I. Read and memorize the following words, word- combinations and word-groups:
LDC (less developed country) — країна, що розвивається
e.g. Most less developed countries (LDCs) are characterized
by both low GNP per capita and slow income growth.
productivity — продуктивність
e.g. Output per unit of input; output per labor hour is a
productivity.
subsistence level — прожитковий рівень
e.g. Most of the population in Haiti fives at the subsistence
level.
hard currency — тверда конвертована валюта
e.g. Governments need «hard» currencies to buy new capital and other imported resources.
debt servicing — обслуговування боргу, капітальної суми
боргу або відсотків
e.g. The interest required to be paid each year on outstanding debt is a debt servicing.
market shortage — недостатня ринкова пропозиція
e.g. The amount by which the quantity demanded exceeds
the quantity supplied at a given price; excess demand.
infrastructure — інфраструктура
e.g. Infrastructure consists of the physical and institutional
features that facilitate economic activity.
World Bank — Світовий банк
e.g. The most prominent lending agency is the World Bank.
II. Give English equivalents of the following:
Світовий банк країни, що розвиваються
задовольняти потреби людини високий рівень народжува
швидке зростання чисельності ності
населення іноземні інвестиції
нестача кваліфікованої робочої середній прибуток сили іноземна допомога позики
III. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
| 1. It is difficult to comprehend just how... the Third World is. 2. High birth rates... a country's ability to raise GNP per capita. 3. In LDCs there is typically a... of skilled labor and managers. 4. Foreign investment is often... by LDC governments. 5. Debt servicing requires an LDC... its export potential. 6. Another... in LDCs is a lack of infrastructure. 7. Most LDCs prefer to use.... 8. All LDCs could benefit from.... | problem nonmarket prices to increase foreign aid poor discouraged limit shortage |
IV. Read and translate the text:
This text provides some perspective on the global gap between rich and poor. As Professor Theodore Schultz has written «Being rich makes it hard to comprehend behaviour of poor people». It is difficult to comprehend just how poor the Third World is.
Most less developed countries (LDCs) are characterized by both low GNP per capita and slow income growth. They are also far less able to satisfy basic human needs (e.g. food, shelter, medical care). High birth rates limit a country's ability to raise GNP per capita. Rapid population growth also tends to retard education, saving and investment. Rapid population growth is only one dimension of the labor problem. Ironically, the other dimension consists of a labor shortage. In LDCs there is typically a severe shortage of skilled labor and managers. Sixty percent of the population is illiterate.
A lack of capital resources poses a second major barrier to growth. The LDCs are desperate for plants and equipment that will raise the productivity of labor. But their average incomes are so low that they can rarely afford to save enough to finance the required investments. Most of the population lives at the subsistence level. Domestic saving can finance only some of the inputs, that is why external financing is usually required. Foreign investment, loans, and aid are all sources of external financing. The improvements in management, technology and labor training accompany foreign investment. Despite its substantial benefits, foreign investment is often discouraged by LDC governments. The resistance reflects a fear of becoming dependent on foreign investors.
Like foreign investment, loans represent an opportunity to increase current investment without reducing current consumption. The most prominent lending agency is the World Bank. Even in the best of political and economic situations, there is a limit to the ability of LDCs to borrow. A loan requires repayment. Hence LDCs that borrow must have the capability to service (repay) that debt. The economy of the LDCs must grow enough to generate a surplus for debt servicing. Debt servicing requires an LDC to increase its export potential in
order to earn hard currency.
Unlike loans, foreign aid refers to money or resources given to LDCs for which no repayment is required. Foreign aid is given on a bilateral basis or through multinational agencies.
Technology, Capital and labor are basic factors of production. However, technology is also a primary determinant of production possibilities. LDCs could greatly increase their growth with improved technology.
Institutional Structure. Another problem in LDCs is a lack of infrastructure. Roads, telephones, schools, hospitals and electricity are all essential ingredients of a viable economy.
Finally, many LDCs are reluctant to rely on the market mechanism to allocate resources and distribute incomes. They prefer to use nonmarket prices to pursue specific economic or political objectives. The end result is a market shortage. This distortion of market process has been a barrier to growth.
Growth strategies. Many economists have concluded that the LDCs will not be able to achieve sustained economic growth until they can master enough resources to overcome all of these barriers simultaneously. Many of the poorest LDCs must choose between agricultural development and industrialization, Agricultural development promises a greater payoff because the vast majority of the population works in agriculture, at low productivity. Improved farm productivity can create food, labor and capital surpluses for industrialization.
There is no «correct» strategy for economic development. Each country confronts a unique set of barriers and growth possibilities. All LDCs, however, could benefit from more foreign aid.
