A) Organic materials
B) Iron and steel industry
C) Electric fans
D)& Cotton textile
E) Forest-based industries
*****
On the basis of source of raw materials, industries are classified on:
A) 8
B) 7
C) 6
D) 5
E)& 4
*****
Furniture is
A)& Forest-based industries
B) Pastoral-based Industries
C) Mineral-based Industries
D) Agro-based Industries
E) Co-operative Sector Industries
*****
Production of Cement is
A) Forest-based industries
B) Pastoral-based Industries
C)& Mineral-based Industries
D) Agro-based Industries
E) Co-operative Sector Industries
*****
Miscellaneous Industries are classified nextcategories
A) Forest-based, Pastoral-based, Mineral-based and Agro-based Industries
B) Private Sector, Public Sector, Joint Sector and Co-operative Sector Industries
C) Heavy and Light Industries
D) Biotechnology, Microelectronics, Robotics, New Medical Industries
E)& Village, Cottage, Consumer, Ancillary, Basic, Capital-Intensive and Labour-Intensive Industries
*****
Handloom and leather work at the artisan's house fall is
A) Village Industries
B)& Cottage Industries
C) Ancillary Industries
D) Basic Industries
E) Labour-Intensive Industries
*****
Railway engines is
A) Village Industries
B) Cottage Industries
C)& Ancillary Industries
D) Basic Industries
E) Labour-Intensive Industries
*****
Flour grinders is
A)& Village Industries
B) Cottage Industries
C) Ancillary Industries
D) Basic Industries
E) Labour-Intensive Industries
*****
Shoe-making is
A) Village Industries
B) Cottage Industries
C) Ancillary Industries
D) Basic Industries
E)& Labour-Intensive Industries
*****
Production of sugar is
A) Village Industries
B) Cottage Industries
C) Ancillary Industries
D)& Consumer Industries
E) Labour-Intensive Industries
*****
Current assets:
A) buildings and constructions
B)& revolving funds and address funds
C) production stocks and incomplete capital construction
D) money and intangible assets
E) computers
*****
The enterprise within one year (360 days) realized production on 500 thousand tenge, the average rest of current assets was equal in that period of 50 thousand tenge. Define duration of one turn of current assets.
A)& 36 days
B) 72 days
C) 18 days
D) 20 days
E) 15 days
*****
Efficiency of use of revolving funds:
A) coefficient of extensiveness
B) capital-armament
C) capital productivity
D)& material capacity
E) capital intensity
*****
Normalized current assets:
A) the goods shipped to a ways
B) money
C) receivables
D)& production stocks
E) cars and equipment
*****
Normalized current assets don't treat:
A) work in progress
B) stocks of raw materials and materials
C) finished goods in a warehouse
D) production stocks
E)& cars and equipment
*****
Sources of formation of current assets don't treat:
A) part of authorized capital
B) net profit of the enterprise
C) steady passives
D) credits of banks
E)& wages fund
*****
In reporting year the mid-annual volume of current assets made 2018,0 tenge., average duration of one turn - 24 days. To find factor of an oborachivayemost and cost of realized production:
A) 15,2 and 30270 tenge
B) 15 and 134,5tenge
C)& 15 and 30270 tenge
D) 3,75 and 7567,5tenge
E) 15,3 and 30774,5tenge
*****
Net weight of the machine - 300 kg, size of the actual waste when processing preparation - 50 kg. As a result of improvement of manufacturing techniques of details of the machine a waste it is planned to reduce by 30 percent. Define metal efficiency before and after technology use
A) 60 and 8,57
B) 0,5 and 0,35
C)& 0,86 and 0,89
D) 0,72 and 0,6
E) 1 and 0,5
*****
Depending on formation sources current assets
A) revolving business assets and address funds
B)& own and extra
C) involved and investments
D) the main and turnaround
E) production and non-productive
*****
Depending on a place in the course of a circulation current assets:
A) own and extra
B) revolving business assets and finished goods
C) funds of the address and fixed assets
D)& revolving business assets and address funds
E) revolving and fixed assets
*****
Define coefficient of an turnover, if output in a year - 1000 units, prime cost of a product - 50 tenge, the price of a product for 30 percent exceeds its prime cost, the mid-annual rest of current assets - 6500 tenge
A) 0,1
B) 7,7
C) 20
D) 12
E)& 10
*****
Define an indicator of extensive loading of the equipment, if actually fulfilled time - 4000 hours, losses of working hours on planned repair of the equipment of 10 percent from regime fund of time, an operating mode - the 3rd replaceable for 6 hours in each change, quantity of the working days in a year - 300.
