The article is a function word. It means it has no lexical meaning and is devoid of denotative function.
The article is a form word that serves as anoun determiner.Since the article is a noun determiner and the noun is the headword in a noun phrase,the syntactical role of the article consists in marking off a noun or a noun phrase as part of the sentence.
The morphological value of the article lies in indicating the substantivization of other parts of speech, mainly adjectives or participles, also pronouns, adverbs, numerals.
In the light of the oppositional theory the system of articles in English is described as one consisting of three articles – the definite article, the indefinite article, and the zero article (Fig. 39).

Fig. 39
The article is one of the main means of conveying the idea ofdefiniteness and indefiniteness.
The indefinite article can be used in three functions (Fig. 40). Each of them is realized under specific contextual conditions.
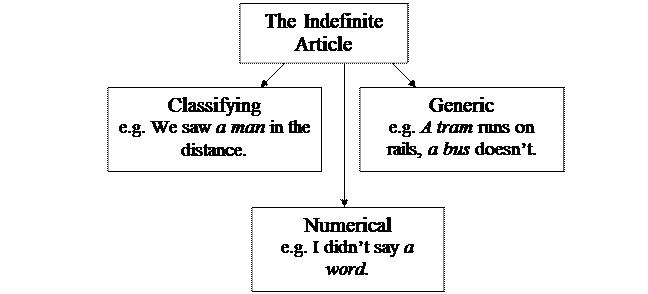
Fig. 40
In its classifying function the article serves to refer an object to the class or group of objects of the same kind.
In its generic function the indefinite article implies that the object denoted by the noun is spoken of as a representative of the class, and therefore what is said about the thing, animal, person, or notion mentioned, refers to any object of the same kind.
In its numerical function the indefinite article retains its original meaning of the cardinal numeral one.
The definite article implies that the speaker or the writer presents a person, a thing or an abstract notion as known to the listener or the reader, either from his general knowledge, or from the situation, or from the context. Hence, the two main functions of the definite article are specifying and generic (Fig. 41).





Fig. 41
The definite article in itsspecifying function serves to single out an object or a group of objects from all the other objects (things, persons, animals, abstract notions) of the same kind. The specification is carried out by means of a restrictive attribute, of the preceding context, the situation or the meaning of the noun.
The definite article in itsgeneric function refers the following noun to the whole class of objects of the same kind.
In most cases the zero article performs the same functions as the indefinite one. The difference is that the combinability of the latter is restricted to the group of countable nouns used in the singular form, whereas the zero article combines with uncountable nouns and countable nouns in the plural.
The plural form without an article corresponds to the classifying and generic uses of the indefinite article and sometimes to the generic use of the definite article (Fig. 42).
When used with the zero article, the noun loses its general grammatical meaning of thingness to a certain degree and acquires the meaning of qualitativeness. For example, the nouns “day” and “night” used with the zero article stand for “light” and “darkness” rather than time units.





Fig. 42






