Parts of the Human Body
1. body - тело
2.  head - голова
head - голова
3. hair - волосы
4. face - лицо
5. cheek - щека
6. eye - глаз
7. ear - ухо
8. mouth - рот
9. tooth (teeth) Ц зуб (зубы)
10. arm - рука
11. leg - нога
12. hand Ц рука (кисть)
13. finger Ц палец (руки)
14. toe - палец (ноги)
15. thumb - большой палец руки
16. foot (feet) нога (ступн€)
17. forehead - лоб
18. nose - нос
19. shoulder - плечо
20. chest Ц грудь (грудна€ клетка)
21. back - спина
22. skin - кожа
23. breast - грудь
24.  navel - пупок
navel - пупок
25. palm - ладонь
26. groin - пах
27. knee - колено
28. hip - бедро
Internal organs
1. heart - сердце
2. lungs - легкие
3. tongue - €зык
4. stomach - желудок
5. liver - печень
6. bladder Ц мочевойпузырь
7. kidney - почка
8. brain - мозг
9. bowels - кишечник
Parts of the Human Body
1. Answer the following questions.
Ј What do you think of your body?
Ј How do you take care of your body?
2. Read the text. Translate it.
The body is wonderfully made, like a complex, perfect machine. Each part is specially constructed to carry out its own function, and to work as a whole with the other parts.
The body has a strong frame work of bones called the skeleton. The skeleton is covered by muscles and other soft tissues, and by skin on the outside.
The human body consists of three parts. They are the head, the trunk and the limbs.
The main part of the head is called the skull. The forehead, the temples, the cheeks, the cheekbones, the two jaws and the mouth compose the face. The teeth and the tongue are loading in the mouth. One chews food with the teeth and tastes food with the tongue. The lips are the two margins of the mouth. We see with the eyes, breathe and smell with the nose.
The trunk consists of the spine, the chest and the pelvic bones. The trunk is divided into two large cavities by diaphragm. The upper cavity of the trunk is called thorax and lower one is called the belly. The lungs and the heart are located above the diaphragms in the upper cavity. In the lower cavity we find interior organs such as stomach, liver, urinary bladder, gallbladder kidneys, spleen and intestines.
The upper limb is divided into the shoulder, the upper arm, the forearm and the hand. The join between upper arm and forearm we call the elbow. The wrist is the joint between forearm and hand. Each hand has five fingers: index, middle finger, ring finger, little finger and a thumb.
The lower limb consists of the thigh-bone, the shin-bone and the fibula. We call the calf the back of the lower leg. The join between the femur and the lower leg is called the knee-joint. This joint is protected by the knee-cap. The joints between lower legs and feet are the ankles. The foot consists of heel, sole and toes.
Vocabulary
1. construct [kən'strʌkt] - строить
2. to carry out - нести
3. to cover ['kʌvə] - покрывать
4. muscle ['mʌsl] - мышца
|
|
|
5. tissue ['tɪʃu:]- ткань
6. trunk [trʌŋk] - туловище
7. limb [lɪm] - конечность
8. skull [skʌl] - череп
9. temple ['templ] - висок
10. chew [ʧu:] - жевать
11. to divide into[dɪ'vaɪd] Ц делитьс€на
12. belly ['belɪ] Ц живот
13. shin-bone Ц большеберцова€ кость
14. thighbone ['θaɪbəun] Ц бедренна€ кость
15. joint - сустав
16. knee-joint Цколенный сустав
17. knee-cap Ц коленна€ чашечка
18. ankle['æŋkl] - лодыжка
19. sole Ц подошва
20. frame [səul] Ц скелет, каркас
21. margin ['mɑːʤɪn]Ц поле, кромка
22. thorax ['θɔːræks] Ц грудна€ клетка
23. cavity ['kævətɪ] Ц полость
24. diaphragm ['daɪəfræm] Ц диафрагма
25. wrist [rɪst] Ц зап€стье
26. thumb [θʌm] Ц большой палец
27. fibula ['fɪbjələ] Ц малоберцова€ кость
28. calf [kɑːf] Ц икра
29. femur ['fi:mə] - бедро
Exercises
1. Make up 5 sentences with new words.
2. Answer the following questions.
Ј What is the human body?
Ј What is skeleton?
Ј What parts of the human body do you know?
Ј What is the main part of head?
Ј What fingers does the hand consist of?
3. Fill the gaps with prepositions.
Ј Each part is specially constructed to carry _____ its own function.
Ј The skeleton is covered ______ muscles.
Ј The human body consists ______ three parts.
Ј The upper limb is divided ______ the shoulder, the upper arm, the forearm and the hand.
Ј The lungs and the heart are located _____ the diaphragms in the upper cavity.
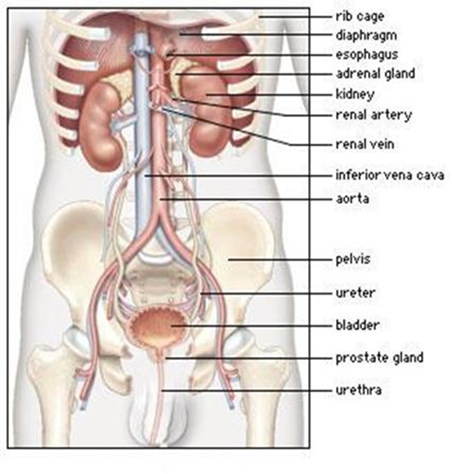
Cavities
Some body parts form spaces called cavities, in which important internal organs are protected.
