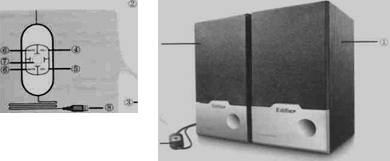
Box content
Ј 1 x Active speaker(with cable)
Ј 1 x Passive speaker(with cable)
Ј 1 x User's manual
1. Passive speaker 5. Volume down
2. Active speaker 6. Mute key
3. In line control pad 7. Power indicator
4. Volume up 8. USB plug
Operational guidance
1.Connect the USB connecting cable attached to the back panel of the active speaker to your PC/laptop.
If you connect the system to your PC / laptop for the first time, all required USB device drivers would be installed automatically, and this may take some time, 2. Adjust the volume to a comfortable level, and then you're ready to enjoy the music loaded in your computer.
Note: R18 USB can only work perfectly with Windows 2000 / XP / Vista / Mac OS X and more advance operating systems.
Specification RMS
Power output: 1.2W x 2
Satellite: (THD = 10%, f0= 1 kHz)
Signal to noise ratio: >80 dBA
Distortion: <2%
Input type: USB
Input sensitivity: 1000±50 mV
Adjustment: Master volume control keys on the in-line control pad
Speaker unit: 50 x 90 mm, magnetically shielded, 4ohm
Dimension: 85 * 166 x 110 mm (W x H x D)
Net weight: Approx 1 kg
Gross weight: Approx 1.3 kg
Warnings:
ХRefer to qualified personnel for servicing.
ХPlease remove the USB plug from your PC /laptop if the system is unused for long period of time.
ХPlease do not expose the system to rain or moisture.
If you have any further questions or concerns regarding Edifier Products
Please visit our website at: www.edifier.com,
or email Edifier Support for further assistance at: [email protected],
If you prefer, you may contact us by phone, Toll Free: 1-877-EDIFIER (334-3437).
ѕитанн€ дл€ самоконтролю:
1.Is it necessary to remove the plug from the mains supply before cleaning the machine?
2. Should the device be used, if there is damage of any kind?
3. Can we use device with wet or moist hand?
–екомендована л≥тература:
ѕол€кова “.ё јнглийский €зык дл€ инженеров.”чебник. ћ.: Bысша€ школа, 2003.- 243 с
ƒидактичне забезпеченн€: ≥нструкц≥њ з використанн€ електроприлад≥в, словники.
—јћќ—“≤…Ќј –ќЅќ“ј є7
“ема: “ехн≥чний переклад та переказ тексту за фахом: Ђ√раф≥чна картаї
«авданн€ до самост≥йноњ роботи:
I. —класти словник незнайомих сл≥в (не менше 10 сл≥в).
Ќаприклад:
| —лово | “ранскрипц≥€ | ѕереклад |
| image | [`imidз] | зображенн€ |
II. ¬ивчити слова на пам'€ть
III. ѕерекласти текст письмово украњнською мовою
IV. —класти анотац≥ю англ≥йською мовою (письмово)
V. ѕереказати текст зг≥дно анотац≥њ.
Graphics card
 A GeForce 4 4200-based graphics card
A GeForce 4 4200-based graphics card
A graphics card or video card is a component of a computer which is designed to convert a logical representation of an image stored in memory to a signal that can be used as input for a display medium, most often a monitor utilising a variety of display standards. Typically, it also provides functionality to manipulate the logical image in memory.
|
|
|
Overview
As was in the past, many graphics cards are separate devices, attached to a PC motherboard via the ISA, PCI, VESA, or AGP buses, with recently-introduced PCI-Express expected to be prominent in the future.
Increasingly, however, the graphics card is no longer a "card" in the strictest sense, but is an integrated section of the motherboard dedicated to the same purpose. Integrated-graphics-displays usually have inferior 3D performance compared with dedicated graphics cards (due to using cheaper chipsets and sharing system memory rather than using dedicated memory); those who require high performance still prefer non-integrated solutions. Integrated graphics displays have gradually become more common since the mid 1990s as advancing technology makes them more practical. Anyone using their computer for office tasks, web browsing, email and such things will be fine with an integrated graphics chip.