V. Answer the following questions:
1. What are the most common features of the LDCs?
2. What are the barriers to the growth?
3. What does the labor problem consist of?
4. What does a lack of capital result in?
5. Can domestic saving finance the whole of inputs?
6. What are the sources of external financing?
7. What is the difference between loan and foreign aid?
8. What is the role of the market mechanism?
9. What are the growth strategies?
VI. Define the terms:
| debt servicing market shortage nonmarket prices market mechanism foreign investment | foreign aid infrastructure subsistence level GNP per capita loan |
VII. Translate info English:
1. Багато міжнародних кредитних установ надають фінансову допомогу країнам третього світу. 2. Низькі прибутки та повільний економічний розвиток є характерними рисами країн третього світу. 3. Населення багатих країн зростає дуже повільно. 4. У бідних країнах чисельність населення зростає дуже швидко, що сповільнює підвищення добробуту. 5. Селяни в країнах, що розвиваються, не довіряють банкам і паперовим грошам. 6. Деякі країни скорочували виробництво споживчих товарів, аби змусити споживачів заощаджувати більше грошей. 7. Експорт допомагає заробляти необхідну валюту. 8. ООН запропонувала розвиненим країнам використовувати 1 відсоток вало
вого національного продукту як іноземну допомогу.
VIII. Read and dramatize the following dialogue:
A.: Most countries continue to experience economic growth. But the relationship between GNP growth is very different in rich and poor countries. B.: What are the differences?
A.: The populations of rich countries are growing very slowly and gains in per capita GNP are easily achieved. In the poorest countries, population is increasing rapidly, making it difficult to raise living standards.
B.: Which countries are rich and which are poor?
A.: Rich countries are the United States, Sweden, Japan and Germany. Peru, Nigeria, Thailand, Honduras, Egypt, Philippines are poor countries, and Pakistan, Kenya, China, Haiti, India, Ephiopia are the poorest. B.: What is the reason for that?
А.: As I have already told, it is low growth. Before growth can accelerate, though, the present barriers to growth must be identified and overcome. В.: What are the barriers?
A.: Some of the major barriers are lack of labor and capital resources.
B.: As far as I know the World Bank makes loans to LDCs for specific development projects.
A.: Yes, the other multinational banks provide financial and technical assistance.
B.: But a loan requires repayment.
A.: During the 1980s the LDCs nearly doubled their external debt. Annual servicing on these loans exceeded $170 billion.
B.: And then, some of the major debtor nations declared a moratorium on debt repayment.
A.: First Mexico, then Brazil and Peru announced that they were stopping or reducing debt servicing. It gave some of the LDCs some «breathing room». They could use this temporary relief to channel more of their export earnings into investment.
B.: Do the United States and other developed countries lose from the debt crises?
A.: The developed (creditor) countries and the developing
(debtor) nations had a joint interest in resolving the debt crises. The resolution has included increased exports by developing countries, a reduction in imports of developing countries, greater priority to investment and growth in LDCs, more loans and aid from developed countries.
B.: It's very convenient, isn't it? And beneficial to both parties.
I'm sure.
IX. Make up your own dialogue using the following «expressions:
low incomes developing countries loans foreign investments
slow growth to raise living standards
to accelerate the growth foreign aid a lack of capital a lack of trained labor
X. Change the following sentences according to the models:
M o d e l A: I insist that he should examine the documents.
I insisted on his examining the documents.
1. We insist that government should favor foreign investment. 2. We insist that government should increase current
investment without reducing current consumption. 3. We insist that the lending agencies should give loans to the LDCs. 4, We insist that the LDCs should rely on the market mechanism to allocate resources.
M o d e l В: You should think it over before you give an answer.
You should think it over before giving an answer.
1. You should visit the country before you analyze its economic situation. 2. You should make an appointment before you see him. 3. You should think the offer over before you
accept it. 4. You should inform the manager of the hotel before you leave.
XI. Complete these sentenses using Gerunds;
1. He is busy (to look through documents). 2. I am fond of (to travel by air). 3. She is afraid of (to be alone). 4. We are sorry for (to be late). 5. They couldn't help (to smile).
6. It is a pleasure (to see you again).
XII. Translate into English using Gerunds:
1. Він захоплювався читанням пригодницьких книжок.
2. Ми наполягали на повторенні досліду. 3. Ми зайняті: обговорюємо шляхи економічного розвитку. 4. Пробачте, що ми турбуємо вас знову. 5. Вони не могли не погодитися з ним.
