Topics 7, 8
TAXATION.
WHAT ARE TAXES?
Taxes are a compulsory financial contribution by a person or body of persons towards the expenditure of a public authority. In modern economies taxes are the most important source of government revenues. Taxes on income (i.e. on wages, salaries, profits, dividends, rent and interest) and on capital are known as "direct" taxes. Taxes on commodities or services are known as "indirect" taxes.
Taxes are considered to have three functions:
(a) fiscal or budgetary, to cover government expenditure, to provide the public authorities with the revenue required for meeting the cost of defense, social services, interest payments on the national debt, municipal services, etc.;
(b) economic, to give effect to economic policy, to promote stable economic growth, to influence the rate of economic growth of the nation;
(c) social, to increase the economic welfare of the community, to lessen inequalities in the distribution of income and wealth.
Direct taxes
Governments finance most of their expenditure by taxation. If they spend more than they levy or change in taxes, they have to borrow money.
Direct taxes are collected by government from the income of individuals and business.
§ Individuals pay income tax on their wages or salaries, and most other money they receive (BrE: corporation tax; AmE: income tax).
§ Most countries have a capital gains tax on profits made from the sale of assets such as stocks or shares. This is usually imposed or levied at a much lower rate than income tax.
§ A capital transfer tax (commonly called death duty in Britain) is usually imposed on inherited money or property. Other names for this tax are inherited tax or estate tax.
§ Companies pay corporation tax on their profits. Business profits are generally taxed twice, because after the company pays tax on its profits, the shareholders pay income tax on any dividends received from these profits.
§ Companies and their employees also have to pay taxes (called national insurance in Britain) which the government uses to finance social security spending – unemployment pay, sick pay, etc.
Indirect taxes
Indirect taxes are levied on the production or sale of goods and services. They are included in the price paid by the final purchaser.
§ In most European countries, companies pay VAT or value –added tax, which is levied at each stage of production, based on the value added to the product at that stage. The whole amount is added to the final price paid by the consumer. In Canada, Australia, New Zealand and Singapore, this tax is called goods and services tax or GST.
§ In the USA, there are sales taxes, collected by retailers, levied on the retail price of goods.
§ Governments also levy excise taxes or excise duties – additional sales taxes on commodities like tobacco products, alcoholic drinks and petrol (BrE: petrol; AmE: gasoline).
§ Special taxes, called tariffs, are often charged on goods imported from abroad.
Income tax for individuals is usually progressive: people with higher incomes pay a higher rate of tax (and therefore a higher percentage of their income) than people with lower incomes. Indirect taxes such as sales tax and VAT are called proportional taxes, imposed at a fixed rate. But indirect taxes are actually regressive: people with a low income pay a proportionally greater part of their income than people with a high income.
Non-payment of tax
To reduce the amount of income tax that employees have to pay, some employers give their staff advantages instead of taxable money, called perks, such as company cars and free health insurance.
Multinational companies often register their head offices in tax havens – small countries where income taxes for foreign companies are low, such as Liechtenstein, Monaco, the Cayman Islands, and Bahamas.
Using legal methods to minimize your tax burden – the amount of tax you have to pay – is called tax avoidance. This often involves using loopholes – ways of getting around the law, because of an error or a technicality in the law itself. Using illegal methods – such as not declaring your income, or reporting it inaccurately – is called tax evasion, a nd can lead to big penalties.
Characteristic of the basic kinds of taxes of Republic of Kazakhstan
Under Kazakhstan law, all Kazakhstan legal entities, whether they have foreign investment or not, are subject to the profit tax law. Foreign entities that have a taxable permanent establishment in Kazakhstan are also taxed under this law.
Kazakhstan taxes provide revenue for two tiers of the budget: republican and local. The major taxes paid to the budget are: Corporate income tax; Value-added tax (VAT); Securities tax; Withholding tax.
Kazakhstan government tries to create a climate in which business can thrive, to keep the tax burden as low as possible. It also attempts to eliminate tax allowances, which deprive the budget of tax revenues, and to improve tax collection.
Tax returns for Kazakhstan legal entities are audited by the tax authorities at the time they are submitted.
When a company resident in one country receives income or gains from a source in another, or when shareholders and company are domiciled in different countries it is
possible that incomes arising will be taxable in each country, i.e. taxed twice. Many countries seek to mitigate the potentially harmful effects of double taxation by entering with other countries into double tax treaties, or arrangements preventing the same income being taxed twice.
A number of countries have problems because of significant taxpayer non-compliance.
Along with cases of illegal evasion of tax obligations there are entirely legal ways of avoidance by which a person may so arrange his affairs as to minimize, or even eliminate, tax liability on his property and income.
1. The corporate income tax
The corporate income tax occupies a significant place inreceipts of the state budget of Kazakhstan.
The mechanism of taxation by corporate income tax defines the order of calculation, payment, condition of collection, privilege and sanction, terms of payment of the tax by the legal person.
The tax is paid by the legal persons, residents of Republic of Kazakhstan receiving income, including noncommercial and budget organizations under the incomes of enterprise activity.