A) 1,2
B) 1,5
C) 0,6
D)& 0,82
E) 1,7
*****
Call the part of the means of production, which cost is transferred on cost of finished goods entirely and at once:
A) fixed non-productive assets
B) fixed business assets
C)& current business assets
D) address funds
E) supplementary funds
*****
Indicators of efficiency of use of current business assets:
A) coefficient of intensity of updating of fixed assets
B) profitability of fixed assets
C) capital intensity
D) capital productivity
E)& material capacity
*****
Current assets are:
A) subjects and instruments of labor
B) finished goods
C) production stocks
D)& set of the money advanced for creation and use of current funds and funds of the address for ensuring of process of production and realization of production
E) the current business assets serving the sphere of production which completely transfer the cost on cost of finished goods
*****
Depending on formation sources current assets
A) current business assets and address funds
B)& own and extra
C) involved and investments
D) the main and turnaround
E) production and non-productive
*****
Depending on a place in the course of a circulation current assets:
A) own and extra
B) current business assets and finished goods
C) funds of the address and fixed assets
D)& current business assets and address funds;
E) current and fixed assets
*****
The relative sizes expressing production efficiency and its factors:
A) quantitative indices
B)& quality indicators
C) volume indicators
D) cost indexes
E) natural indicators
*****
Funds of the address consist of:
A) work in progress
B) raw materials and materials necessary for production
C)& production ready to realization
D) the spare parts intended for use in production
E) cars and equipment
*****
Efficiency of use of current funds characterizes:
A) coefficient of extensiveness
B) capital-armament
C) capital productivity
D)& material capacity
E) capital intensity
*****
Izokvanta is
A)& line of an equal product
B) line of equal expenses
C) budgetary straight line
D) curve of production capabilities
E) production function
*****
Sources of financing of capital investments:
A) fund of insurance of workers
B) wages fund
C) general fund of insurance
D)& own means and debt financial means
E) pension fund
*****
The depreciation rate determines:
A)& the amount of the annual depreciation charges on formation of a depreciation fund
B) depreciation of fixed assets, intangible assets
C) a part of cost of the fixed business assets which in the course of work was transferred on a newly created product
D) set of the money advanced for creation and use of revolving funds and funds of the address for providing a production process and sales of products
E) the revolving business assets serving the sphere of production which completely transfer the cost on cost of finished goods
*****
Indicators of extensive use of the fixed business assets:
A) capital productivity
B) capital-output ratio
C) extensiveness coefficient
D) intensity coefficient
E)& load factor and working in shifts coefficient
*****
What interferes with capital productivity growth?
A) equipment performance improvement
B) increase of coefficient of working in shifts of work of the equipment
C) improvement of use of time and capacity
D) replacement of a manual work with the machine
E)& capital-output ratio increase
*****
Integrated indicators of use of the equipment:
A) extensiveness coefficient
B) intensity coefficient
C) materials consumption
D) power consumption
E)& capital-output ratio and capital productivity
*****
The part of the population, which has the necessary physical development, knowledge and experience to work in the economy is:
A) labour market
B) labour
C)& manpower
D) economic activity
E) unemployment
*****
Economic definition of manpower:
A) total supply of personnel available or engaged for a specific job or task
B) part of the population, which has the necessary physical development, knowledge and experience to work in the economy
C) different from the commodity market because a labor force is a specific commodity
D)& Total labour force of a nation, including both men and women
E) the form of relative overpopulation
*****
Labor market is
A) total supply of personnel available or engaged for a specific job or task
B) part of the population, which has the necessary physical development, knowledge and experience to work in the economy
C)& different from the commodity market because a labor force is a specific commodity
D) Total labour force of a nation, including both men and women
E) the form of relative overpopulation
*****
“Substitution effect” is shown
A) when peoples, proposing his labor force only for sale of the alternative use of the time
B) when peoples, proposing his labor force only for faces of the alternative use of the time (correlation of the free time)
C)& when worker, proposing his labor force for sale, faces the choice of the alternative use of the time (correlation of the free and working time)
D) when worker, proposing his quantity force for your labour (correlation of working time)
E) when worker, proposing his sale
*****
Synonym of word “Unemployment”:
A) non-working
B)& joblessness
C) the quantity of employed
D) Substitution effect
E) population points working
*****
When people are without work and actively seeking work are
A) labour market
B) labour
C) manpower
D) economic activity
E)& unemployment
*****
What international organization made the next definition: The unemployed is person, who wants to work, can work, but has not got workplace
A) World Trade Organization
B) International Monetary Fund
C)& International organization of labour
D) Andean pact
E) European Union
*****
The formula of level of population's economic activity
A) Pup= ((Eа-O)/Eа)*100
B) L= ((Q-Eip)/Q)*100/Q
C) Pup= ((Eа-O)/Eа)
D) L= Q-Eip/Q
E)& L= ((Q-Eip)/Q)*100
*****
The level of unemployment is determined by this formula
A)& Pup= ((Eа-O)/Eа)*100
B) L= ((Q-Eip)/Q)*100/Q
C) Pup= ((Eа-O)/Eа)
D) L= Q-Eip/Q
E) L= ((Q-Eip)/Q)*100
*****
Types of unemployment, this is occurs when real wages for a job are set above the market-clearing level, causing the number of job-seekers to exceed the number of vacancies
A) cyclical
B) involuntary
C)& classical
D) full
E) structural
*****
“Minimum wage laws raise the cost of laborers with few skills to above the market equilibrium, resulting in people who wish to work at the going rate but cannot as wage enforced is greater than their value as workers becoming unemployed” - Call the type of unemployment
