
The brain keeps the body in order. It helps to control all of the body systems and organs, keeping them working like they should. The brain also allows us to think, feel, remember and imagine. In general, the brain is what makes us behave as human beings.
The brain communicates with the rest of the body through the spinal cord and the nerves. They tell the brain what is going on in the body at all times. This system also gives instructions to all parts of the body about what to do and when to do it.
SpinalCord

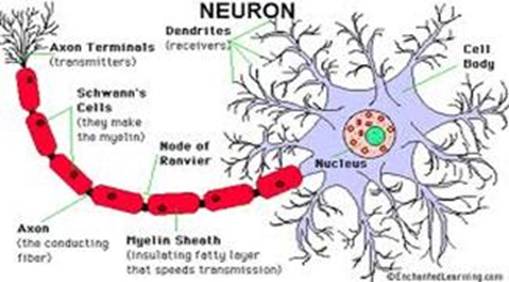
Nerves divide many times as they leave the spinal cord so that they may reach all parts of the body. The thickest nerve is 1 inch thick and the thinnest is thinner than a human hair. Each nerve is a bundle of hundreds or thousands of neurons (nerve cells). The spinal cord runs down a tunnel of holes in your backbone or spine. The bones protect it from damage. The cord is a thick bundle of nerves, connecting your brain to the rest of your body.
CentralNervous. "Senses"

Senses
There are five main senses - touch, smell, taste, hearing and sight. These are the external sensory system, because they tell you about the world outside your body. Your senses tell you what is happening in the outside world. Your body's sense organs constantly send signals about what is happening outside and inside it to your control center - the brain.
The cerebrum is part of the forebrain. The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum. Certain areas of the cerebral cortex are involved with certain functions.

Sensory areas such as touch, smell, taste, hearing and sight receive messages from the skin, nose, mouth, ears and eyes. We feel, taste, hear and see when these messages are received by the sensory parts of the brain.
The Peripheral Nervous System
The nervous system is made up of nerve cells or neurons that are "wired" together throughout the body, somewhat like communication system. Neurons carry messages in the form of an electrical impulses. The messages move from one neuron to another to keep the body functioning.
Vocabulary
to keep the body in order Ц поддерживатьтеловпор€дке to allow Ц позвол€ть rest Ц остаток bundle Ц пучок external Ц внешний forebrain Ц передниймозг cerebral cortex Ц кора involve Ц вовлекать to wire Ц св€зывать
Questions
1. What is the function of brain?
2. How does the brain communicate with the rest of the body?
3. What senses do you know?
4. What is neuron?
5. What is the function of neuron?
Quiz
Instruction: Fill the blank
Ј Eyes, Ј Nose, Ј Tongue, Ј Skin, Ј Ears, Ј Detect sound, Ј Detect color and light, Ј Detects scents, Ј Detects tastes: sweet, salty, sour and bitter, Ј Detects pain, pressure, heat and cold
| Sense | Organ | Job |
| Sight | ||
| Hearing | ||
| Smell | ||
| Taste | ||
| Touch |
|
|
|
Quiz
Instruction: FindWords

 Test 4
Test 4
The Brain
Instructions: Select the correct answer from the choices listed.
1. What is the largest part of your brain? Circle Answer
a) cerebrum
b) cerebellum
c) hypothalamus
d) medulla oblongata
2. What does the central nervous system contain? Circle Answer
a) the cerebral cortex
b) the eyes and ears
c) the brain and spinal cord
3. What is found at the base of the brain? Circle Answer
a) the cerebellum
b) the brain stem
c) the hypothalamus
4. Which part of the brain smooths out movement? Circle Answer
a) the cerebellum
b) the hypothalamus
c) thecerbral cortex
5. What part of the brain controls hunger and thirst? CircleAnswer
a) cerebellum
b) cerebrum
c) hypothalamus
d) medulla oblongata
6. The __________ are membranes that cover the brain. Circle Answer
a) pons
b) meninges
c) meningitis
d) fissures
7. The cerebrum consists of two halves called the left and right ____________. Circle Answer
a) lobes
b) fissures
c) hemispheres
d) cortex
8. The brain contains: Circle Answer
a) neurons
b) glial cells
c) blood vessels
d) all of the above
9. Very early in life, brain cells stop: Circle Answer
a) functioning
b) increasing in number
c) increasing in size
10. The control center for thinking is the: Circle Answer
a) meninges
b) medulla oblongata
c) cerebellum
d) cerebrum
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM

All animals need oxygen to live. Land animals get oxygen from the air. Without the oxygen in the air we cannot survive more than a few minutes. Breathing happens automatically, we do not have to even think about it.
We breathe in order to take oxygen into our bodies and get rid of carbon dioxide. The oxygen is carried in the blood to all the body's cells. The air we breath out has 100 times more carbon dioxide than the air we breath in.
Vocabulary
1. land animals Цсухопутныеживотные
2. to survive - выживать
3. to get rid - избавл€тьс€
4. carbon dioxide Ц углекислыйгаз
Nose and Nasal Cavity

The respiratory system is made of body parts that are in charge of your breathing. It includes your nose and nasal cavity. You air though your nose. As you inhale, small specks of dirt are trapped by many tiny hairs in your nose. This cleans the air. The hairs stop the dirt from going further in your body. The moist inside surface in your nose traps even smaller pieces of dirt. The nasal cavity, the air passage behind the nose, plays an important role in breathing. The nasal cavity is divided into a right and left passageway. The tissue that covers the wall of your nasal cavity contains many blood vessels. Heat from the blood in the vessels helps warm the air as you breath. Moisture is added to the air you breath by special cells in the walls of the nasal cavity. The air is warmed and moistened before it reaches your lungs.
Vocabulary
1. nasal cavity носова€полость
2. to inhale - вдыхать
3. speck - покрывать
4. moist - влажный
5. surface - поверхность
6. to trap - ловить
7. passageway - отверстие
8. moisture - влага
9. to add - добавл€ть
Windpipe and Bronchial Tree 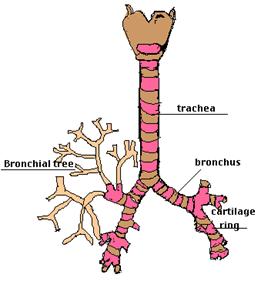
The windpipe (trachea) joins the upper respiratory tract to the lungs. If you gently touch the front of your throat you can feel the trachea. The bottom of the trachea splits into two branches called bronchi. One enters the right lung and one goes to the left lung.
|
|
|
The bronchial tree's job is to spread the air from the trachea over a very wide area as quickly as possible. The air passing through the windpipe divides into two branches. These divide into twigs called bronchioles. These twigs open into little bags called alveoli.
We have about 300 million alveoli (air sacs) in each lung. The alveoli gives our lungs a huge surface for absorbing oxygen from the air.
Lungs

Lungs provide the breath of life. Our lungs are about the size of a pair of footballs. They fill our chest from the neck to the ribs. The lungs are protected by our ribs. The lungs are the pickup place for oxygen and the drop off place for carbon dioxide. The lungs are always working, breathing in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide.
Blood is pumped into the lungs from the heart through the pulmonary arteries. Blood with oxygen leaves the lungs through the pulmonary veins and travels to the heart. Oxygen is the fuel that makes all the body processes run.
Vocabulary
1. gently Ц м€гко
2. bottom Ц низ
3. to split Ц расщепл€ть
4. twig Ц ветка
5. to provide Ц обеспечивать
6. pickup Ц перевозка
7. pulmonary arteries Ц легочныеартерии
8. fuel Цгорючее
Questions
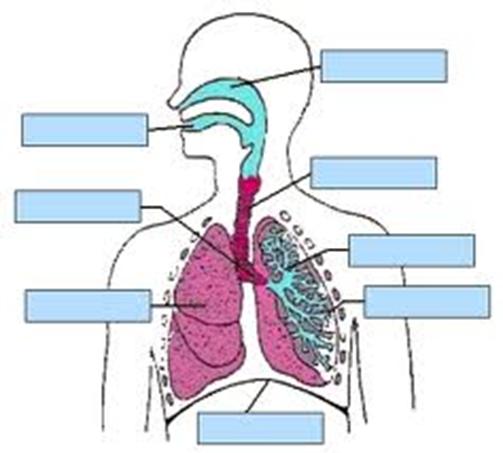
1. What organs are made up respiratory system?
2. What do lungs provide?
3. What protect lungs?
Quiz
Instruction: Write down organs of respiratory system
| Crossword | |

| 
|
| Across 2. One of two places where air enters your body. 4. When we exhale we breathe this plus carbon dioxide. 7. You do this when something irritates your nose. 8. You do this when you don't get enough oxygen to your blood. 11. A gas that you breathe out. It is a waste gas. 14. The place where oxygen enters the blood. 16. You do this when something irritates your diaphragm. 17. Breathe out. 19. Large muscle that controls the lungs. | Down 1. This prevents food from going down your lungs. 3. All animals need this gas to make energy from food. 5. Scientific name for the windpipe. 6. Inhale and exhale. 9. Common name for the trachea. 10. Fish have these instead of lungs. 11. You do this when something irritates your trachea or bronchi. 12. Two tubes that connect the trachea to the lungs. 13. Breathe in. 15. One of two places where air enters your body. 18. Whatwebreathe. |
WordSearch