Object of taxation is:
1) taxable income;
2) income taxed at a source of payment;
3) net income of the legal person-of nonresidents who is carrying out activity in Republic of Kazakhstan through constant establishment.
2. Individual income tax
The payers of individual income are the physical persons, foreign physical persons.
Object of taxation is the income taxed at a source of payment and the income, not taxed at a source of payment.
To the incomes of tax bearer taxed at a source of payment concern: the income of the worker (incomes, charged by the employers reduced for the sum of tax deductions; the income of the worker in the natural form; income as a material benefit); other incomes of natural persons of fiscal agents, the income of single payments; pension payments from accumulated pension funds; the income of dividends, compensations, prizes; the grants (expect for paid the trainee in organizations of education, in the sizes established by the legislation of Republic of Kazakhstan for the state grants); income under the contracts of insurance.
Indirect taxes
Indirect taxes express fiscal interests of the state. Their reasonable application can positively influence on process of pricing and on pattern of consumption.
Use of consumption taxes what excises are, the tax from sales, the value-added tax, is more preferable, as:
· from them it is more difficult to evade;
· to them it is less connected with economic infringements;
· they reduce stimulus to work less;
· for them anonymity is characteristic.
Receipts concern to indirect taxes from foreign trade activities (customs incomes as the customs, taxes to export and import, a variation in prices of the goods sold on a home market and their invoice cost) also.
4. Value added tax (VAT)
The payer of the tax compensates suffered as a result of its payment to the state of loss by increase of the prices and shifts payment of the tax on the buyer.
Object of taxation is taxed turnover and taxed import.
Taxed turnover is the turnover made by the payer of the tax to added cost:
1) on realization of the goods (jobs, services), expect for free turnover;
2) on purchase of jobs, services from nonresident, tax, not being the payer, to added cost in Republic of Kazakhstan;
3) on the rests of goods (including basic means), on which the tax to added cost was referred to offset.
The size of a taxed turnover is defined on the basis of cost of the sold goods, jobs, services proceeding from the used prices and tariffs, without inclusion in them the VAT.
Taxed import are the goods imported on territory of Republic of Kazakhstan (expect for released from tax to added cost), declaring according to the customs legislation of Republic of Kazakhstan.
The rate of tax during its action consistently reduces from 28% up to 26%, 20%,16% and then –up to 12% in 2009. to the size of taxable turnover and taxable import).
5. Excises
Excises - taxes to the goods included in the prices and paid by the buyer. The excises are paid by the manufacturers of the goods having by virtue of the specific properties exclusively high prices and steady demand. Within excises service can be taxed, thus the sum of the tax is included in the tariff.
Under excise goods in Kazakhstan are: all kinds of spirit; alcoholic production; tobacco production; petrol (except for air), diesel fuel; cars (except for automobiles with manual management specially intended for the invalids); crude petroleum, gas condensate. Under excise a kind of activity of the organization and realization of lotteries.
6. Special taxes called tariffs are often charged on goods imported from abroad.
Social tax
Object of taxation for the payer are the charges of the employers paid to the workers as incomes and also incomes of the foreign personnel and payments to the physical persons (except for payments to the individual businessmen, private notaries and lawyers) under the contracts of compensated rendering of services. For the private notaries, lawyers, legal persons – residents of Republic of Kazakhstan object of taxation by social tax is the number of workers, including payers.
Since 2008 the rates of the tax have been established from 13% up to 5% from the size of object of taxation in 2009 – 11%.
8. Property tax
Property tax includes: the land tax, property tax of physical and legal persons, tax to vehicles.
Property tax acts in the local budgets. Besides fiscal, these taxes have the purpose stimulation of efficiency of use property, as the rates of the taxes are established to external signs – sizes of property, but not its profitability.
Notes
1 the body of tax legislation being increased by each year's Finance Act – причем налоговое законодательство расширяется за счет новых налогов, вводимых ежегодно при принятии финансового акта (самостоятельный причастный оборот – см. Note 3 в Unit 1)
2 The United Kingdom operates a "scheduler" system... – В Великобритании существует система «шедул»... (т.е. частей, на которые поделены доходы в зависимости от их источника)
3 The larger the income, the bigger proportion of it is paid as tax. – Чем выше доход, тем большая доля его выплачивается в качестве налога.
Конструкция со сравнительной степенью прилагательных используется для того, чтобы сравнить действия, происходящие одновременно.