A) cyclical
B) involuntary
C)& classical
D) full
E) structural
*****
Types of unemployment, this is occurs when there is not enough aggregate demand in the economy to provide jobs for everyone who wants to work
A)& cyclical
B) involuntary
C) classical
D) full
E) structural
*****
Antonym of word “cyclical unemployment”
A) Adamian
B) Ricardian
C) Short-Run Phillips
D) Long-Run Phillips
E)& Keynesian
*****
Call the type or model of unemployment on this picture:

A) Short-Run Phillips
B) Long-Run Phillips
C) AD-AS model
D)& IS-LM model
E) structural
*****
Call the type or model of unemployment on this picture:

A) cyclical
B) involuntary
C) classical
D)& full
E) structural
*****
Call the type or model of unemployment on this picture:

A) cyclical
B) involuntary
C) classical
D) full
E)& structural
*****
Types of unemployment, this is occurs when a labour market is unable to provide jobs for everyone who wants one because there is a mismatch between the skills of the unemployed workers and the skills needed for the available jobs
A) hidden
B) classical
C) full
D) frictional
E)& structural
*****
The time period between jobs when a worker is searching for, or transitioning from one job to another is
A) hidden
B) classical
C) full
D)& frictional
E) structural
*****
Former homemakers is
A) employed worker
B)& re-entrants
C) graduating students
D) new entrants
E) potential workers
*****
Unemployment of potential workers that is not reflected in official unemployment statistics, due to the way the statistics are collected is
A)& hidden
B) classical
C) full
D) frictional
E) structural
*****
In the Shapiro-Stiglitz model of efficiency wages, workers …
A) is not reflected in official unemployment statistics, due to the way the statistics are collected
B) the time period between jobs when a worker is searching for, or transitioning from one job to another
C) occurs when a labour market is unable to provide jobs for everyone who wants one because there is a mismatch between the skills of the unemployed workers and the skills needed for the available jobs
D) occurs when there is not enough aggregate demand in the economy to provide jobs for everyone who wants to work
E)& are paid at a level that dissuades shirking
*****
The type of management of an organization's workforce, or human resources is
A) innovation management
B) strategic management
C) organization management
D)& human resource management
E) management of labour
*****
The rate of growth of the population outweighs that of the employed and unemployed together is
A) fixed assets rate
B)& the labor force participation rate
C) working assets rate
D) turnover of working capital
E) the growth labour rate
*****
The amount of goods and services that a worker produces in a given amount of time is
A) the labor force participation rate
B)& workforce productivity
C) overall Labor Effectiveness
D) unpaid labor
E) formal labor
*****
The percentage of perfect or saleable product produced is
A)& quality
B) availability
C) performance
D) workforce jobs
E) productivity
*****
Form of remuneration paid periodically by an employer to an employee, the amount and frequency of which may be specified in an employment contract is
A) a wage labourer
B) wage labour
C)& salary
D) employment
E) method of payment
*****
Person whose primary means of income is from the selling of his or her labour in this way is
A)& a wage labourer
B) wage labour
C) salary
D) employment
E) method of payment
*****
The work done could be paid "in cash" (a money-wage) or "in kind" (through receiving goods and/or services), or in the form of "piece rates" where the wage is directly dependent on how much the worker produces is called
A) a wage labourer
B) wage labour
C) salary
D) employment
E)& method of payment
*****
How many functions have the wages:
A) 2
B)& 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
*****
Reproductive function of wages
A) forms and systems of the wage should stimulate the high-performance work
B)& supplying with extended production of the qualitative labor force of the work-hand and members of his family
C) stimulating of the labor influx to a certain branches and its outfall from others
D) pecuniary expression of the labor force commodity value or its price
E) A form of remuneration paid periodically by an employer to an employee, the amount and frequency of which may be specified in an employment contract
*****
Stimulating function of wages
A)& forms and systems of the wage should stimulate the high-performance work
B) supplying with extended production of the qualitative labor force of the work-hand and members of his family
C) stimulating of the labor influx to a certain branches and its outfall from others
D) pecuniary expression of the labor force commodity value or its price
E) A form of remuneration paid periodically by an employer to an employee, the amount and frequency of which may be specified in an employment contract
*****
Distributive function of wages
A) forms and systems of the wage should stimulate the high-performance work
B) supplying with extended production of the qualitative labor force of the work-hand and members of his family
C)& stimulating of the labor influx to a certain branches and its outfall from others
D) pecuniary expression of the labor force commodity value or its price
E) A form of remuneration paid periodically by an employer to an employee, the amount and frequency of which may be specified in an employment contract
*****
Payment of value and cost of the labor force commodity depending on measure making per the unit time is
A) wage plus-bonus system
B) piece plus-bonus system
C)& job wage
D) nominal wage
E) net remuneration
*****
This types of wage is depends on uninterrupted work of equipment, labor complexity that is expressed by the certain tariff grades and wages
A) wage plus-bonus system
B) piece plus-bonus system
C) job wage
D)& t ariff system of payment
E) net remuneration
*****
… connects tariff grades and rates of the labor inputs by a certain functional dependence:
A)& wage plus-bonus system
B) piece plus-bonus system
C) job wage
D) t ariff system of payment
E) net remuneration
*****
… provides for paying for the worker of the certain sum for the overtime work
A) wage plus-bonus system
B)& piece plus-bonus system
C) job wage
D) t ariff system of payment
E) net remuneration
*****
Money that labor gets for the selling of his labor force is:
A) wage plus-bonus system
B) piece plus-bonus system
C) job wage
D)& nominal wage
E) net remuneration
