О.П. РОЖКО
ENGLISH FOR
TECHNICAL STUDENTS

Вінниця – 2012
Рецензент: Осьмірко Г.В. - голова комісії філологічних дисциплін, викладач-методист
Рожко О.П. Engiish for Technical Students: Навчальний посібник,- Вінниця: ВК ВКНУХТ, 2011.- 115с.
Навчальний посібник вміщує добірку текстів та тренувальних вправ. Може використовуватись як основний підручник для студентів третьою курсу спеціальності «Експлуатація теплотехнічного і теплотехнологічного устаткування і систем теплопостачання».
Даний посібник спрямований на поглиблення теоретичних знань студентів, набуття практичних умінь та навичок у спілкуванні іноземною мовою.
О.П.Рожко, викладач іноземної мови
ЗМІСТ
1 Heat. Nature of Heat………………………………………..……..5
2 Unit of Heat. Temperature………………………………….…..…8
3 Unit of Heat. Changes of Phase…………………………..……...11
4 Heat and Work……………………………………………….…..14
5Heat and Work examples…………………………………….…...16
6 Heat a Form of Energy…………………………………….……..18
7 Different Methods of Heating and Ventilation……………….….22
8 Natural Ventilation………………………………………….…....24
9 Artificial and Vacuum Ventilation………………………….…… 27
10 Plenum Ventilation…………………………………………...… 30
11 Direct Systems of Heating…………………………………....… 33
12Ventilation and Water Heating……………………………….…. 35
13How Water Supply to Buildings…………………………….…...37
14Tank and Cylinder Systems………………………………….….. 39
15 Distributing Mains and Pipes…………………………..….…..... 41
16 Туре of Supply. Service Pipes…………………………………. 43
17 Tubing. Tube Connectors and Flexible Hose……………….…...45
18 Pipe Materials………………………………………...………….47
19 Stress Corrosion Cracking…………………………….…………49
20 Welding-Safety Rules……………………………….….………..51
21 Boilers………………………………………………….………...53
22 Water Tube Boilers…………………………………….………...55
23 Steam Engines…………………………………………..………..58
24 Steam Turbines…………………………………………..……....60
25 Hydraulic Turbines……………………….………….….………..63
26 Basic Elements of Hydraulic System…………...…….….………65
27 Elementary Hydraulic Systems……………………….….………67
28 Hydraulic Machines. Water Tap…………………….……………69
29 Hydraulic Machines. Pumps………………………….………......71
30 Future Profession of Heat and Work Technician……..……….....73
31 Texts for Additional Reading…………………………...………..75
32 Second Law of Thermodynamics………………………………...76
33 Steam Engine……………………………………………………..77
34 CIVIL ENGINEERING…………………………………………..78
35 INDIRECT SYSTEMS…………………………………………...79
36 Список використаних джерел……………………….………….80
Передмова
Курс технічної мови передбачає використання набутих під час вивчення попередніх навчальних дисциплін знань, умінь і навичок для їх подальшого вдосконалення та розвитку.
Мета дисципліни - дати майбутнім спеціалістам теплотехнічного фаху знання з англійської технічної мови, розвивати навички усного і писемного мовлення в межах фахової тематики, навчити використовувати набуті знання в практичній діяльності, а також повторити й закріпити лексичний матеріал.
Завдання:
· Навчити майбутнього фахівця вільно орієнтуватися в сучасному англомовному інформаційному потоці з метою поглиблення фахових знань та отримання нової інформації;
· Удосконалити навички вільного читання й розуміння текстів професійної спрямованості;
· Збагатити словниковий запас фаховою термінологією;
· Удосконалити комунікативні вміння та навички володіння англійською мовою та формувати власну думку щодо прочитаного;
· Навчити реферувати тексти технічного характеру англійською мовою та формувати власну думку щодо прочитаного;
· Опанувати лексичний матеріал обсягом 800-1000 лексичних одиниць.
Навчальний матеріал забезпечує мовне опрацювання широкого спектру тем, пов’язаних з теплотехнічними науками.
