–≈÷≈ѕ“ќ–џ —≈–ѕјЌ“»ЌЌќ√ќ “»ѕј, —ќѕ–я∆≈ЌЌџ≈ — √≈“≈–ќ“–»ћ≈–Ќџћ» √“‘-—¬я«џ¬јёў»ћ» Ѕ≈Ћ јћ»
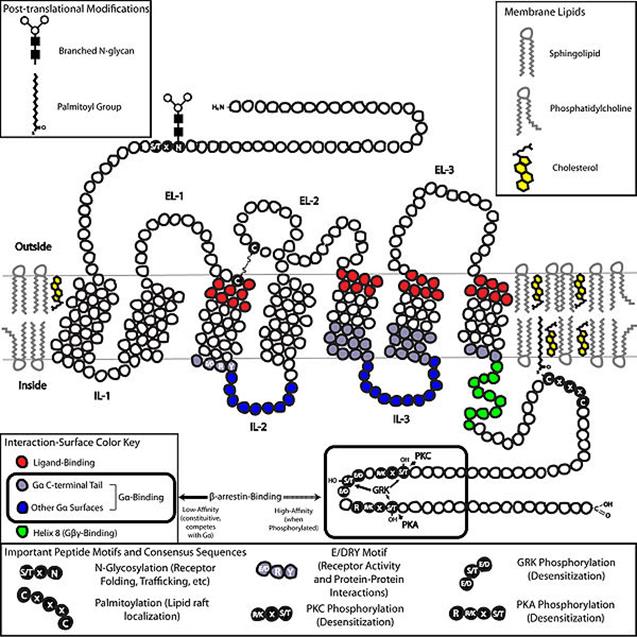
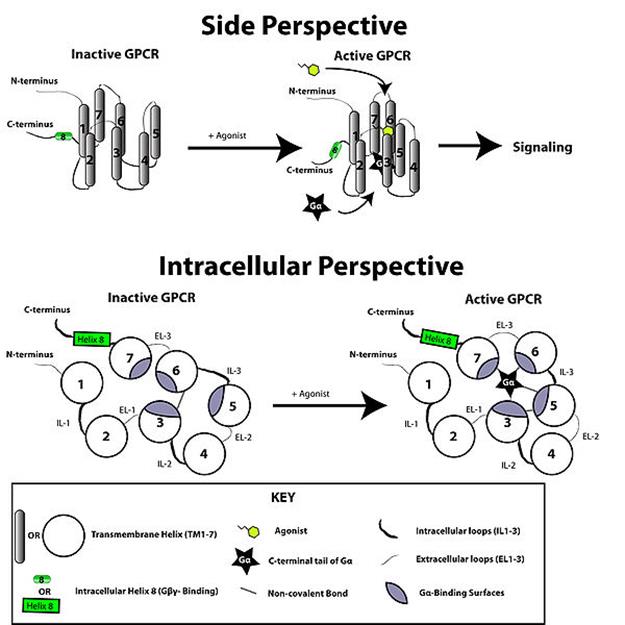
—в€зывание лиганда приводит к нарушению ионных св€зей между E/DRY-мотивом, который локализован в “ћ-3, и анионными остатками, локализованными в “ћ-6. ¬ результате конформаци€ рецептора мен€етс€ и он активирует a-субъединицу G-белка.

÷икл активации и дезактивации гетеротримерных √“‘-св€зывающих белков
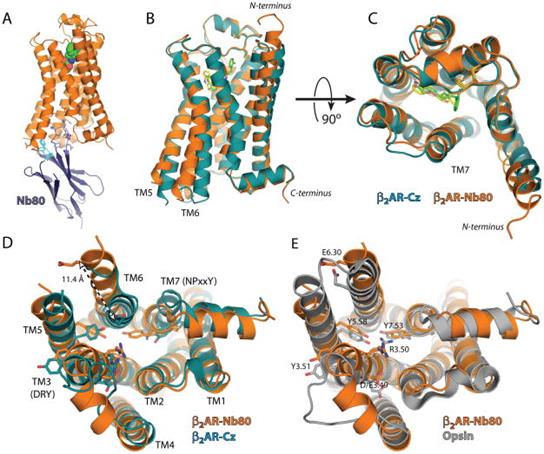
—табилизаци€ агонистом и Nb80-антителами β2-адренергического рецептора.

—труктура δ-опиоидного рецептора в сравнении с другими рецепторами

—в€зывание известных антагонистов с A2A-аденозиновым рецептором (кристаллическа€ структура).