1. The cranial cavity or skullЦ contains the brain
2. The thoracic cavity or chest contains:
Ј the lungs
Ј the air passagesЦ trachea and bronchial tubes
Ј theoesophagus or food pipe, which lies behind the trachea
Ј the heart
Ј the great blood vessels, and the thoracic duct (the largest lymphatic vessel)
3. The abdominal cavity, which is separated from the thoracic cavity by a dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm. It contains:
Ј the stomach
Ј the small intestine
Ј the large intestine or bowel
Ј the liver
Ј the spleen
Ј the kidneys
Ј the ureters
Ј the pancreas
4. The pelvic cavity which contains:
Ј the reproductive organs
Ј the bladder when empty (when full it rises into the abdominal cavity)
Ј the rectum
Vocabulary
1. cranial cavity ['kreɪnɪəl] Ц черепна€коробка
2. thoracic cavity [θə'rasik] Ц грудна€полость
3. trachea [trə'ki:ə] Ц трахе€
4. bronchial tubes ['brɔŋkɪəl] Ц бронхиолы
5. oesophagus [i:'sɔfəgəs] Ц пищевод
6. abdominal cavity [æb'dɔmɪn(ə)l] Ц брюшна€полость
7. dome-shaped Ц куполообразный
8. ureter [juə'ri:tə] Ц мочеточник
9. pancreas ['pæŋkrɪəs] Ц поджелудочна€железа
10. pelvic cavity Ц тазова€полость
11. rectum ['rektəm] Ц пр€ма€кишка
Cells
All living things, including the human body, are made up of living cells. The cell is the structural and the functional unit with which the human body is built.
|
|
|
Tissues
Tissues are materials made up of groups of similar cells. Cells are of various types, and tissues vary according to the types of cells in their structure.
Vocabulary
1. cell Ц клетка
2. to vary ['vɛərɪ] - мен€ть
Organs and Systems
Tissues are jointed into larger units called organs, such as the heart, lungs, brain, liver. Each organ is made up of types of tissue, which enable it to do its special work. A system is a group of organs, which together carry out one of the essential functions of the body. There are nine systems, listed below. All of these systems work harmoniously together in a healthy body.

| SkeletalSystem | 
| Support, movementandprotection |
| MuscularSystem | 
| Movements and production of heat |
| NervousSystem | 
| Controlofbodyactivities |
| CirculatorySystem | 
| Transport of food and oxygen, waste products, etc |
| RespiratorySystem | 
| Taking in of oxygen and giving off carbon-di-oxide |
| DigestiveSystem | 
| Taking in food, breaking it down into nutrients for use by body cells |
| ExcretorySystem | 
| Removal of waste matter from the body |
| EndocrineSystem | 
| Production of hormones, which influence the activity of cells |
| ReproductiveSystem | 
| Enable s new individuals to be born |
Vocabulary
1. harmoniously [hɑː'məunɪəslɪ] Ц гармончно
2. muscular ['mʌskjələ, 'mʌskjulə] Ц мышечна€система
3. circulatory [,sɜːkju'leɪt(ə)rɪ] Ц циркулирующий
4. respiratory [rɪ'spɪrət(ə)rɪ] Ц дыхательный
5. igestive [daɪ'ʤestɪv] Ц пищеварительный
6. excretory [eks'kri:tərɪ] Ц выделительный
7. endocrine ['endəukraɪn] - эндокринный
8. support - поддержка
9. movement - движение
10. protection - защита
11. heat - жара
12. waste - отходы
13. nutrient Ц питательное вещество
14. removal - перемещение
15. influence - вли€ние
16. enable - возможный
Exercises
1. Place in the table the organs or part of the organs with the systems that they belong.
Ј brain
Ј veins
Ј lungs
Ј esophagus
Ј maxillary
Ј spinal cord
Ј abdominals
Ј thymus gland
Ј aorta
Ј heart
Ј biceps
Ј clavicle
Ј femur
Ј trachea
Ј nose
Ј mouth
Ј salivary glands
Ј tongue
Ј sweat glands
Ј Achilles tendon
cerebellum
| System | Organ | Organ | Organ |
| Digestive | |||
| Endocrine | |||
| Muscular | |||
| Nervous | |||
| Respiratory | |||
| Skeletal | |||
| Circulatory |
 2. Fill in the blanks to complete the paragraph with the appropriate preposition from the list. Use each only one time.
2. Fill in the blanks to complete the paragraph with the appropriate preposition from the list. Use each only one time.
Ј into
Ј by
Ј of
Ј against
Ј in
Ј for
Ј through
a. The immune system protects the body ________ infections, and diseases. It is formed _______ the lymphatic system and the skin.
b. There are 206 bones ______ our body; the bones are always busy. They store calcium and contain the bone marrow, which produces the bodyТs red and white blood cells and platelets.
c. The purpose ______ the respiratory system is to take oxygen _______ the body and get rid of carbon dioxide (a waste product).
d. The muscle system is responsible _______ the bodyТs flexibility and movement.
e. The senses function _________ specialized organs, all of which are related to the nervous system.