XIII. Communicative situations:
1. Identify an LDC and discuss its recent growth experience.
2. Speak about external financing.
3. Speak about debt servicing and debt crisis.
V O C A B U L A R Y A
accept [ək'sept] приймати; визнавати; акцептувати account [ə'kaunt] рахунок
account for [ə'kaunt fɔ:] пояснювати; звітувати(ся), нести відпові
дальність
accountant [ə'kauntənt] бухгалтер accounting [ə'kauntiŋl бухгалтерський облік adaptation [,ædæp'teijn] пристосування add [æd] додавати; приєднувати adopt methods [ə'dopt 'meθədz] переймати методи (методику) advantage [ədˈvɑːntɪdʒ] перевага
advertise ['ædvətaιz] розміщувати оголошення, рекламувати agency [ˈeɪdʒənsi] чинник, засіб (виконання); агентство; орган,
бюро; представництво
aggregate ['agπgιt] сукупний* зібраний в одне ціпе aggregate demand ['ægrιgτt 'dr'mα:nd] сукупний попит aggregate income ['ægπgιt 'ιnkəm] сукупний прибуток aggregate output ['ægπgιt Output] загальний обсяг виробництва aggregate price level ['ægπgιt prais lev]] загальний рівень цін aggregate spending ['ægπgπ 'spendιo] сукупні витрати aggregate supply ['ægrιgιt sə'plar] сукулна пропозиція allocate fæfəkeιt] розміщувати; виділяти; асигнувати
allocation [,ælə'keιjn] розміщення, розподіп; асигнування, від
рахування; виділення (дефіцитних або фондових ресурсів); класифікація
amount [ə'maιmt] кількість; сума; підсумок, основна сума і відсотки з неї
amount of moneγ [ə'maυnt əv 'тлт] сума, кількість грошей annual ['ænjuə]] річний applicant ['æplιkənt] заявник; кандидат на посаду applicant for credit ['æplιkənt fo: 'kredιt] особа, що звертається
за кредитом
applicant for shares ['æplτkənt fo: 7εəz] особа, що бажає купити
акції
apply for [ə'plai fy] подавати заяву appreciation [ə,pri:JYeiJn] зростання вартості, приріст вартості
основного капіталу
approach [ə'proutj] метод, підхід appropriate [ə'prouprnt] відповідний, придатний; властивий
assets ['æsets] активи { балансу)
assistance [ə'sιstəns] допомога, сприяння; підтримка adjustment [ə^AStmənt] assistance визначена допомога assume [ə'sjικm] брати (на себе); вживати (заході) attend [ə'iendj відвідувати attract a large amount of capitai [ə'trækt ə lα:eft ə'maunt əv 'kæpitl]
залучати великий капітал
attract customers ['ətrækt 'kAStəməz] залучати покупців attract financial resources [ə'trækt faι'næn/əl ri'so:siz] залучати
фінансові ресурси
auction [':κkfn] аукціон
authority [o:'θoritij орган влади, адміністрація; право, повноваження, влада посадової особи; авторитет (визначний спеціаліст)
available [ə'veιləbl] придатний, корисний; що € в розпорядженні, наявний; доступний В
background ['bækgraund] підготовка, освіта; кваліфікація; тло
balance sheet ['bæbns Ji:t] балансовий звіт bank services [bæŋk 'sə:vιsιz] банківські послуги banking ['bæŋkϊŋ] банківська справа barter ['bα:tə] мінова торгівля, бартер be on commission [bi: on kə'mijn] одержувати комісійні з торгівлі benefit ['bemfit] n користь; вигода; пенсія; допомога; v давати прибуток; отримувати користь
bidder ['bιdə] учасник аукціону board of directors [bo:d əv di'rektəz] рада директорів bond [bond] облігація; боргове зобов'язання book-keeper t'bυk,ki:pə] обліковець; бухгалтер borrow [уЬзґои] позичати
brand name [brænd nemi] торгова марка
business ['bιznιs] справа; підприємство; підприємництво; торгова операція; ділові кола
buyer [T>aiə] покупець
by-laws ['baι ιo:z] статут, правила внутрішнього розпорядку (що приймаються правлінням фірми)

calculate ['kælkjuleιt] обчислювати, підраховувати; калькулювати carry on a business ['kærr зп ə 'bιznιs] вести справу, займатися
підприємницькою діяльністю
cash transfer [kæj træns'fə:] допомога грішми, грошовий переказ catch on [kaetj on] стати модним
chain [tjein] мережа роздрібних магазинів або банківських філій ланцюгового підпорядкування (ам.)
chain movement [tjeιn 'mu:vmənt] рух до об'єднання channels of distribution ['tjænlz əv.chstn'bju:Jn] система збуту charge [tjα:dj] ціна; відповідальність charge prices [tjα:eft 'praιsιz] призначати, встановлювати ціни charitable institution fljæntəbl,msti'tju:Jn] благодійна установа chart [tjα:t] схема checking account ['tjekιŋ ə'kaunt] чековий (поточний) рахунок choose the company's officers [tju:z ði 'kAmpəniz'ofisəz] вибирати
адміністративний виконавців компанії
circumstance ['sə:kəmstəns] обставини coincident wants [kou'msrdənt wants] потреби, що збігаються collusion [кдУІи:зп] зговір, таємний зговір
commodity [kə'modιtι] продукт; товар; предмет ужитку common stock ['komən stok] спільні акції