Overall architecture of the 5-HT1B receptor bound to ERG and comparison of the ligand binding pocket shapes of the 5-HT1B receptor and the 5-HT2B receptor

Comparison of ligand-receptor interactions in 5-HT1B/ERG and 5-HT2B/ERG structures. (DandE) Diagram representation of ligand interactions in the binding pockets of 5-HT1B and 5-HT2B receptors
√етеротримерные G-белки
Quot;G protein" usually refers to the membrane-associated heterotrimeric G proteins. These proteins are activated by G protein-coupled receptors and are made up of alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) subunits, the latter two referred to as the beta-gamma complex.
Alpha subunits
Reconstitution experiments carried out in the early 1980s showed that purified Gα subunits can directly activate effector enzymes. The GTP form of the α subunit of transducin (Gt) activates the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase from retinal rod outer segments, and the GTP form of the α subunit of the stimulatory G protein (Gs) activates hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase.
Gα subunits consist of two domains, the GTPase domain, and the alpha-helical domain. There exist at least 20 different Gα subunits, which are separated into four main families. This nomenclature is based on their sequence homologies:
| G-protein-family | α-subunit | Gene | Signal transduction | Use/Receptors (examples) | Effects (examples) |
| Gi-family | |||||
| Gi/o | αi, αo | GNAO1, GNAI1, GNAI2, GNAI3 | Inhibition of adenylate cyclase, opens K+-channels (via β/γ subunits), closes Ca2+-channels | Muscarinic M2 and M4, chemokine receptors, α2-Adrenoreceptors, Serotonin 5-HT1 receptors, Histamine H3 and H4, Dopamine D2-like receptors | Smooth muscle contraction, depress neuronal activity |
| Gt | αt (Transducin) | GNAT1, GNAT | Activation of phosphodiesterase 6 | Rhodopsin | Vision |
| Ggust | αgust (Gustducin) | GNAT3 | Activation of phosphodiesterase 6 | Taste receptors | Taste |
| Gz | αz | GNAZ | Inhibition of adenylate cyclase | ? | Maintaining the ionic balance of perilymphatic and endolymphatic cochlear fluids. |
| Gs-family | |||||
| Gs | αs | GNAS | Activation of adenylate cyclase | Beta-adrenoreceptors; Serotonin 5-HT4, 5-HT6 and 5-HT7; Dopamine D1-like receptors, Histamine H2 | Increase heart rate, Smooth muscle relaxation, stimulate neuronal activity |
| Golf | αolf | GNAL | Activation of adenylate cyclase | olfactory receptors | Smell |
| Gq-family | |||||
| Gq | αq, α11, α14, α15, α16 | GNAQ, GNA11, GNA14, GNA15 | Activation of phospholipase C | α1-Adrenoreceptors, Histamine H1, Serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, Muscarinic M1 M3, and M5 | Smooth muscle contraction, Ca2+ flux |
| G12/13-family | |||||
| G12/13 | α12, α13 | GNA12, GNA13 | Activation of the Rho family of GTPases | Cytoskelatal functions, Smooth muscle contraction |

|
|
|
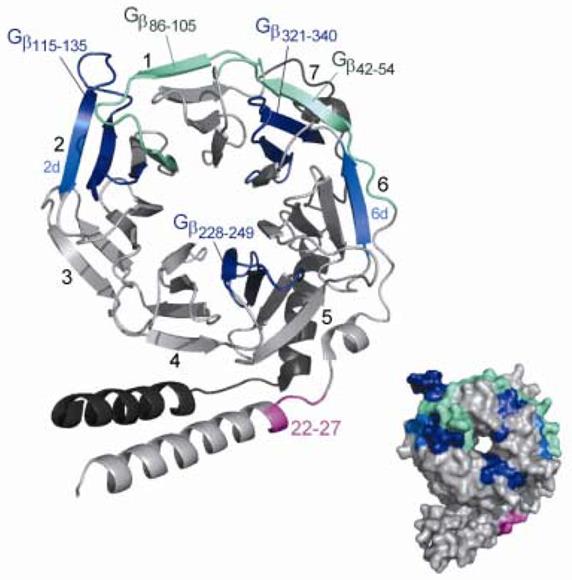
—убъединица

—труктура β2AR-Gs-комплекса
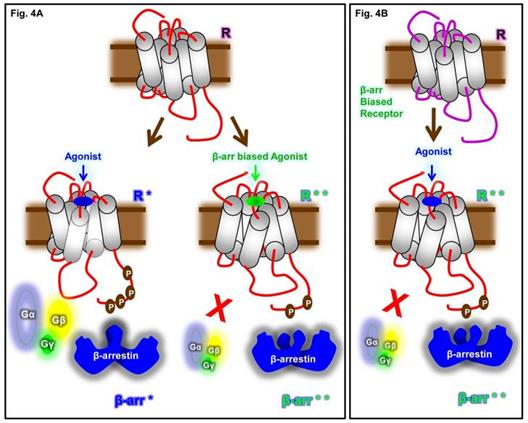
ј) —в€зывание Ђunbiasedї лиганда индуцирует активную конформацию рецептора (R*), в то врем€ как св€зывание β-аррестин-Ђbiasedї лиганда вызывает другую активную конформацию рецептора (R**). –азличные конформации рецептора способны эффективно взаимодействовать с различными конформаци€ми β-аррестина (β-arr* и β-arr**), что приводит к различным функциональным результатам. (b) —в€зывание Ђunbiasedї агониста с β-аррестин-Ђbiasedї рецептором также индуцирует различные конформации рецептора, которые сходны с таковыми, вызываемыми β-аррестин-Ђbiasedї лигандом в первом случае.