*****
Quantity of goods and services that labor can acquire for his wage under the certain level of the prices and losing of tax is:
A) wage plus-bonus system
B) piece plus-bonus system
C) job wage
D) nominal wage
E)& net remuneration
*****
For the determination of the net remuneration, index of the nominal wage is divided by …
A) wage plus-bonus system
B) piece plus-bonus system
C)& index of life cost
D) payment for labor
E) net remuneration
*****
“A basket of goods” (living/subsistence wage) includes:
A) wage and pension
B) net remuneration
C)& assortment of goods and services
D) transport and metallurgy
E) electro-energy and house products
*****
The total compensation that an employee receives in exchange for the service they perform for their employer is
A) wage plus-bonus system
B) piece plus-bonus system
C) job wage
D) nominal wage
E)& remuneration
*****
Remuneration includes:
A) budgetary appropriations and wages
B) deposits of other state enterprises, wages and salaries
C) apprenticeship allowances, wages and cashes
D)& apprenticeship allowances, wages and salaries
E) benefits, salaries and apprenticeship allowances
*****
Cash, including securities, information, works and services, other property, other rights attached investor in the objects of investment activity in order to obtain profit is
A) innovation
B)& investments
C) investments activity
D) budget
E) wages
*****
Investing and action – for profit and (or) achieve a beneficial effect is
A) innovation
B) investments
C)& investments activity
D) budget
E) wages
*****
Capital investment is
A) feasibility study, volume and timing of capital investments, while activated design estimates and business plan (action on implementation of the investment)
B) an investment project, the total volume of capital investment which meets the requirements and the legislation which is included in the list, approved by the Government
C)& an investment in fixed assets, including the costs of new construction, expansion, reconstruction and modernization of existing businesses, the acquisition of machinery, equipment, tools, equipment, project survey work and other costs
D) a complex of activities from the adoption investment decision until the final stage of the investment project
E) subjects of investment activities, which take decision to invest his own, borrowed and borrowed property and intellectual property in investment objects
*****
Investors:
A) feasibility study, volume and timing of capital investments, while activated design estimates and business plan (action on implementation of the investment)
B) an investment project, the total volume of capital investment which meets the requirements and the legislation which is included in the list, approved by the Government
C) an investment in fixed assets, including the costs of new construction, expansion, reconstruction and modernization of existing businesses, the acquisition of machinery, equipment, tools, equipment, project survey work and other costs
D) a complex of activities from the adoption investment decision until the final stage of the investment project
E)& subjects of investment activities, which take decision to invest his own, borrowed and borrowed property and intellectual property in investment objects
*****
Investment Project is
A)& feasibility study, volume and timing of capital investments, while activated design estimates and business plan (action on implementation of the investment)
B) an investment project, the total volume of capital investment which meets the requirements and the legislation which is included in the list, approved by the Government
C) an investment in fixed assets, including the costs of new construction, expansion, reconstruction and modernization of existing businesses, the acquisition of machinery, equipment, tools, equipment, project survey work and other costs
D) a complex of activities from the adoption investment decision until the final stage of the investment project
E) subjects of investment activities, which take decision to invest his own, borrowed and borrowed property and intellectual property in investment objects
*****
Investment cycle is
A) feasibility study, volume and timing of capital investments, while activated design estimates and business plan (action on implementation of the investment)
B) an investment project, the total volume of capital investment which meets the requirements and the legislation which is included in the list, approved by the Government
C) an investment in fixed assets, including the costs of new construction, expansion, reconstruction and modernization of existing businesses, the acquisition of machinery, equipment, tools, equipment, project survey work and other costs
D)& a complex of activities from the adoption investment decision until the final stage of the investment project
E) subjects of investment activities, which take decision to invest his own, borrowed and borrowed property and intellectual property in investment objects
*****
Priority investment project is
A) feasibility study, volume and timing of capital investments, while activated design estimates and business plan (action on implementation of the investment)
B)& an investment project, the total volume of capital investment which meets the requirements and the legislation which is included in the list, approved by the Government
C) an investment in fixed assets, including the costs of new construction, expansion, reconstruction and modernization of existing businesses, the acquisition of machinery, equipment, tools, equipment, project survey work and other costs
D) a complex of activities from the adoption investment decision until the final stage of the investment project
E) subjects of investment activities, which take decision to invest his own, borrowed and borrowed property and intellectual property in investment objects
*****
Investment cycle consists of... main periods:
A) two
B) four
C) ten
D) twenty
E)& three
*****
Call the phase of recovery value for money in investment process:
A)& operating phase
B) phase investment
C) pre-investment phase
D) main phase
E) non-investment phase
*****
Series of repeated cycles of investment:
A)& investment process
B) investment complex
C) portfolio
D) investment cycle
E) investment project
*****
Investment in securities in order to follow the game on economic entity is
A) investment process
B) investment complex
C)& portfolio
D) investment cycle
E) investment project
*****
Real investments are composed of two different components. What?