4 are under a big question mark – находятся под большим вопросом
VOCABULARY LIST
taxation  - n налогообложение, взимание налогов
- n налогообложение, взимание налогов
compulsory  - adj обязательный, принудительный
- adj обязательный, принудительный
tax on income  -подоходный налог
-подоходный налог
tax on wages  -налог на заработную плату
-налог на заработную плату
tax on salary  -налог на жалование служащих
-налог на жалование служащих
tax on profits -налог на прибыль
tax on dividends- налог на дивиденды
tax on rent -налог на рентные платежи
tax on interest -налог на процентный доход
tax on capital -налог на капитал
estate tax – налог на имущество
direct taxes  -прямые налоги
-прямые налоги
death duty – налог на наследство
inherited (moneyor property) – унаследованные (деньги или имущество)
national insurance -государственное страхование
social security – социальное обеспечение
perk – привилегия
tax haven – налоговый оазис
tax burden -налоговое бремя
loopholes -лазейка
commodity – товар, продукт
penalty -штраф
indirect 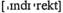 taxes -косвенные налоги
taxes -косвенные налоги
interest payments -процентные платежи
budgetary - бюджетный
municipal services  -муниципальные услуги
-муниципальные услуги
to give effect  (to) -осуществлять, приводить в исполнение, проводить в
(to) -осуществлять, приводить в исполнение, проводить в
жизнь
rate – ставка, темп
welfare  of the community -благосостояние общества
of the community -благосостояние общества
inequality  of incomes -неравенство доходов
of incomes -неравенство доходов
wealth - богатство
lessen – уменьшать
partnership -товарищество, компания
receipts – приход (бух.).
gross - валовой, большой
forms of taxes -виды налогов
treat - v обращаться, обходиться
levy  - v облагать налогом
- v облагать налогом
corporate income tax -налог на корпоративный доход
yield – доходы (плоды)
impose  - v облагать (пошлиной, налогами), налагать
- v облагать (пошлиной, налогами), налагать
liable - подлежащий
double  tax burden -бремя двойного налогообложения
tax burden -бремя двойного налогообложения
after-tax income -доход после удержания (за вычетом) налога
stock-holder  - n акционер, держатель акций
- n акционер, держатель акций
personal income -личный доход
code - n кодекс
tax law  -налоговое законодательство
-налоговое законодательство
body of tax legislation 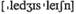 -содержание налогового законодательства
-содержание налогового законодательства
Finance Act -финансовый акт
operate- v (зд.) использовать, пользоваться
whereby – посредством чего
tax assessments  -установление налоговых ставок; определение размера
-установление налоговых ставок; определение размера
облагаемого налогом дохода
return  - n налоговая декларация
- n налоговая декларация
to issue  a return -выдать налоговую декларацию
a return -выдать налоговую декларацию
Board  of Inland Revenue ("Inland Revenue") -Налоговая служба
of Inland Revenue ("Inland Revenue") -Налоговая служба
Великобритании
to complete a return -заполнить налоговую декларацию
submit  - v представлять
- v представлять
annual  accounts -годовой отчет; (зд.) финансовая отчетность
accounts -годовой отчет; (зд.) финансовая отчетность
computation  - n расчет, вычисление
- n расчет, вычисление
taxable  profit -налогооблагаемая прибыль
profit -налогооблагаемая прибыль
system of self-assessment -система, при которой размер облагаемого налогом дохода определяется самим налогоплательщиком
capital gains -доход от прироста капитала
foreign investment -иностранные капиталовложения
taxable permanent establishment -постоянно работающее предприятие, облагаемое
налогом
tier 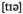 - n уровень, ярус, ряд
- n уровень, ярус, ряд
value-added tax (VAT)  - налог на добавленную стоимость
- налог на добавленную стоимость
securities  tax -налог на ценные бумаги
tax -налог на ценные бумаги
withholding tax  -налог с суммы дивидендов
-налог с суммы дивидендов
thrive [өraiv] - процветать, преуспевать
audit  - v подвергать(ся) аудиторской проверке
- v подвергать(ся) аудиторской проверке
deprive -лишать
tax authorities  -налоговые органы
-налоговые органы
submit – представлять на рассмотрение (подчиняться)
to lodge an appeal 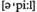 -подавать апелляционную жалобу
-подавать апелляционную жалобу
asses - оценивать
assessment – обложение
appropriate – соответствующий
organ – орган
harmful – вредный
comply – подчиняться (закону)
affair – дело, занятие, государственные дела
resident  - adj проживающий, постоянно находящийся в стране
- adj проживающий, постоянно находящийся в стране
domicile 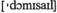 - v поселиться на постоянное место жительства
- v поселиться на постоянное место жительства
seek (sought) - v искать, стремиться
mitigate  - v смягчать, уменьшать
- v смягчать, уменьшать
double taxation -двойное налогообложение
double tax treaty  -договор об избежание двойного налогообложения
-договор об избежание двойного налогообложения
arrangements  - n (зд.) меры, мероприятия
- n (зд.) меры, мероприятия
prevent  - v препятствовать, мешать, предупреждать
- v препятствовать, мешать, предупреждать
evasion 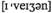 of tax obligations -уклонение от налоговых обязательств
of tax obligations -уклонение от налоговых обязательств
avoidance  - n уклонение
- n уклонение
tax liability  -обязательства по уплате налогов
-обязательства по уплате налогов
charge – цена, плата за услуги (free of charge – бесплатно).
Match the verbs from (a) with nouns from (b) below:
a) to reduce b) economic welfare
to improve taxes
to correct inequality
to increase revenue
to check imports
to withhold business
to tax adverse balance of payments






