| Mrs J.H. Harris Rockford Arms Hotel Rockford, CO 33322 | |||
| September 15, 2005 | |||
| Enjoy Travel, Inc Fifth Avenue Greenburg, VT 11111 | |||
| Attention: World Travel Reservations | |||
| Please reserve one seat on your Around-the-World tour leaving Greenburg on March 30, returning My 30. I am enclosing a down payment of $500.00 (five hundred dollars) by personal check. | |||
| Yours truly, | |||
| Mrs J.H. Harris |
 «јƒјЌ»≈ N 26 отправить сообщение разработчикам
«јƒјЌ»≈ N 26 отправить сообщение разработчикам
“ема: ќформление конверта
Ќачало формы
онец формы
ѕеред ¬ами конверт.
—оотнесите информацию под определенным номером на конверте с тем, что она обозначает.

| the sender | |||
| the house number in the return address | |||
| the ZIP Code in the return address | |||
| the addressee | |||
| the street name in the mailing address | |||
| the state name in the mailing address |
 «јƒјЌ»≈ N 27 отправить сообщение разработчикам
«јƒјЌ»≈ N 27 отправить сообщение разработчикам
“ема: ќформление резюме, письма-за€влени€, письма-уведомлени€, письма-запроса, контракта, служебной записки
Ќачало формы
онец формы
ќпределите, к какому виду делового документа относитс€ представленный ниже отрывок.


| Invitation Letter | ||
| Cover Letter | |||
| Letter of Complaint | |||
| Contract |
 «јƒјЌ»≈ N 28 отправить сообщение разработчикам
«јƒјЌ»≈ N 28 отправить сообщение разработчикам
“ема: ќформление электронного сообщени€, факса, меморандума (служебной записки)
Ќачало формы
онец формы
¬ыберите слова или словосочетани€ дл€ заполнени€ пропусков так, чтобы они отражали особенности оформлени€ служебной записки:
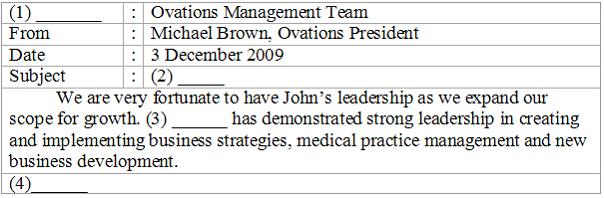
| To | |||
| Welcoming John Smith | |||
| John | |||
| Michael Brown |
 «јƒјЌ»≈ N 29 отправить сообщение разработчикам
«јƒјЌ»≈ N 29 отправить сообщение разработчикам
ейс-задани€: ѕодзадача 1
Ќачало формы
онец формы
ѕрочитайте текст и выполните задани€
Globalization
1. Humans have interacted over long distances for thousands of years. The overland Silk Road that connected Asia, Africa, and Europe is a good example of the transformative power of translocal exchange that existed in the ЂOld Worldї. Philosophy, religion, language, the arts, and other aspects of culture spread and mixed as nations exchanged products and ideas.
2. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Europeans made important discoveries in their exploration of the oceans, including the start of transatlantic travel to the ЂNew Worldї of the Americas. Global movement of people, goods, and ideas expanded significantly in the following centuries.
3. Early in the 19th century, the development of new forms of transportation (such as the steamship and railroads) and telecommunications that Ђcompressedї time and space allowed for increasingly rapid rates of global interchange. In the 20th century, road vehicles and airlines made transportation even faster. The advent of electronic communications, most notably mobile phones and the Internet, connected billions of people in new ways.
|
|
|
—одержанию текста соответствует утверждение Е

| Since the beginning of the 20th century, the pace of globalization has intensified significantly due to advances in transportation and telecommunications. | ||
| Four basic aspects of globalization are trade and transactions, capital and investment movements, migration of people and the dissemination of knowledge. | |||
| Environmental challenges such as climate change, cross-boundary water and air pollution, and over-fishing of the ocean are linked with globalization. | |||
| Globalizing processes affect and are affected by business and work organization, economics, socio-cultural resources, and the natural environment. |
–ешение:
ƒл€ того чтобы правильно выполнить задание, следует знать алгоритм обработки текстовой информации и, прочитав текст, определить наличие в тексте информации, соответствующей его содержанию.
”тверждение ЂSince the beginning of the 20th century, the pace of globalization has intensified significantly due to advances in transportation and telecommunicationsї (Ђ— начала 20-го века темпы глобализации значительно увеличились благодар€ достижени€м в области транспорта и св€зиї) соответствует содержанию текста: ЂIn the 20th century, road vehicles and airlines made transportation even faster. The advent of electronic communications, most notably mobile phones and the Internet, connected billions of people in new waysї (Ђ¬ 20-м веке автотранспортные средства и авиакомпании способствовали более быстрой перевозке. ѕо€вление электронных средств св€зи, в первую очередь мобильных телефонов и »нтернета, соединили миллиарды людей новым способомї) (фрагмент 3).
 «јƒјЌ»≈ N 30 отправить сообщение разработчикам
«јƒјЌ»≈ N 30 отправить сообщение разработчикам
ейс-задани€: ѕодзадача 2
Ќачало формы
онец формы
ѕрочитайте текст и выполните задани€
Globalization
1. Humans have interacted over long distances for thousands of years. The overland Silk Road that connected Asia, Africa, and Europe is a good example of the transformative power of translocal exchange that existed in the ЂOld Worldї. Philosophy, religion, language, the arts, and other aspects of culture spread and mixed as nations exchanged products and ideas.
2. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Europeans made important discoveries in their exploration of the oceans, including the start of transatlantic travel to the ЂNew Worldї of the Americas. Global movement of people, goods, and ideas expanded significantly in the following centuries.
3. Early in the 19th century, the development of new forms of transportation (such as the steamship and railroads) and telecommunications that Ђcompressedї time and space allowed for increasingly rapid rates of global interchange. In the 20th century, road vehicles and airlines made transportation even faster. The advent of electronic communications, most notably mobile phones and the Internet, connected billions of people in new ways.
|
|
|
«авершите утверждение согласно содержанию текста.
Globalization refers to processes of the Е