A) basic and auxiliary
B) the subsidiary and the collateral
C) initial investment, the extensive investment and reinvestment
D) short-term investments and long-term investments
E)& investment in fixed capital and investment in inventories
*****
Real investments are composed of two different components. What?
A)& internal and external
B) short-term investments and long-term investments
C) the subsidiary and the collateral
D) initial investment, the extensive investment and reinvestment
E) basic and auxiliary
*****
Investments by the time factor consist of
A) basic and auxiliary
B) the subsidiary and the collateral
C) initial investment, the extensive investment and reinvestment
D)& short-term investments and long-term investments
E) investment in fixed capital and investment in inventories
*****
Investments by the nature of use consist of
A) basic and auxiliary
B) the subsidiary and the collateral
C)& initial investment, the extensive investment and reinvestment
D) short-term investments and long-term investments
E) investment in fixed capital and investment in inventories
*****
The gross investment consist of
A) basic and auxiliary
B) the subsidiary and the collateral
C)& initial investment and extensive investment
D) internal and external
E) net investment and reinvestment
*****
The development of new customer value through solutions that meet new needs, unarticulated needs, or old customer and market needs in new ways is
A)& innovation
B) investments
C) investments activity
D) budget
E) wages
*****
Diffusion of innovation research was first started in
A)& 1903
B) 1904
C) 1905
D) 1906
E) 1907
*****
Diffusion of innovation research was first started in 1903 by seminal researcher:
A) Adam Smith
B) David Ricardo
C) Joseph Schumpeter
D) John Maynard Keynes
E)& Gabriel Tarde
*****
If Adam Smith is the patron saint of classical economics and John Maynard Keynes of Keynesian economics, who is the patron saint of innovation economics
A) Adam Smith
B) David Ricardo
C)& Joseph Schumpeter
D) John Maynard Keynes
E) Gabriel Tarde
*****
Innovative train locomotive and rolling stock manufacturing is product of
A) Research Triangle Park in North Carolina, USA
B) Genome Valley in Hyderabad, India
C) South Yorkshire, United Kingdom
D) Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
E)& Beijing, China
*****
Innovative petrochemical complexes is product of
A) Research Triangle Park in North Carolina, USA
B) Genome Valley in Hyderabad, India
C) South Yorkshire, United Kingdom
D)& Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
E) Beijing, China
*****
Innovative high-technology and life sciences is product of
A)& Research Triangle Park in North Carolina, USA
B) Genome Valley in Hyderabad, India
C) South Yorkshire, United Kingdom
D) Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
E) Beijing, China
*****
Call the biggest Research park of Russia
A) Silicon Valley
B) Research Triangle Park
C)& Skolkovo Park
D) Genome Valley
E) UniScienTech Park
*****
Call the biggest Research park of Karaganda region, Kazakhstan
A) Silicon Valley
B) Research Triangle Park
C) Skolkovo Park
D) Genome Valley
E)& UniScienTech Park
*****
Decree of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan, dated to May 17, 2003, approved
A) A state program of development of the Kazakhstan sector of the Caspian Sea till 2015
B)& Strategy of Industrial-Innovational development of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2003-2015
C) Strategy of long-term development of the Republic of Kazakhstan till 2030
D) Strategy of the forced industrial and innovative development of RK for 2010-2014
E) Transport strategy of the Republic of Kazakhstan till 2015
*****
The value of money that has been used up to produce something, and hence is not available for use anymore is
A) wage
B) sales
C)& cost
D) income
E) salary
*****
Operating revenues earned by a company for selling its products or rendering its services is
A) wage
B)& sales
C) cost
D) income
E) salary
*****
The formula of net sales
A) net sales = gross wages – (customer discounts, returns, allowances)
B) net sales = gross cost – (customer discounts, returns, allowances)
C) net sales = gross income – (customer discounts, returns, allowances)