Unit 1
I term
INTRODUCTION HEAT. THE NATURE OF HEAT
1. Memorize the following words and expressions: heat - тепло
Ø contained - присутній, входити до складу
Ø to some extent — до деякої міри
Ø substance – речовина
Ø to be made up of- складатися з
Ø particle – частка
Ø atom – атом
Ø molecule - молекула, молекулярний
Ø carbon – вуглець
Ø hydrogen – водень
Ø constant – постійний
Ø motion – рух
Ø to result from - відбуватися в результаті (чогось)
Ø to exist – існувати
Ø solid - твердий стан
Ø liquid - рідкий, рідина
Ø gas - газ; газоподібний стан
Ø steam — водяна пара
Ø vapor - пари
Ø rate - інтенсивність, швидкість (характеристика процесу), темп (процесу)
Ø to increase - зростати, збільшуватися; рости; підсилюватися to cause - послужити причиною, приводом (для чогось) a cube of - шматочок
Ø application - застосування, використання, уживання; додаток; застосовність
Ø separation - поділ; розщеплення
Ø to speed up - збільшувати швидкість, прискорювати
Ø volume - обсяг, маса
Ø to expand - розширювати(ся); збільшувати(ся) в обсязі; розтягувати(ся)
Ø to destroy - руйнувати, валити, зносити; ліквідувати; стирати з особи землі
Ø in relation to - відносно; що стосується intense – інтенсивний
2. Read the text, study it. Find in the text examples to illustrate the properties of heat in a substance.
Heat. The Nature of Heat
Heat is a form of energy contained to some extent in every substance on
earth. All known elements are made up of very small particles, known as atoms, which, when joined together, form molecules. These molecules are particular to the form they represent. For example, carbon and hydrogen in certain combinations form sugar and in others form alcohol.
Molecules are in a constant state of motion. Heat is a form of molecular energy that results from the motion of these molecules. The temperature of the molecules
dictates to a degree the molecular activity within a substance. For this reason, substances exist in three different states or forms — solid, liquid, and gas. Water, for example, may exist in any one of these states. As ice, it is a solid; as water, it is a liquid; and as steam, it is a gas (vapor).
When heat is added to a substance, the rate of molecular motion increases, causing the substance to change from a solid to a liquid, and then to a gas (vapor). For example, in a cube of ice, molecular motion is slow, but as heat is added, molecular activity increases, changing the solid "ice" to a liquid "water" (Fig. 6-1). Further application of heat forces
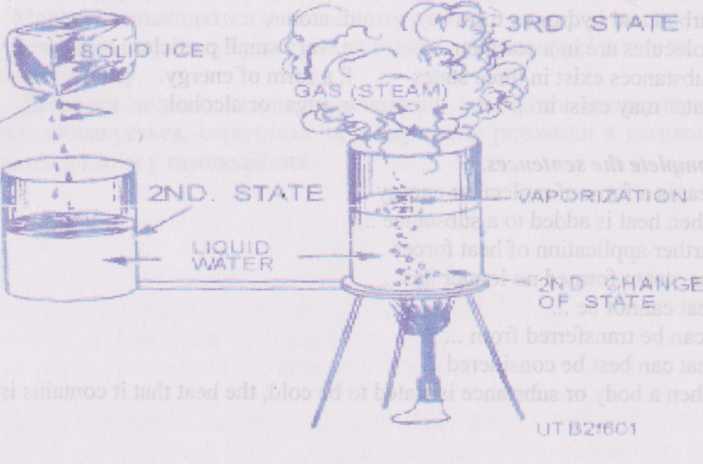
the molecules to greater separation and speeds up their motion so that the water changes to steam. The steam formed no longer has a definite volume, such as a solid or liquid has, but expands and fills whatever space is provided for it. Heat cannot be destroyed or lost, However, it can be transferred from one body or substance to another or to another form of energy. Since heat is not in itself a substance, it can best be considered in relation to its effect on substances or bodies. When a body or substance is stated to be cold, the heat that it contains is less concentrated or less intense than the heat in some warmer body or substance used for comparison.
Match the words or notions with their definitions.
1. Heat is... a. three states.
2. All known elements are made of.., b. solid, liquid, gas.
3. Particles are known as... c. state of motion.
4. Carbon and hydrogen form... d. atoms.
5. Molecules are in a constant... e. very small particles.
6. Substances exist in three states -. f. a form of energy.
7. Water may exist in … g. sugar or alcohol
Complete the sentences.
1. Heat is a form of molecular energy...
2. When heat is added to a substance..,
3. Further application of heat forces...
4. The steam formed no longer has...
5. Heat cannot be...
6. It can be transferred from...
7. Heat can best be considered...
8. When a body or substance is stated to be cold, the heat that it contains is….