company ['клтрзпг] компанія, товариство (акціонерне), фірма, корпорація
compel [kəm'pel] примушувати, підпорядковувати compete [kam'pi:t] конкурувати; змагатися competent ['kompjtənt] компетентний, що задовольняє потреби competition [Jcompi'tiJn] конкуренція, конкурентна боротьба; зма
гання
competitive [kəm'petιtιv] конкуруючий, конкурентоспроможний
competitor [kəm'petιtə] конкурент
complicate [lomplιkeιt] ускладнювати
compound ['kompaund] складний
concern [kən'sə-n] концерн, фірма, підприємство; структурний
підрозділ
conclude a deal [kən'klu:d ə di:l] укладати угоду
consequence ['konsιkwəns] наслідок
consideration [kən,sidə' reijn] розгляд, обміркування; відшкоду
вання, компенсація
consult a partner [kən'sAlt ə 'pα:tnə] консультуватися з партнером consume [kən'sju:m] споживати; витрачати consumer [kən'sju:mə] споживач
Consumer Price Index [kən'sju:mə praιs 'mdeks] показник спожив
чої вартості
consumption [kən'SAmpJən] споживання; витрачання
control the profit [kən'troul ði 'profit] контролювати прибуток controller [kən'troulə] головний фінансист; ревізор conversely ['kon'və:slϊ] навпаки copyright ['kəpιraτt] авторське право
corporate charter ['ka:pənt 'tjα:tə] корпоративний патент
corporate stock ['ko:pəπt stok] акціонерний капітал corporation [yko:pə'reiJn] корпорація; товариство cost [kost] ціна; вартість; витрати, видатки cover costs ['kAvð kosts] покривати витрати credit terms ['kredιt tə:mz] кредитні умови currency ['клгепзі] валюта, гроші current prices ('клгет 'praιsιz] існуючі ціни
curve ['kə:v] крива; графік, креслення
customer accounting ['kAStəmə ə 'kauntil}] облік покупців (клієнтів)
cyclical unemployment ['saιklιk(ə)] 'Amm'pbimənt] циклічне
безробіття D
dairy ['dεərι] молочарня; молочна ферма; молочний магазин damage ['dæmκfe] збиток, шкода
deal [di:l] угода debt [det] борг debt celling [det'sι:lτŋj максимальний розмір боргу debt funding [det 'fondiŋ] утворення грошового фонду підприєм-
ства за допомогою науки
debt servicing [det 'sə:vιsιŋ] виплата боргу та відсотків decide [dι'saιd] вирішувати
declare personal bankruptcy [dr'klεə'pə*s(ə)n(ə)l 'bæŋkrəptsr] ого
лосити власне банкрутство
decline [dι'klaιn] v зменшуватися; погіршуватися; занепадати; п занепад; зниження; падіння
decrease ['di:kri:s] л зменшення, скорочення; v [di:'kri:s] зменшу
вати
deduct [dι'dλkt] відраховувати, віднімати default [dι'fo:ltj неплатіж; невиконання договору deficit ['defιsιtj дефіцит deficit ceiling ['defιsιt 'si:lιη] максимальний розмір дефіциту
bafance-of-payments deficit ['bæləns əv 'peιmənt 'defιsιt] дефіцит платіжного балансу
deflate [di'fleιt] знижувати ціни
deflation [di'fieijn] дефляція delay [dι'let] затримка; відкладання deliver [dϊlιvə] доставляти; постачати
delivery [dι'lrvəπ] постачання
demand [dϊ'mα:nd] попит
demand-puil inflation інфляція, спричинена попитом denomination (dl.nomi 'neιjn] найменування, назва department store [dι'pα:tmənt st у ] універмаг depreciation [d[,pri:JYei/n] знецінювання derived demand [dι'raιvd dι'mα:nd] попит на засоби виробництва determine [dι'tə:mιn] визначати disadvantage [^dιsəd'vα:ntιdj] недолік
disaster [dι'zα:stə] лихо, біда
discount ['dιskaunt] знижка discount coupon ['dιskaunt 'ku:pon] талон, який надає право при
дбати товар за низькими цінами
discount house ['dιskaunt haus] магазин з відносно низькими цінами
на товар
disposable income [dιs'pouzəbl 'mkəm] прибуток, що £ в наявності distribute profits and losses [dιs'trιbjut "profits ənd 'losιz]
розподіляти прибутки і збитки
distribution Ldistri'biu:jn] збут: розподіл
distribution operation [,dιstπ'bju:jn ppə'reijn] операція з розподілу dividend ['dividend] дивіденд
division of labor [di'v^n əv'leibə] розподіл праці do books [du buks] вести бухгалтерський облік domain [də'mem] володіння; територія; галузь, сфера domestic currency [də'meslik 'kArənsi] місцева валюта domestic market [də'mestιk 'mα^kιt] внутрішній ринок drawback ['dro:bæk] недолік, негативний бік; перешкода dump [гїлтр] звалище
durability [,djuərə'bϊlιtι] міцність Е
earn [ə:n] заробляти; отримувати прибуток
economics [j:kə'nomιks] економіка {навчальна та наукова дис
ципліна); економічна теорія
economist [i:'konəmιst] економіст economy [i:'konəmι] економіка, народне господарство, еконо
мія, бережливість; економіка (як сфера знання) effect [ι'fekt] вплив
efficiency [i'fj/ənsϊ] ефективність; продуктивність
efficient [ι'fιjənt] ефективний, дійовий; кваліфікований, умілий elastic [ι'læstιk] еластичний; гнучкий elasticity [,əlæs4isiti] гнучкість; еластичність