D)& net sales = gross sales – (customer discounts, returns, allowances)
E) net sales = gross salary – (customer discounts, returns, allowances)
*****
The sum of all sales during a time period is
A) net sales
B) gross wages
C) net income
D) gross salary
E)& gross sales
*****
The formula of total cost
A) AVC = VC/Q
B) AFC = FC/Q
C) ATC = TC/Q
D) MC = dC/dQ
E)& TC = FC + VC
*****
The formula of marginal cost
A) AVC = VC/Q
B) AFC = FC/Q
C) ATC = TC/Q
D)& MC = dC/dQ
E) TC = FC + VC
*****
The formula of average total cost
A) AVC = VC/Q
B) AFC = FC/Q
C)& ATC = TC/Q
D) MC = dC/dQ
E) TC = FC + VC
*****
The formula of average fixed cost
A) AVC = VC/Q
B)& AFC = FC/Q
C) ATC = TC/Q
D) MC = dC/dQ
E) TC = FC + VC
*****
The formula of average variable cost
A)& AVC = VC/Q
B) AFC = FC/Q
C) ATC = TC/Q
D) MC = dC/dQ
E) TC = FC + VC
*****
Opportunity costs that involve direct monetary payment by producers are
A) unit costs
B) implicit costs
C) opportunity costs
D)& explicit costs
E) marginal costs
*****
Opportunity costs that in factors of production that a producer already owns are
A) unit costs
B)& implicit costs
C) opportunity costs
D) explicit costs
E) marginal costs
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:

A)& a typical marginal cost curve with marginal revenue overlaid
B) typical short run average cost curve
C) typical long run average cost curve
D) typical marginal cost curve
E) cost curves in competition compared to marginal revenue
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:

A) a typical marginal cost curve with marginal revenue overlaid
B) typical short run average cost curve
C) typical long run average cost curve
D) typical marginal cost curve
E)& cost curves in competition compared to marginal revenue
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:

A) a typical marginal cost curve with marginal revenue overlaid
B) typical short run average cost curve
C) typical long run average cost curve
D)& typical marginal cost curve
E) cost curves in competition compared to marginal revenue
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:

A) a typical marginal cost curve with marginal revenue overlaid
B) typical short run average cost curve
C)& typical long run average cost curve
D) typical marginal cost curve
E) cost curves in competition compared to marginal revenue
*****
The process of thinking about and organizing the activities required to achieve a desired goal is:
A) working
B)& planning
C) involving
D) production
E) capacity
*****
An economic mechanism for resource allocation and decision-making held in contrast with the market mechanism is
A) state planning
B)& economic planning
C) strategic planning
D) directive planning
E) indicative planning
*****
Large corporations allocate resources internally among different divisions and subsidiaries through …
A) working
B)& planning
C) involving
D) production
E) capacity
*****
An organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy is
A) state planning
B) economic planning
C)& strategic planning
D) directive planning
E) indicative planning
*****
In many organizations, strategic planning is viewed as a process for determining where an organization is going
A)& over 1 to 20 year
B) over 1 to 200 days
C) over 1 to 12 months
D) over 1 days to 10 months
E) over 20 days to 10 months
*****
The one part of key components of strategic planning include
A) calculation
B) understanding
C) production program;
D)& vision
E) business plan
*****
The one part of key components of strategic planning include
A) calculation
B) understanding
C) production program;
D)& mission
E) business plan
*****
The cost of fixed assets determined by operating market prices
A) balance cost
B) initial cost
C)& current cost
D) residual cost
E) regenerative cost
*****
Long-term view and concentrates on the future of enterprises is called
A) mission
B) strategy
C)& vision
D) values
E) understanding
*****
Defines the fundamental purpose of an enterprise, succinctly describing why it exists and what it does to achieve its vision is
A)& mission
B) strategy
C) vision
D) values
E) understanding
*****
Its drive an organization's culture and priorities and provide a framework in which decisions are made. What?