The most powerful graphics hardware, usually geared towards 3D graphics for games, is still card-based. Their processing engines are sometimes called GPUs (graphics processing units). The longterm goal of graphics cards manufacturers (and game developers) appears to be realtime photorealistic rendering. New products and technologies are often touted to provide "Hollywood quality" - 3dfx used claims of movie-quality effects to promote their Voodoo 5 cards with T-Buffer technology, allowing motion blur, depth of field and full screen anti-aliasing effects. nVidia talked about "The dawn of cinematic computing" when introducing its GeForce FX chip with the Dawn technology demo. Others use the new technology for more impressive, but unrealistic rendering, such as cel shading.
Conversely, sometimes 3D-graphics capabilities are not relevant to the choice of high-performance graphics card; 2D graphics and fine visual-quality fill specialised niches in areas such as medical imaging. The original hardware accelerated 3D Tenderers come on a board that was used in conjunction with a normal graphics card. The card would add 3D graphics to the 2D rendering from the graphics card via a pass-through cable. The first consumer-level 3D hardware was the Voodoo by the now defunct 3dfx.
ѕитанн€ дл€ самоконтролю:
1. What is video card?
2. Is the graphics card a "card" in the strictest sensenowerdays?
3. What is called 3 dfx?
–екомендована л≥тература:
1. √альперин ».–., ћедникова Ё.ћ. Ѕольшой англо-русский политехнический словарь. Ц ћосква: –усский €зык, 1987.
2. ‘едоршин ќ.ѕ., ™вст≥фЇЇв ѕ.‘., –€бушенко “.Ћ. јнгл≥йська мова. ѕрактикум з науково-техн≥чного перекладу, Ц “ерноп≥ль Ќавчальна книга Ц Ѕогдан, 2002 Ц 52с.
3. „ебурашкин Ќ.ƒ. ’рестомати€ по техническому переводу. Ц ћосква: ѕросвещение, 1987.
ƒидактичне забезпеченн€: текст, словники.
—јћќ—“≤…Ќј –ќЅќ“ј є8
“ема: “ехн≥чний переклад та переказ тексту за фахом: ЂЅ≥л √ейтс Ц король програмного забезпеченн€ї
«авданн€ до самост≥йноњ роботи:
I. ¬ивчити слова з тексту на пам'€ть
Ahead - у майбутньому
Competitor Ц конкурент
Curious - допитливий
Fierce Ц несамовитий
Huge Ц величезний
Life Scount rank - дов≥чний титул бойскаута
Operating system - система функц≥онуванн€
PC - personal computer
|
|
|
Scouting - д≥€льн≥сть бойскаут≥в
Security system - —истема безпеки
Software - програмне забезпеченн€
Solid-state - твердий
The develop - розробл€ти
Tiny - дуже маленький
To be obsessed - бути захопленим
To entertain oneself - розважатис€
To inspire - надихати
To perform - виконувати
To predict - пророкувати
Troop - заг≥н
Wallet-size - розм≥ром з гаманець
Wizard - чар≥вник, маг
Worth - €кий маЇ
II. ѕрочитайте та переклад≥ть статтю украњнською мовою усно.

ЂBill Gates, the Software Kingї
1. Most of the computers in the world use software invented by Bill Gates, the founder of Microsoft Inc. of Redmond, Wash. Software is the set of programs that make computers Ч whether business or personal Ч perform various tasks.
2. Gates was born in Seattle, Washington, in 1955. As a boy, he was bright and curious. He was active in Scouting, reaching Life Scout rank in Troop 186. He especially loved hiking, camping and other outdoor adventures.
3. But Gates was obsessed with computers. While a student at Harvard University in 1975, Gates and a friend Paul Allen, developed a computer language for an early version of the personal computer. Microsoft was born. Gates went on to develop operating systems, such as MS-DOS and software programs.