eligible for a loan ['elrcbsb! fa ə'loun] підходящий; прийнятний для позики (тобто визнаний платоспроможним)
eliminate [ι'lιmιneιt] ліквідувати, знищувати embargo [em'bα:gou] ембарго
eminent ['emιnənt] піднесений; видатний, визначний, знаменитий employee ^empbj'i:] службовець; робітник employer [ιm'pbιə] роботодавець; наймач
2П
employment [im'pbiment] робота (за наймом); зайнятість; заняття enable [ґпеїЬЇ] давати право, можливість encourage (ш'клпс^] заохочувати
endowment [ιn'dauməαt] внесок; вклад; дар, пожертва enhance [rn'ha:ns] збільшувати; посилювати entrepreneur [pntrəprə'nə:] підприємець entrepreneurship [pntrəprə'nə:jϊp] підприємство
environment [ιn'vaι^rənmənt] навколишнє середовище equilibrium [,i:kwι']ιbπəm] збалансованість, рівновага equipment [ι'kwιpmənt] спорядження; обладнання; транспортні з за
соби
equity ['ekwιtι] власний капітал establish [ιs'tæblιj] засновувати; встановлювати evaluate [ι'væljuett] оцінювати; визначати вартість evolve [ι'voiv] розвиватися; розгортатися
exceed {ιk'si:d] перевищувати exchange [iks't/emcfe] обмін
exchange department [rks't/emcfe dϊ'pα:rtmənt] відділ обміну ва
люти
exchange rate [iks't/emcfe re*tj валютний курс exchange ratio [iks'tjemck Yei/юи] цінове відношення
exclude [iks'klu:d] виключати executive [ig'zekjutiv] керівник; адміністратор; виконавча влада
expansion [ιks'ρæn/ιι] розширення expectation [,ekspek'teijn] очікування; сподівання
expenditure [iks'pendjt fə] витрати; видатки experience [iks'pjəriðns] досвід, практика explicit [iks'plisit] певний; точний export ['eksps:t] вивезення, експорт exports {'ekspo:ts] товари, що вивозяться
extending credit [ιks'tendιŋ 'kredιt] довгостроковий кредит
external funds [eks'lə:nl f4ndz] зовнішні (іноземні) фонди
externality [yekstə:'næliti] зовнішній ефект (економічної діяльності) F
facilitate [fVsihtert] полегшувати; допомагати
factors of production ['fæktəz əv prə'dAkfn] чинники виробни
цтва
fail [feil] зазнавати поразки
fair market (fεə 'mα:kιtl сприятливі ринкові умови
familiar (fə'mιljə] близький; добре знайомий; поінформований
family's real income ['fæmιϊιz πəl 'tnkəm] реальний прибуток сім'ї
fee [fi:] винагорода; гонорар; внесок; збирання
feed the information into the computer [fi:d ðι,infə'meijn '\ntu
ə kəm'pju-tə] вводити дані в комп'ютер
fertilizer [Tə:tilaizə] добриво file [fail] прийняти для виконання (замовлення)
filthy ['fιlθι] забруднений
final authority ['faιnl o:'θorm] вирішальне слово financial condition [faι'naenjəl kəi/dijn] фінансовий стан financial statement [fai'nænjəl 'steitmənt] фінансовий звіт fire ['faιə] звільняти з роботи fiscal [Tiskəl] фіскальний; фінансовий fiscal year ['fιskəijə:] фінансовий, бюджетний рік
flexible exchange rate [fleksəbl iks 'tjemcfc reit] гнучкий валютний
курс
fluctuation [/Uktju'eijn] коливання
follow a legal procedure ['folou ə'li:gəl prə'si:dfeə] дотримуватись
юридичної процедури
forbid [fə'bid] не дозволяти, забороняти foreign currency ['form 'клгаїш] іноземна валюта
foreign exchange market ['form iks'tjemcb 'mα:kιt] ринок іноземної
валюти
foreign trade balance ['foπn treid 'bæləns] баланс міжнародної
торгівлі
foreman ['famən] майстер, прораб, бригадир
foul [faul] смердючий; брудний free enterprise system [fri: 'entəpraιz 'sιstəm] система вільного
підприємництва
frictional unemployment ['fπkfəπl 'лпіт 'pioιmənt] тимчасове
безробіття
fuel [fjuəl] пальне; паливо

gain [gem] прибуток get a raise [get ə reiz] отримати підвищення
give instructions fgiv m'strAkJənz] давати інструкції go Into business ['gou 'intu 'brznιs] займатися бізнесом go up [gou лр] зростати gold reserves [gouid ri'zəvz] золотий запас gold standard [gouid 'stændəd] золотий стандарт
goods [gudz] товар, товари; вантаж
gross [grous] валоеий, сумарний; брутто
gross investment [grous m'vestmənt] валова інвестиція
gross national product (GNP) [grous 'næjənt 'prodəkt] валовий
національний продукт
GNP per capita [rfμ: en pi: pə:'kæpitə] валовий національний про
дукт з розрахунку на душу населення
gross pay (grous реї] плата з відрахуванням
н
handle ['hændl] керувати; торгувати (ам.) harmful ['hα:mful] шкідливий
have voting rights [hæv 'voutiŋ ratts] мати право голосу
hire ['haιə] наймати на роботу hoard [ho:d] запасатися; накопичувати house hold [haus hould] сім'я, домашнє господарство
I
implicit [im'pjjsit] не виражений прямо, прихований imply [ιm'plaj] означати; мати на увазі; передбачати Import ['ιmpo-t] імпорт, ввезення imports ['impD:ts] товари, що ввозяться