A) mission
B) strategy
C) vision
D)& values
E) understanding
*****
The analysis of the organization and its environment as it is at the moment and how it may develop in the future, is
A) business analysis
B)& situational analysis
C) SWOT analysis
D) PEST analysis
E) STEER analysis
*****
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats. Its components of... analysis
A) business analysis
B) situational analysis
C)& SWOT analysis
D) PEST analysis
E) STEER analysis
*****
Subset of strategic work planning is
A) business analysis
B) situational analysis
C) SWOT analysis
D) PEST analysis
E)& operational analysis
*****
The complete process of bringing a new product to market is
A) capital productivity
B) capital intensity
C) certificated production
D)& new product development
E) hourly average development
*****
"Fuzzy front end" of the NPD process is often called
A) idea screening
B) concept development and testing
C)& idea generation
D) technical implementation
E) commercialization
*****
Logistics plan consist in
A) idea screening
B) concept development and testing
C) idea generation
D)& technical implementation
E) commercialization
*****
Considered post-NPD is often called
A) idea screening
B) concept development and testing
C) idea generation
D) technical implementation
E)& commercialization
*****
Formal statement of a set of business goals, the reasons they are believed attainable, and the plan for reaching those goals is
A) calculation
B) understanding
C) production program;
D) mission
E)& business plan
*****
Translate in Russian: “cover page and table of contents of business plan”
A) миссия бизнес плана
B) производственный план бизнес плана
C)& титульный лист и содержание бизнес плана
D) стратегия бизнес плана
E) вводные и заключительные части бизнес плана
*****
The process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products is
A) situational analysis
B) business planning
C)& capacity planning
D) financial planning
E) economic planning
*****
The broad classes of capacity planning are
A)& lead, lag and match strategy
B) short-term and long-term strategy
C) economic and social strategy
D) situational, overall and structural structural strategy
E) lead, overall and match strategy
*****
Innovation is:
A) Purchase of the repaired tractors
B)& An investment of means in the economy, providing equipment and technology change
C) Repair of buildings and constructions
D) Construction of intraeconomic roads
E) Replacement of system of hourly compensation by the price-work
*****
More moderate strategy in capacity planning
A) lead strategy
B)& match strategy
C) lag strategy
D) overall strategy
E)situational strategy
*****
The ability and performance of a firm, sub-sector or country to sell and supply goods and services in a given market, in relation to the ability and performance of other firms, sub-sectors or countries in the same market is
A)& competitiveness
B) system
C) quality
D) life cycle
E) quantity
*****
Models of highlight the advantages of networks is
A) quality
B) chains
C)& clusterization
D) life cycle
E) economic districts
*****
The tendency toward extreme, unhealthy competition has been termed
A) highly competitiveness
B) budget competitiveness
C)& hyper competitiveness
D) direct competitiveness
E) substitute competitiveness
*****
Competition, where products which are close substitutes for one another compete
A) highly competitiveness
B) budget competitiveness
C) hyper competitiveness
D) brand competitiveness
E)& substitute competitiveness
*****
Competition, where products which perform the same function compete against each other
A) highly competitiveness
B) budget competitiveness
C) hyper competitiveness
D)& brand competitiveness
E) substitute competitiveness
*****
Included in this category is anything on which the consumer might want to spend their available money. The broadest form of competition is typically called
A) highly competitiveness
B)& budget competitiveness
C) hyper competitiveness
D) brand competitiveness
E) substitute competitiveness
*****
Brand competition also called
A)& category competition
B) substitute competitiveness
C) hyper competitiveness
D) budget competitiveness
E) indirect competition
*****
The idea of internal competition was first introduced by Alfred Sloan at... in the 1920s
A)& General Motors
B) General Electric
C) Nissan Company
D) Procter & Gamble
E) Nokia
*****
How many aspects of quality in a business context
A) 4
B)& 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 3
*****
Perceptual, conditional and somewhat subjective attribute and may be understood differently by different people is
A) competitiveness
B) system
C)& quality
D) life cycle
E) quantity
*****
Providing something in aspects of quality
A) checking
B) quality control
C)& producing
D) quality management
E) quality assurance
*****
Confirming that something has been done correctly in aspects of quality
A)& checking
B) quality control
C) producing
D) quality management
E) quality assurance
*****
Controlling a process to ensure that the outcomes are predictable in aspects of quality
A) checking
B)& quality control
C) producing
D) quality management
E) quality assurance
*****
Directing an organisation so that it optimises its performance through analysis and improvement in aspects of quality
A) checking
B) quality control
C) producing
D)& quality management
E) quality assurance
*****
Obtaining confidence that a product or service will be satisfactory in aspects of quality
A) checking
B) quality control
C) producing
D) quality management
E)& quality assurance
*****
The business meanings of quality by Philip B. Crosby are given below
A) quality combines people power and process power
B) the characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs
C)& conformance to requirements
D) concentrating on "the efficient production of the quality that the market expects,"
E)quality in a product or service is not what the supplier puts in. It is what the customer gets out and is willing to pay for
*****
The business meanings of quality by W. Edwards Deming are given below
A) quality combines people power and process power
B) the characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs
C) conformance to requirements
D)& concentrating on "the efficient production of the quality that the market expects,"
E)quality in a product or service is not what the supplier puts in. It is what the customer gets out and is willing to pay for
*****
The succession of strategies used by business management as a product goes through its life-cycle is
A) quality management
B)& product life-cycle management
C) innovation management
D) human resource management
E) management of labour
*****
The concept of product life cycle (PLC)
A) to reduce time to market
B) to improve product quality, reduce prototyping costs
C)& the life of a product in the market with respect to business/commercial costs and sales measures
D) to identify potential sales opportunities and revenue contributions
E) to reduce environmental impacts at end-of-life
*****
Characteristics of stage: costs are very high, slow sales volumes to start, little or no competition, demand has to be created, customers have to be prompted to try the product, makes no money at this stage. What is stage?
