that coal reserves in the world could supply energy for human use for another ______ years.
A) 200 years
B) 50 years
C) 60 years
D) 20 years
24. Resources in Neoclassical Economics are considered as:
A) Resources exist in fixed (finite) amounts.
B) Expanded idea of resources: labor, knowledge, and capital.
C) Renewable and non-renewable resources.
D) None of the above
25. According to classic supply and demand theory, when demand is high supply is low, and market equilibrium occurs when supply equals demand.
A) True
B) False
26. All the following represent features of a Sustainable Commons EXCEPT for:
A) community members should live on resource
B) each community member may bring as many animals to the Commons as he/she needs
C) resource and use are to be actively monitored
D) effective conflict resolution mechanisms
E) Communal Resource Management Systems
27. The biggest off-shore oil deposit in Kazakhstan is
A) Tengis
B) Kashagan
C) Karachaganak
D) Kalamkas
28. Dominating Biome in Kazakhstan:
A) deserts
B) steppes
C) semi-deserts
D) forests
29. What is the major cause of all other environmental problems?
A) wars
B) overpopulation
C) depletion of resources
D) loss of biodiversity
E) pollution
30. Primary reason of Aral sea ecological catastrophe is
A) industrialization of Aral sea basin area
B) global climate change
C) overfishing and overhunting
D) poorly managed irrigation system
B. Fill in the blanks (0.5 x 2 = 1 point):
1. Sustainable development is such development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
2. Thermal pollution is raising water temperatures from normal level that negatively affects water quality and aquatic life.
C. Answer the following questions (5 pts):
1 (3 pts). Define the following major type of ecological problems: DEPLETION OF RESOURCES.
Justify your answer with proper examples.
Depletion of resources means that resources such as minerals, fuels, soil, and timber are depleted or used up. There are three ways of depletion; the first is when substance can be destroyed, converted to something else. For example, coal is converted to ashes which is converted to gas. The second way is when substance is considered lost if it is diluted or not usable. For example, Iron ore is subject to mining if it contains more that 40%
2(2 pts). Define ACID RAIN and list its major components.
D. Solve the following problems (8 pts):
1(5 pts). The distance between Almaty and Taraz is 524 km. Driving on a highway from Almaty to Taraz, SakenТs automobile consumed full tank of gasoline AI-92. Next time when Saken visited Taraz dring the same car, he took gravel road and his gasoline consumption increased up to 68L.
A) Find fuel efficiency rates of his car on two types of road. Which road results in higher fuel efficiency? Justify your answer.
B) Find car emissions produced during one trip for each of these roads. Calculate their ratio.
|
|
|
C) How much money does Saken save per one trip Almaty Ц Taraz by taking highway instead of gravel road?
Use the following data: car emission coefficient = 2.42 kg CO2/L;
tank size for SakenТs car = 60 L;
price of gasoline AI-92 is 91 tenge/L
gravel road Ц грунтова€ дорога; дорога, покрыта€ гравием
2(3 pts). LED mobile advertising boards consume 50% less electricity than fluorescent advertising displays (using fluorescent bulbs) at the same light intensity. One advertising board is 1000W in power and illuminating city 8 hours per day.
A) Find monthly savings of electricity (in kWh) when using LEDs instead of fluorescent bulbs.
B) Estimate reduction in greenhouse gas emissions per month due to such replacement.
C) Calculate absolute (in tenge) and relative (in%) monthly financial gain per one advertising
board.
CO2 Emissions Coefficient for Electricity = 0.75 kg CO2/kWh
Ignore cost of the bulbs, use electricity cost 10.10 tenge/kWh
E. Graph analysis (8 pts).
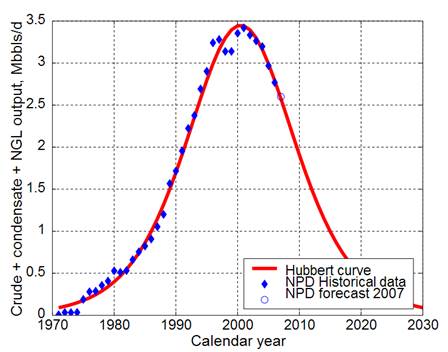
The graph below is Hubbert curve for Norwegian oil & gas production in Mbrls/day.
Explain the shape of this curve.
a) What was the maximum of daily oil & gas production in Norway in Mbls/day? When?
b) What was the level of daily oil & gas production in Norway in 2100 (in Mbls/day)?
d) Calculate the decline in oil & gas production (in %) within decade 2000-2010?
c) Estimate maximum annual production level in Norway (in Gbls/year).