impose [ιm'pouz] накладати; обкладати; обманювати, обманом
продавати; нав'язувати
impose a duty on goods [tm'pouz ə'dju:t! on gudz] обкладати това
ри митом
impose restriction [ιm'pouz rτs'trιkjn] вводити обмеження
incentive [in'sent! v] стимул, заохочення incinerator [ιn'sməreιtə] сміттєспалювальна піч
income ['mkəm] прибуток
income statement ['mkəm 'steιtmənt] звіт про прибуток incorporate [m'ko:pəreιt] об'єднуватися
indirect channels [jndι'rekt 'tjænlz] непряма, опосередкована си
стема
indirect trade [,ιnd('rekt trerd] непряма торгівля
induce [in'dju-s] спонукати; стимулювати inflation [m'fleijn] інфляція inflation rate [m'fleijn re it] темп інфляції
inflow ['ιnflou] приплив (грошей) influence ['ιnfluərιs] n вплив; v впливати
Influence the market ['ιnfluəns ðə 'mα:kιt] мати вплив на ринок infrastructure ['infrə'strAkt/ə] інфраструктура Injury ['meftəπ] ушкодження, травма in-kind transfer [ιn'kamd 'trænsfə:] допомога товарами
innovation [,mou'veιjn] нововведення, інновація innovative [jnou'veιtιv] здатний до нововведень, технічно про
гресивний
input ['mput] витрати insurance [in'Juərəns] страхування insure [m'juə] страхувати
integration [,mti'greijn] інтеграція; об'єднання interact [/tntər/ækt] взаємодіяти interchangeable [jntə'tjeτrκfeəbl] взаємозамінюваний
interest ['mtrιst] частка (пай); відсотковий прибуток, фіксований відсоток
intermediary [,mtə'mi:djəπ] посередник intermediate goods [,mtə'mi:djət gudz] напівфабрикати Internal funds [rn'tə:nl fλndz] внутрішні кошти
international market ['mtə'næjənl 'mα:kιt] міжнародний ринок international transaction [^ntə'næ/ənl træn'zækfn] міжнародна
угода
Inventory ['mvəntπ] інвентар, матеріально-виробничі запаси
invest [m'vest] вкладати гроші investment [ιn'vestmənt] капіталовкладення irrelevant [I'relivənt] недоречний; що не стосується справи
issue stock ['ιsju: stok] випускати акції Hems ['aιtəmz] товари labor resources ['leιbə n'so:siz] трудові ресурси lack of mobility [tæk əv mou'biliti] недостатня мобільність
law [b:] закон; юриспруденція
lawyer ['b:jə] юрист; адвокат; законодавець legal advice ['li:gəl əd'vaιs] юридична порада level ['levl] рівень levy ['levι] оподатковувати
liabilities [,laiəybiljtiz] пасив (балансу); борги, заборгованість limited liabilities [limitid,)aiə'bilitiz] обмежена юридична від
повідальність
link [lrJ}k] п зв'язок, кільце; v пов'язувати, з'єднувати living standard ['lιvιg 'stændəd] прожитковий рівень loan [loιιn] n позика, позичка; ^ позичати, давати у позику
long-term investment ['bŋtə:m m'vestmənt] довгостроковий вклад long-term loan ['bŋtə:m ϊoυn] довгострокова позика
loss-leader item ['bs'li:də 'aϊtəmz] товари, які продаються за низькими цінами (і^об залучити покупців)
losses ['bsιz] збитки lower [louə] знижувати; зменшувати

machinery [mə'/i:nəπ] машинне устаткування; машини; механізми
mail-order house ['meιl'o:də haus] посилторг
make a decision [meik ə di s 13n] приймати рішення make a loan to [meik ə loun tə] надавати позику комусь
make a right choice [meιk ə raιt tjois] зробити правильний вибір manufacture [,mænjιι 'fæktjə] л виробництво; v виробляти, виго
товляти, обробляти
market ['mα:kιt] л ринок; v продавати
market prices ['mα:kιt 'praιsιz] ринкові ціни
market shortage ['mα:kιt 'Jo:tidhj] дефіцит
marketing ['mækιtιŋ] продаж; збут; маркетинг
marketing research ['mα:kmŋ n'sə:tj] вивчення ринку збуту measurable ['me3ərəbl] вимірний
measure ['теза] вимірювати measures of economic activity ['mesəz əv ^:kə'nomιk ək'Uviti] заходи економічної діяльності
median income ['mi:djən 'mkəm] середній прибуток meet one's expences [mi:t wλπz iks'pensiz] задовольняти чиїсь ви
трати
merchandise ['mə:tj(ə)nda]z] товари; торгівля merchant wholesaler ['mə:tj(ə)nt 'hou^serlə] оптовий торговець,
оптовик
merger ['mə-ebə] об'єднання (підприємств)
microeconomics ['maιkrouj:kə'nomιks] мікроекономіка middleman ['πιιdlmæn] посередник mining industry ['такті} 'ιndλstπ] видобувна промисловість monetary policy ['тлшізп 'pshsι} грошова політика money illusion [тлпі ι'lu^n] грошова ілюзія mutual funds ['mju:tjuəl fлп d z] спільні фонди N
national income accounting ['næjənl 'mkəm ə'kauntiŋ] облік націо
нального доходу
need a lawyer [ni:d ə'b:jə] мати потребу в юристі negative Income tax [negətiv 'mkəm tæks] зменшення грошової
допомоги
negotiable [nι'gou/ϊəbl] оборотний
net assets [net 'æsets] вартість майна з відрахуванням зобов'язань net investment [net m'vestmənt] чистий вклад net national product (NNP) [net 'næjənl 'prodəkt] чистий націо