4. Thanks to Microsoft. Gates is now one of the richest men in America. He is worth more than $8 billion
5. A technical wizard and a fierce business competitor. Gates sees great things ahead for computers. He says they "are really going to change a lot of things in the world Ч the way we work, the way we play and entertain ourselves and even the way we are educated.Ф
THE BINARY NUMBER SYSTEM
6. Early digital computers inspired by Howard Aiken's Mark I were huge, sometimes filling an entire room. That was because thousands of switches were needed to compute his binary number system.
7. In the binary number system, only two digits are recognized by the Computer: 0 when a switch is off, and 1 when the switch is on. Different combinations of those two digits can represent thousands of letters and numbers.
8. The binary number system is still used in today's computers. The difference is that the thousands of electrical switches have been replaced by one tiny solid-state chip than does the translations electronically. That's why your computer only fills up part of your desk, not your whole bedroom.
COMPUTERS IN YOUR FUTURE
9. Microsoft's Bill Gates and other computer experts see great things ahead. In the next few years, you will be able to sit at your computer and see high-quality video sent from any place on earth.
10. They predict you will also have a wallet-size personal computer. With it you will be able to store photographs, pay bills, get the news, send messages, see movies and open locks with digital keys.
11. At home on your TV size PC you will be able to see and talk with friends in other states, get medical advice, check magazine articles and pictures in a far-off library and order a pizza.
12. A computerized control system at home will regulate your lighting, temperature and security system.
13. Big dreams?
14. Perhaps. But engineers are working to make it reality.
From "Boys'Life"
III. ѕерекласти письмово украњнською мовою абзаци є3,6,7, 9-12
IV. —класти анотац≥ю англ≥йською мовою (письмово)
V. ѕереказати текст зг≥дно анотац≥њ.
«авданн€ дл€ самоконтролю:
«верн≥ть увагу на твердженн€. якщо твердженн€ в≥рне, поставте Ђ+ї, €кщо Цпомилкове Ђ-ї, €кщо мова про це не йшла - Ђ0ї.
1.Most of computers in the world use software invented by Bill Gates.
2. Gates was obsessed with aircraft industry.
3. When Microsoft was born, Gates stopped to develop operatining systems.
4. While a professor at Harvard University, Bill and his friend developed a computer language.
5. In the binary number system only two digits are recognized by the computer.
|
|
|
6. Computer experts predict you will also have a wallet-size TV-set.
7. With personal computer you will not be able to store photos, pay bills, sent messages.
8. A computerized control system at home will regulate your security system.
9. Bill Gates was active in hiking.
10. Software is the set of programs that make computers perform only one task.
–екомендована л≥тература:
1. √альперин ».–., ћедникова Ё.ћ. Ѕольшой англо-русский политехнический словарь. Ц ћосква: –усский €зык, 1987.
2. ‘едоршин ќ.ѕ., ™вст≥фЇЇв ѕ.‘., –€бушенко “.Ћ. јнгл≥йська мова. ѕрактикум з науково-техн≥чного перекладу, Ц “ерноп≥ль Ќавчальна книга Ц Ѕогдан, 2002 Ц 52с.
3. „ебурашкин Ќ.ƒ. ’рестомати€ по техническому переводу. Ц ћосква: ѕросвещение, 1987.
4. Bill Gates, the Software King.//Boy`s life. Musters of invention. Digest 13, 2005.
ƒидактичне забезпеченн€: текст, словник.
—јћќ—“≤…Ќј –ќЅќ“ј є9
“ема: ќсновн≥ документи дл€ працевлаштуванн€. –езюме. —кладанн€ власного резюме.
«авданн€ до самост≥йноњ роботи:
I. «аписати, перекласти та вивчити мовленнЇв≥ зразки розд≥лу Ђƒ≥лова англ≥йська моваї:
To look for, work experience, employment, multinational company, license, customer services, taxation, to seek an employment, customs, fluent, male, female, translator, part-time, public relations, estate, project managing, university degree, further information, computer experience, guide company, driverТs license, reliable, responsible, qualified, research centre, considerable abilities.