| world-wide exchanges of views, products and ideas | ||
| local exchanges of national and cultural resources | |||
| development of new forms of transportation | |||
| development of new forms of telecommunication |
–ешение:
ƒл€ того чтобы правильно выполнить задание, следует знать алгоритм обработки текстовой информации и, прочитав текст, завершить утверждение согласно содержанию текста.
”тверждение ЂGlobalization refers to processes of the Еї(Ђ√лобализаци€ относитс€ к процессамЕї) следует закончить вариантом ответаЂworld-wide exchanges of views, products and ideasї (Ђвсемирного обмена мнени€ми, продуктами и иде€миї), так как именно это утверждение соответствует содержанию текста.
—огласно тексту: ЂGlobal movement of people, goods, and ideas expanded significantly in the following centuriesї (Ђ√лобальное перемещение людей, товаров и идей значительно расширилось в последующие векаї) (фрагмент 2).
 «јƒјЌ»≈ N 31 отправить сообщение разработчикам
«јƒјЌ»≈ N 31 отправить сообщение разработчикам
ейс-задани€: ѕодзадача 3
Ќачало формы
онец формы
ѕрочитайте текст и выполните задани€
Globalization
1. Humans have interacted over long distances for thousands of years. The overland Silk Road that connected Asia, Africa, and Europe is a good example of the transformative power of translocal exchange that existed in the ЂOld Worldї. Philosophy, religion, language, the arts, and other aspects of culture spread and mixed as nations exchanged products and ideas.
2. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Europeans made important discoveries in their exploration of the oceans, including the start of transatlantic travel to the ЂNew Worldї of the Americas. Global movement of people, goods, and ideas expanded significantly in the following centuries.
3. Early in the 19th century, the development of new forms of transportation (such as the steamship and railroads) and telecommunications that Ђcompressedї time and space allowed for increasingly rapid rates of global interchange. In the 20th century, road vehicles and airlines made transportation even faster. The advent of electronic communications, most notably mobile phones and the Internet, connected billions of people in new ways.
ќтветьте на вопрос:
When did the first signs of globalization appear?

| They appeared in the ЂOld Worldї. | ||
| They appeared in the ЂNew Worldї. | |||
| They appeared in the 16th century. | |||
| They appeared in the 20th century. |
–ешение:
ƒл€ того чтобы правильно выполнить задание, следует знать алгоритм обработки текстовой информации при изучающем чтении, уметь анализировать получаемую информацию и, чита€ текст, находить ответ на поставленный вопрос.
ѕравильный ответ на вопрос Ђ огда по€вились первые признаки глобализации?ї Ц ЂThey appeared in the УOld WorldФї (Ђќни по€вились в У—таром —ветеФї), так как согласно тексту: ЂThe overland Silk Road that connected Asia, Africa, and Europe is a good example ofЕ translocal exchange that existed in the УOld WorldФї (Ђ—ухопутный Ўелковый ѕуть, который соедин€л јзию, јфрику, ≈вропу, €вл€етс€ хорошим примеромЕ транслокального обмена, который существовал в У—таром —ветеФї) (фрагмент 1).
 «јƒјЌ»≈ N 32 отправить сообщение разработчикам
«јƒјЌ»≈ N 32 отправить сообщение разработчикам
ейс-задани€: ѕодзадача 4
Ќачало формы
онец формы
ѕрочитайте текст и выполните задани€
Globalization
1. Humans have interacted over long distances for thousands of years. The overland Silk Road that connected Asia, Africa, and Europe is a good example of the transformative power of translocal exchange that existed in the ЂOld Worldї. Philosophy, religion, language, the arts, and other aspects of culture spread and mixed as nations exchanged products and ideas.
2. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Europeans made important discoveries in their exploration of the oceans, including the start of transatlantic travel to the ЂNew Worldї of the Americas. Global movement of people, goods, and ideas expanded significantly in the following centuries.
3. Early in the 19th century, the development of new forms of transportation (such as the steamship and railroads) and telecommunications that Ђcompressedї time and space allowed for increasingly rapid rates of global interchange. In the 20th century, road vehicles and airlines made transportation even faster. The advent of electronic communications, most notably mobile phones and the Internet, connected billions of people in new ways.
|
|
|
ќсновной идеей текста €вл€етс€ Е

| The process of globalization has a long history and is still developing. | ||
| Europeans made great discoveries in the 15th and 16th centuries. | |||
| Mobile phones and the Internet are great inventions of the 20th century. | |||
| Trade on the Silk Road was a significant factor in the development of the civilizations. |