нальний продукт
net worth [netwə:θ] вартість майна; власний капітал підприємства new brand [njυ: braend] нова марка (товару) nominal income ['nomml 'ιnkəm] номінальний доход nominal GNP ['nnmml φi: ən pi:] номінальний валовий національний
продукт
nominal wage ['nomml weidj] номінальний заробіток
normalize ['n^məlaιz] нормалізувати note [nout] боргова розписка
O
objective [Db'dfeektiv] мета; завдання
offer ['ofəj пропонувати off-even pricing [of'i:vən 'praιsιo] ціна, що не доходить круглої
цифри
officer ['ofιsə] службова особа; службовець; службовець з числа керівного складу
official poverty line [o'fijl 'povətϊ lam] офіційна межа бідності оИ prospecting [oil pros'pekttŋ] видобування нафти opportunity [ppə'tju:nrtj] можливість, шанс opportunity costs [ppə'tju:mti kosts] збитки при невикористанні
альтернативного курсу; оптимальні витрати чи доходи
option ['op/ən] вибір; право заміни outflow ['aυtflou] відплив (грошей) outlet ['autlet] ринок збуту; торговельна точка
output ['autput] продуктивність; випуск продукції, виробництво outsell [auf'seϊ] продавати більше бід конкурентів over-all ['ouvəro:ŋ загальний, повний own [oun] володіти ownership I'ounəjip] власність P
packaging ['pækəefeιŋ] упаковка
partnership ['pα:tnəjφ] партнерство, товариство, компанія passbook ['pα:sbuk] банківська розрахункова книжка, депозитна
книжка; ощадна книжка
patent ['peιtənt} патент pay [peιj платити payment ('petmənt) виплата, оплата percentage [pə'senUcfeJ відсоток, процент perfect [pə'fekt] v удосконалювати, поліпшувати; ['pə:fιkt] ədj дос
коналий, точний
perform [pə'fo-m] виконувати peril ['peril] небезпека; ризик personal assets ['pə:snl 'æsets] приватне майно pervasive [pə:'veιsιv] поширений скрізь; той, що проникає pesticides ['pestιsaιds] пестициди
piece of advice [pi:s əv əd'vais] порада
pillar ['pιlə] опора
pollution [pə'lu:jn] забруднення portability [,po:tə'bilm] портативність position [pə'zrjn] становище; посада possess [pə'zes] володіти
2J7
R
raise the price [reiz ði prais] піднімати ціну
rate [reit] n розмір, норма; ставка, курс, такса; ціна, оцінка; темп, швидкість; пропорція, відсоток; коефіцієнт, показник, ступінь; місцевий податок, комунальний податок; v оподатковувати; підраховувати
ratio analysis ['reιjιou ð'næləsιs] аналіз коефіцієнті» ration ['ræjn] розподіляти; нормувати; видавати rational ['raefənlj раціональний
real estate [πəl rs'teit] нерухоме майно
real GHP [nəl <fei: ən pi:] реальний валовий національний продукт
real income [πəl 'rnkəm] реальний прибуток
real wage [rιəl werφ] реальний заробіток reasonable ['ri:məbl] поміркований; розважливий receipt [π'si:t] грошові надходження
recession [ri'sejn] падіння виробництва; зниження темпів reciprocal wants [π'sφrəkə! wonts] взаємні потреби record freko:d] n запис; документи, протокол; {π'ko:d] v запису
вати; реєструвати
recovery [n'kAvən] відновлення
red-tape ['red 'teιp] бюрократична канцелярська робота reduce [n'dju:s] скорочувати; зменшувати reimburse kri:ιm'bə:s] відшкодовувати reinvest ['ri:iiTvest] знову вкладати relationship [ri'leijnfip] відносини, стосунки
relative ['relətiv] відносний
relative price [Velənv prais] відносна ціна
rely (on, upon) [rrlaij покладатися; довіряти rent [rent] n рента; орендна плата; квартирна плата; v здавати в оренду; орендувати; давати напрокат
repair shop [rι'pεə jbpj майстерня report [ri'po:t] повідомляти; доповідати reputation [,repju:'teijn] репутація
request [n'kwesi] запит; виклик, заявка; попит; прохання resource [rι'so:s] ресурси
responsibility [nsspansə'biliti] відповідальність responsible for [ris'p:msəbi fo] відповідальний за restrict [ns'tnkt] обмежувати restriction [ris'tnkfn] обмеження resume ['rezju:meι] резюме; підсумок; висновок retailer [ri:'teιlə] роздрібний торговець
retailing [ri:'teιlιιj] роздрібний продаж
return [π'tə-n] n повернення; повернений товар; повернені чеки; прибуток; обіг; звіт; податкова декларація; v повертати; давати прибуток
revenue ('revτnju-] прибуток
reward [π'wo:d] заохочення, винагорода rivalry ['raιvəlπ] суперництво, конкуренція
run a risk [гдп ə rrsk] ризикувати S
safeguard ['seιfgα:d] n гарантія; охорона; охоронне свідоцтво; обережність; v гарантувати; охороняти
safety deposit box ['seιftr dι'pozιt boks) сейф дня депозитів, що
надається приватним особам у банку
salary ['sæləπ] заробітна плата sale [sell] продаж; збут; торгівля; торговельна угода; розпродаж
(за зниженими цінами), мн. товарообіг salesman {'seιlzmən] продавець satisfy ['sætιsfaι] задовольняти savings [ 'serviŋz] заощадження; накопичення