II. ѕрочитайте та запамТ€тайте:
ўо таке резюме? –езюме Ц це стисл≥ данн≥ з тих д≥л€нок вашого досв≥ду, що Ї вагомими дл€ посади на €ку ви претендуЇте. « €ких основних положень або пункт≥в воно складаЇтьс€?
–езюме граЇ велику роль при влаштуванн≥ на роботу. ƒобре складене резюме повинно давати повне у€вленн€ про ¬аш трудовий досв≥д та ¬ашу квал≥ф≥кац≥ю.
–езюме складаЇтьс€ з таких основних пункт≥в:
1. ≤мТ€, ѕр≥звище, адреса, телефон, в≥к.
2. ќсв≥та та квал≥ф≥кац≥€ (необх≥дно почати з останнього учбового закладу, €кий ¬и зак≥нчили, а також з останнього м≥сц€ роботи та перерахувати все в зворотному пор€дку).
3. ѕосаду, €ку ви бажаЇте займати.
4. –екомендац≥њ.
What is resume? Resume Ц is a summery of somebodyТs experience areas, which are necessary for position he applies for.
What main rules or points is it consisted of?
A resume takes a great part at finding a job. The good made resume must give the complete picture of your work experience and your qualification.
A resume consists of such main points:
1. Name, the last Name, address, telephone, age.
2. Education and qualification (it is necessary to begin with the last educational establishment you graduated, and also from the last place of work and to transfer all in a reverse order).
3. Position, which you desire to occupy.
4. References.
III. «апиш≥ть та переклад≥ть приклад: Уmini-resumeФ
| 376 West 186th Street, Apartment 6-J. New York, #4. 10033 tel.(212) 973-6792 Objective: A position of a programmer. Summary: 15 yers of experience in software programming. Familar with different kinds of computer languages. Experience:IBM (Research Centre) 2004 - presentSoftware programmer. Educat ion:Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1995-2003Dr. Sci. (Mathematics). Personal:Married, two children |
IV. —клад≥ть та запиш≥ть власне резюме за планом:
1. Name, surname, age;
2. Address, telephone, mob. telephone;
3. Education;
4. Qualification;
5. Work experience (сл≥д почати з останнього м≥сц€ роботи та перерахувати все у зворотньому пор€дку)
|
|
|
6. Personal;
7. Interests.
ѕитанн€ дл€ самоконтролю:
1. What is resume?
2. What are the main points of resume?
3. Must we be honest writing resume?
4. Will you follow the advice: УDonТt go to an interview without a record of former employment.Ф?
–екомендована л≥тература:
1. Business Writing Clear and Simple Copyright © 2007 Learning Express, LLC
2.David Chappell, Derek Marshall Vinsent, Power-Smith Simon Cavender. Building Contract Dictionary.Third Edition.
3.John Forster.Effectiv writing skills for Public Relations. Forth Edition.
ƒидактичне забезпеченн€: словники, навчально-методичний матер≥ал.
—јћќ—“≤…Ќј –ќЅќ“ј є10
“ема: ќсновн≥ документи дл€ працевлаштуванн€. јнкета.
«авданн€ до самост≥йноњ роботи:
≤. ¬ивч≥ть слова та словосполученн€, €к≥ сл≥д знати при заповненн≥ анкети.
An offer of employment-пропозиц≥€ працевлаштуванн€
Apprenticeship training-практика
Attend-в≥дв≥дувати
Degree-ступ≥нь
Dependants-утриманц≥
Divorced-розлучений
Duration-продовжуван≥сть
Duties-обовТ€зки
Employer-роботодавець
Income-дох≥д
Language proficiency Цволод≥нн€ ≥ншими мовами
Major subjects-головн≥ предмети
Married-одружений
Never married Цн≥коли не був одружений
Physical and mental disability-ф≥зична чи розумова вада
Primary school-початкова школа
Regarding-стосовно
Relationship-в≥дносини
Reside-проживанн€
Salary-зарплатн€
Secondary school-середн€ школа
Separated-проживанн€ окремо
Suffer-страждати
Trade qualification-профес≥йна квал≥ф≥кац≥€
Trade-профес≥€
Training-навчанн€
Unemployment-безроб≥тт€
Widowed-вдова\вд≥вець
≤≤. ”€в≥ть, що ви зак≥нчили навчальний заклад, маЇте трудовий досв≥д ≥ Ї претендентом на м≥сце програм≥ста у американськ≥й ф≥рм≥. «аповн≥ть надану вам ф≥рмою анкету англ≥йською мовою:
QUESTIONNAIRE
There are dirrerent types of questionnaires in every country, they are used when people apply for a job or a university, join the army, or ask for various allowances.