A)& market introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) saturation and decline stage
E) early majority stage
*****
Characteristics of stage: costs become counter-optimal, sales volume decline, prices, profitability diminish, profit becomes more a challenge of production/distribution efficiency than increased sales. What is stage?
A) market introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D)& saturation and decline stage
E) early majority stage
*****
Characteristics of stage: costs reduced due to economies of scale, sales volume increases significantly, profitability begins to rise, public awareness increases, competition begins to increase with a few new players in establishing market, increased competition leads to price decreases. What is stage?
A) market introduction stage
B)& growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) saturation and decline stage
E) early majority stage
*****
Right elements of a Quality Management System
A) quality
B)& maintenance
C) quantity
D) control
E) improvement
*****
How much principles form the basis for the quality management system standard ISO 9001:2008
A)& 8
B) 7
C) 6
D) 5
E) 4
*****
Quality function deployment, also known as
A) the facility of quality approach
B) the room of quality approach
C) the building of quality approach
D)& the house of quality approach
E) the faculty of quality approach
*****
What did the organization created the Quality Management System (QMS) standards in 1987
A) World Trade Organization
B) The International Monetary Fund
C) The International organization of labour
D)& The International Organization for Standardization
E) European Union
*****
The consumption and savings opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, that is generally expressed in monetary terms is
A) salary
B) revenue
C) profit
D) wage
E)& income
*****
Income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers is
A) salary
B)& revenue
C) profit
D) wage
E) income
*****
Component of (implicit) costs, and so not a component of business profit at all is
A) salary
B) revenue
C)& normal profit
D) wage
E) income
*****
Revenue exceeds the opportunity cost of inputs, noting that these costs include the cost of equity capital that is met by normal profits is
A) salary
B) revenue
C)& economic profit
D) wage
E) income
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:

A) uncompetitive market
B) legal market
C) shadow market
D)& competitive market
E) economic market
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:

A)& uncompetitive market
B) legal market
C) shadow market
D) competitive market
E) economic market
*****
Tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses (corporations or other legal entities) is
A) salary
B) revenue
C) economic profit
D) wage
E)& income tax
*****
Call the right types of income tax
A) legal
B) capital
C) heritance
D) non-corporate
E)& payroll
*****
Money used by entrepreneurs and businesses to buy what they need to make their products or provide their services or to that sector of the economy based on its operation, i.e. retail, corporate, investment banking, etc.
A) lending capital
B) working capital
C) fixed capital
D)& financial capital
E) physical capital
*****
The value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time is
A) future value of money
B) annual income
C)& time value of money
D) income tax
E) value of perpetuity
*****
The value of an asset or cash at a specified date in the future that is equivalent in value to a specified sum today is
A)& future value of money
B) annual income
C) time value of money
D) income tax
E) value of perpetuity
*****
An infinite and constant stream of identical cash flows is
A) future value of money
B) present value of an annuity
C) time value of money
D)& present value of perpetuity
E) future value of an annuity
*****
Assistance paid to a business or economic sector or producers is
A) wage
B)& subsidy
C) salary
D) profit
E) income
*****
Redistribution of income in the market system is
A) subsidy
B)& transfer
C) salary
D) profit
E) income
*****
Labor productivity is defined:
A) relation of the general product to the enterprise income.
B) relation of a limiting product to the general product.
C) the relation of number of PPP to volume of made production.
D) the quantity of time spent for production of all production.
E)& quantity of production made in unit of time.
*****
At what system of compensation earnings are put in direct dependence on results of work of workers served by it:
A) straight line price-work
B) the simple time
C) accord and price-work
D)& indirect and price-work
E) time and bonus
*****
Technological labor input includes:
A) Expenses of work of auxiliary workers.
B) Expenses of work of all workers.
C) Expenses of work of all categories of workers.
D) Expenses of work of heads and technical performers.
E)& Expenses of work of the main workers, pieceworkers and time-rate pay
*****
Call the type or model of unemployment on this picture: & IS-LM model

*****
Call the type or model of unemployment on this picture: & full

*****
Call the type or model of unemployment on this picture: structural 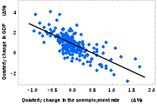
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:
 & a typical marginal cost curve with marginal revenue overlaid
& a typical marginal cost curve with marginal revenue overlaid
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:
 & cost curves in competition compared to marginal revenue
& cost curves in competition compared to marginal revenue
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:
 & typical marginal cost curve
& typical marginal cost curve
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:
 & typical long run average cost curve
& typical long run average cost curve
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:
 & competitive market
& competitive market
*****
Call the curves of costs types on this picture:
 & uncompetitive market
& uncompetitive market