3. Give the full answer.
What do you think is the most important system in your body? Why?
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
|
|
|
Review
1. The human body is a single structure but it is made up of billions of smaller structures of four major kinds: cells, tissues, organs, and systems.
2. An organ is an organization of several different kinds of tissues so arranged that together they can perform a special function.
3. A system is an organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform complex functions for the body.
4. Ten major systems include the skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and the reproductive system.
5. Body functions are the physiological or psychological functions of body systems. Survival of the body depends on the body's maintaining or restoring homeostasis, a state of relative constancy, of its internal environment.
6. Human life process includes organization, metabolism, responsiveness, movements, reproduction, growth, differentiation, respiration, digestion, and excretion. All these processes work together, in fine-tuned balance, for the well-being of the individual and to maintain life.
7. Life depends on certain physical factors from the environment, which include water, oxygen, nutrients, heat, and pressure.
|
The human body is the entire physical structure of a human organism
The human body is an example of highly developed multicellular organism. It develops from a fertilized egg cell. This cell continues to multiply rapidly and forms all the tissues of the body. Each tissue has its function. A tissue is an aggregation of morphologically similar cells and associated intercellular matter that form an organ. A group of physiologically or anatomically complementary organs form a system. The systems carry out one of the main functions of the body. The human body has nine systems: skeletal, muscular, respiratory, digestive, circulatory, excretory, reproductive, nervous and glandular.
The anatomical parts of the body are the head, the trunk, and the upper and lower limbs. The vital organs of digestion, respiration, circulation and response to the environment lie in cavities in the head and trunk. The limbs that are used for locomotion or grasping are outgrowths from the trunk.
The adult body is made up of:
100 trillion cells
206 bones
600 muscles
22 internal organs
Do you know that
more than half the bones in the human body are in the hands and feet? the highest recorded "sneeze speed" is 165 km (102 miles) per hour? the heart beats about 3 billion times in the average person's lifetime? a newborn baby has 350 bones, but a fully-grown adult has only 206? blood is a liquid organ? everyone is colorblind at birth? the surface area of the lungs is approximately the same size as a tennis court? food will get to your stomach even if you're standing on your head? skin is the largest body organ? the average adult is made up of 100 trillion cells?
The human body is like a complex organization that has an important job to get done on a tight deadline. In order to get everything done perfectly and on time, it has to use a system. Actually, the human body uses many systems that work side by side.
|
|
|
Quiz
Instruction: Find out the following words
| E | Y | J | K | C | W | M | P | A | R | M | F | Q | Z | Y | B | S | H | P | N |
| K | J | K | H | Q | Z | L | N | G | T | S | N | S | C | V | Z | F | Q | N | E |
| G | E | Y | E | S | Y | F | I | N | G | E | R | P | M | R | U | R | T | B | I |
| G | P | B | X | S | U | X | L | J | F | L | J | I | Z | P | G | P | W | L | S |
| F | N | W | S | K | I | N | H | K | Z | P | T | N | S | E | A | R | S | I | N |
| U | Y | P | B | W | Q | Z | E | M | Z | F | P | E | T | L | E | G | C | T | I |
| R | E | D | S | M | A | W | A | E | F | S | B | S | E | I | T | J | S | O | E |
| O | N | F | X | U | W | E | D | N | O | P | K | W | S | P | O | A | B | N | V |
| H | D | R | G | S | S | L | U | B | N | L | A | E | A | D | E | E | L | G | O |
| S | I | E | G | C | L | A | G | R | H | A | K | M | G | Z | Y | S | A | U | Y |
| C | K | N | H | L | I | V | H | A | A | K | K | S | G | H | V | O | D | E | P |
| F | O | O | T | E | V | U | H | I | N | H | N | G | L | E | K | N | D | R | R |
| X | E | B | I | S | E | E | B | N | D | X | U | C | U | A | O | P | E | S | Z |
| Z | I | L | H | X | R | K | B | D | O | G | J | Y | D | R | R | Y | R | U | B |
| O | H | A | Y | S | C | H | E | X | W | Y | M | N | T | T | J | D | Y | P | X |
| U | O | F | T | J | X | D | G | H | B | G | N | X | L | U | N | G | S | F | A |
| HEART | EARS | LIVER | SKIN |
| TOE | FINGER | HEAD | BRAIN |
| MUSCLES | FOOT | BONE | TONGUE |
| SPINE | EYES | NOSE | LEG |
| LUNGS | KIDNEY | ARM | |
| BLADDER | VEINS | HAND |
Test 1
Human Body
Instruction: Chose the correct answer.
1. _____________ investigates the body's structure, whereas __________ investigates the processes or functions of living things.
a. Physiology, cytology
b. Physiology, anatomy
c. Anatomy, histology
d. Histology, cytology
e. Anatomy, physiology