To fill in a questionnaire is not just a formality, how a person does it may change a lot in his life, influence his professional career.
The questionnairy given below is most frequently used, when it is demanded a detailed information about a
person's professional qualification.
DETAILS OF TRAINING AND EXPERIENCE
Full names Mr/Mrs/Miss
Address
Married/Never married/ Widowed/Divorced/Separated___________
Date of birth_____________________________________________
Nationality_______________Country of birth__________________
Do you or any of your dependendants suffer, or have any of you ever suffered from any physical or mental disability? (Yes or No)_______
If yes, give full details_____________________________________ _______________________________________________________
Number and ages of children over the age of 1,5 years:
| Name | Age | Qualification |
| For official use |
Have you ever resided in the USA, if so,
please give details
Items (A) and (D) must be completed by all applicants
Items (B) and (C) must only be completed if applicable
(A) School education: total number of years From To
Primary school ___________________________________________
Secondary/High school ____________________________________
Professional school _______________________________________
Highest examinations passed ________________________________
Major subjects ___________________________________________
(B) Higher education or special training:
Name of college, university or institution attended _______________ _______________________________________________________
Prescribed duration of course _______________________________
Period attended: From________________to____________________
Major subjects ___________________________________________
What degree, diploma or certificate obtained____________________
(C) Trade qualifications:
Duration of apprenticeship training; from__________to___________
Trade in which qualified____________________________________
(D) Record of employment: (these details must be in date
order including periods of unemployment for the last 20
years)
| Name of firm | City/Town in which located | From To | Nature of work |
(E) Describe briefly your present/last duties ____________________ _______________________________________________________
(F) What is the trade or business of your present/last
employer? _______________________________________________
|
|
|
(G) What is your present/ last monthly salary or income?__________
(H) What occupation do you intend following in USA? ___________
(I) Do you receive a pensio or do you have a private
income? If so, please give details ____________________________
(J) Have you an offer of employment in USA? If so, attach copy of the offer ________________________________________________
(K) Language proficiency: __________________________________
(a) What is your mother tongue? _____________________________
(b) What is your proficiency in other languages? (Answer YES or NO under the different headings)
| Language | Speak | Read | Write |
| English | |||
(L) Details regarding relatives and friends in the USA
| Name | Address | Relationship |
Date _____________________________________________________
≤≤≤. ѕисьмово переклад≥ть вс≥ пункти анкети украњнською мовою.
ѕитанн€ дл€ самоконтролю:
1. Are there dirrerent types of questionnaires in every country?
2. When are questionnaires used?
3. To fill in a questionnaire is just a formality, isn`t it?
4. Can a questionnairy influence one`s professional career?
–екомендована л≥тература:
1. Business Writing Clear and Simple Copyright © 2007 Learning Express, LLC.
2.David Chappell, Derek Marshall Vinsent, Power-Smith Simon Cavender. Building Contract Dictionary.Third Edition.
3.John Forster.Effectiv writing skills for Public Relations. Forth Edition.
ƒидактичне забезпеченн€: анкета, украњнсько-англ≥йський словник.
—јћќ—“≤…Ќј –ќЅќ“ј є11
“ема: “ехн≥чний переклад та переказ тексту за фахом: Ђ омп`ютерна наукаї
«авданн€ до самост≥йноњ роботи:
≤. «найд≥ть у прав≥й колонц≥ украњнськ≥ екв≥валенти англ≥йських сл≥в та словосполучень
| 1. to deal (with) | а. програмне забезпеченн€ |
| 2. to elaborate (to work out) programs | b. в≥дпов≥дати сучасним вимогам |
| 3. computer-aided design | с. апаратна частина |
| 4. computer-aided manufacturing | d. мати справу з(кимось або чимось) |
| 5. to meet up-to-date demands (requirements) | е. автоматизоване проектуванн€ |
| 6. software | f. захищати в≥д в≥рус≥в |
| 7. hardware | g.пропонувати р≥шенн€ |
| 8. to offer solutions | h. разробл€ти програми |
| 9. to solve problems | i. автоматизоване виробництво |
| 10. to defend from viruses | j. вир≥шувати проблеми |
≤≤. ѕереклад≥ть письмово украњнською мовою слова-≥нтернац≥онал≥зми, що зустр≥чаютьс€ у текст≥:
specialist, productivity, optimal, problem, logic, operation, program, virus, expert, instruction, method, computer, mathematics, designer, manager, calculator.
≤≤≤. ѕрочитайте та письмово пнреклад≥ть текст украњнською мовою:
ЂComputer Scienceї
Computer science is a part of an applied mathematics. Specialists in computer science say that this field of knowledge is very interesting because it deals with computer-aided-design (CAD) and computer-aided-manufacturing (CAM).
Computers are intended to improve the productivity of labour of scientists, designers, engineers, managers, and other specialists, because computers offer quick and optimal solutions. One of the main goals of using CAD/CAM is to shorten tjje time between designing and manufacturing.
Moreover, computers came in our life and to our houses and now we can solve our everyday problems with their help.
Computers can be divided into simple and complex devices. Simple computers such as calculators can perform addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. As far as complex computers are concerned they can do different logical operations and some of them even have artificial intelligence.
Thus in order to elaborate up-to-date and inexpensive programs as well as to defend them from viruses, it is important to know some programming languages.
There are low-level programming languages such as a machine language and an assembly language and high-level programming languages, for instance, FORTRAN, PASCAL, ADA, C, BASIC, etc.
≤V. ”сно перекаж≥ть текст англ≥йською мовою.
ѕитанн€ дл€ самоконтролю
1. What do specialists in computer science deal with?
2. What are the computers used for?
3. What operations can simple devices perform?
4. What operations do complex computers perform?
5. What are CAD/CAM systems intended to do?
6. What high-level programming languages do you know?
–екомендована л≥тература:
1. √альперин ».–., ћедникова Ё.ћ. Ѕольшой англо-русский политехнический словарь. Ц ћосква: –усский €зык, 1987.
2. ‘едоршин ќ.ѕ., ™вст≥фЇЇв ѕ.‘., –€бушенко “.Ћ. јнгл≥йська мова. ѕрактикум з науково-техн≥чного перекладу, Ц “ерноп≥ль Ќавчальна книга Ц Ѕогдан, 2002 Ц 52с.
3. „ебурашкин Ќ.ƒ. ’рестомати€ по техническому переводу. Ц ћосква: ѕросвещение, 1987.
4. ѕол€кова “.ё јнглийский €зык дл€ инженеров. ”чебник. ћ.: Bысша€ школа, 2003.- 243 с
5. Ћоскутова √.¬. ќ компьютере по-английски. Ц —анкт-ѕитербург: ј–ќ. Ц 2004
6. IBM PC дл€ пользовател€. Ц раткий курс. Ц ћ.: »Ќ‘ј. Ц 1999
ƒидактичне забезпеченн€: текст, словник.
—јћќ—“≤…Ќј –ќЅќ“ј є12
“ема: “ехн≥чний переклад та переказ тексту за фахом: Ђѕоходженн€ терм≥ну обробка словаї
«авданн€ до самост≥йноњ роботи:
I. —класти словник незнайомих сл≥в(не менше 10 сл≥в).
Ќаприклад:
| —лово | “ранскрипц≥€ | ѕереклад |
| challenge | [t∫əlendÁ] | претендент |
II. ¬ивчити слова на пам'€ть
III. ѕерекласти 1, 5 абзаци тексту письмово украњнською мовою
IV. —класти анотац≥ю англ≥йською мовою (письмово)
V. ѕереказати текст зг≥дно анотац≥њ.
ЂInternetworking challengersї
The Internet is the world's largest computer network. It is a global information infrastructure comprised of millions of computers organized into hundreds of thousands of smaller, local networks. The term "information superhighway" is sometimes used to describe the function that the Internet provides: an international, high-speed telecommunications network that offers open access to the general public.
The Internet provides a variety of services, including electronic mail (e-mail), the World Wide Web (WWW), Intranets, File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Telnet (for remote login to host computers), and various file-location services.
Electronic mail, or e-mail, is the most widely used function used on the Internet today. Millions of messages are passed via Internet lines every day through-out the world. Compared to postal service, overnight delivery companies, and telephone conversations, e-mail via the Internet is extremely cost-effective and fast. E-mail facilities include sending and receiving messages, the ability to broadcast messages to several recipients at once, storing and organizing messages, forwarding messages to other interested parties, maintaining address books of e-mail partners, and even transmitting files (called "attachments") along with messages.
Internet e-mail messages are sent to an e-mail address. The structure of an e-mail address is as follows: PersonalID@DomainName
The personal identifier could be a person's name or some other way to uniquely identify an individual. The domain is an indicator of the location of that individual, and appears to the right of the "at" (@) sign. A domain name is the unique name of a collection of computers that are connected to the Internet, usually owned by or operated on the behalf of a single organization (company, school, or agency) that owns the domain name. The domain name consists of two or more sections, each separated by a period.
From right-to-left, the portions of the domain name are more general to more specific in terms of location. In the United States, the rightmost portion of a domain is typically one of the following:
comЧindicating a commercial enterprise
eduЧindicating an educational institution
govЧindicating a governmental body
milЧindicating a military installation
netЧindicating a network resource
orgЧindicating a nonprofit organization
In November of 2000 seven new domain names were created and made available: biz,.info,.name,.pro,.aero,.coop, and.museum.
In non-U.S. countries, the rightmost portion of a domain name is an indicator of the geographic origin of the domain. For example, Canadian e-mail addresses end with the abbreviation "ca."
SPAM.
Commercial abuse of e-mail continues to be problematic as companies attempt to e-mail millions of online users in bulk. This technique is called "spam," so named after a skit by the comedy troupe Monty Python that involved the continuous repetition of the word. Online users are deluged with a massive amount of unwanted e-mail selling a wide array of products and services. Spam has become a network-wide problem as it impacts information transfer time and overall network load. Several organizations and governments are attempting to solve the spam problem through legislation or regulation.
VIRUSES.
Computer viruses spread by e-mail have also grown as the Internet has grown. The widespread use of e-mail and the growing numbers of new, uninformed computer users has made it very easy to spread malicious viruses across the network. Security issues for both personal computers and for network servers will continue to be a crucial aspect of the ongoing development of the Internet and World Wide Web.
WORLD WIDE WEB
The World Wide Web (WWW) is a system and a set of standards for providing a graphic user interface (GUI) to Internet communications. The WWW is the single most important factor in the popularity of the Internet, because it makes the technology easy to use and gives attractive and entertaining presentation to users.
Graphics, text, audio, animation, and video can be combined on Web pages to create dynamic and highly interactive access to information. In addition, Web pages can be connected to each other via hyperlinks. These hyperlinks are visible to the user as high-lighted text, underlined text, or images that the user can click to access another Web page.
BROWSERS.
Web pages are available to users via Web browsers, such as Mozilla/Firefox, Netscape Navigator, or Microsoft's Internet Explorer. Browsers are programs that run on the user's computer and provide the interface that displays the graphics, text, and hyper-links to the user. Browsers recognize and interpret the programming language called Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). HTML includes the ability to format and display text; size and position graphics images for display; invoke and present animation or video clips; and run small programs, called applets, for more complex interactive operations. Browsers also implement the hyperlinks and allow users to connect to any Web page they want.