savings account ['seιvιŋz ə'kaunt] ощадний рахунок зі встановле
ним відсотком
scarce [skεəs] дефіцитний; рідкісний; недостатній scarcity ['skεəsιtι] недостатня кількість, брак (чогось)
schedule ['jedju:l] розробляти план
security [SJ'kjuənti] безпека; надійність; захист; гарантія, забезпечення, застава; довірена особа, мн. цінні папери
security exchange [si'kjuənU ikstjemds] фондова біржа
seller ['selə] продавець
service fsə:vis] послуга; обслуговування
service industry ['sə:vιs 'ιndəstπ] підприємства сфери обслугову
вання
set [set] встановлювати set the price [set ðə prais] визначати ціну
sewage ['sjιnife] стічні води; каналізація share [jεə] n частка, пай; v розподіляти, ділити
shareholder ['jεə,houldə] акціонер, власник акцій shift [jiU] п переміщення; перестановка; зміна; (робоча) зміна, робочий день; v переміщати, змінювати
shopping centre ['jDpiŋ'seniə] торговельний центр shopping guide ['jDPl9 9aid] довідник магазинів short-term loan ['Jo:t'tə:m loun] короткострокова позика significant [sjcj'mfjkənt] значний, істотний; характерний, показний; вірогідний; значущий
skill [skιŋ досвід society [sə'sarətι] суспільство; організація; об'єднання; асоціація; кооперативний союз, кооперативне товариство sole [soul] єдиний, виключний, одноосібний
sole proprietorship [soul prə'praiələ/ip] одноосібне володіння solution [sə'iu:Jn] вирішення, розв'язання
solve mathematical problems {sdIv,mæθι'mætιkəl 'ρrobləmz] роз
в'язувати математичні задачі source [sd:s] джерело
span [spæn] інтервал, період; тривалість specialize ['spejəϊaιz] спеціалізуватися
split [split] солодка страва
standard of living ['stændəd əv 'lιvιŋ] рівень життя state bank [steit bæŋk] державний банк; банк штату
statement ['steιtmənt] звіт
stepping-stone ['stepιŋstouπ] засіб для досягнення мети (для поліпшення становища)
stock [siokj акція
stock-broker ['stok,broukə] біржовий маклер stock certificate [stok sə'trfikit] акція
stockholder ['stokjiouldə] акціонер, власник акцій storage ['slo:πdj] зберігання
structural unemployment ['strAkt/ərəl 'Anirrt'pbimənt] структурне
безробіття
subjective [səb'cfeektiv] суб'єктивний subsidy ['sAbsidi] субсидія, дотація
substitute ['sAkbstitju:t] n заступник; заміна; v змінювати; заміщати sue [sju:] порушувати кримінальну справу supply [sə'plaι] n пропозиція; збут; постачання; v постачати surplus ['sə:pləs] лишок; активне сальдо switch (switj] перехід, переключення Т
take title to the goods придбати товар як власність
take advantage of smth. [teιk əd'vα:ntιe^] скористатися (чим-не будь)
tangible ['tæncfcəbl] відчутний; реальний tariff ['tæπf] тариф tax [tæks] податок
tax benefits [tæks 'benιfιts] пільги з обкладання податком toll ['tσul] додаткова плата за послуги; мито
total ['toutІ] підсумовувати total sale ['tout! seil] сукупний продаж track [træk] курс; keep track дотримуватися курсу trade [treid] торгівля; професія; ремесло
trade-in-allowance [treid in ə'iauəns] сума грошей, повернута за
crapy річ І внесена в рахунок придбання нової
trademark ['trerdrnα:k] торгова марка traffic ['træfιk] торгівля; транспорт: перевезення
transaction [træn'zækjn] справа, угода, ведення ділових операцій;
банківська операція
transfer ['træπsfə:] п передача {права власності); перехід (грошей); V [træns'fə:] передавати; переказувати
transportation costs ^traenspat'teijn kosts] транспортні витрати transporting [trsens'p^Ur)] транспортування
Treaty ['tri:tι] договір, конвекція; переговори trend [trend] тенденція; загальна спрямованість
true unemployment [tru- 'Anim'pbimənt] реальне безробіття U
ultimate consumer [41timit kən'sju:mə] кінцевий споживач unadequate [λn'ædιkwϊt] недостатній, що не відповідає умовам uncertainty [An'sə:tnti] невизначеність; непевність undermine kAndə'marn] підривати, руйнувати unemployment ['Anim'pbimənt] безробіття uniformity [ju:nι'fa:mιtι] незмінність, постійність unit of account ['ju:nιt əv ə'kaunt] одиниця обчислення unlimited liability [An'liimtid ylaiə'bilm] необмежена юридична
відповідальність
unreasonable price [An'ri:znəbl prais] нерозважлива ціна unsound [An'saund] безпідставний; ненадійний user ['ju-zə] споживач
utilities [ju:'tιhlιz] підприємства громадського користування; комунальні послуги

valuable ['væljuəbl] п pL цінності; коштовності; adj цінний; той,
що має грошову вартість; важливий, корисний
value ['vaelju:] п вартість; цінність; валюта; розмір, значення; важливість; V оцінювати
value added [vælju: 'ædιd] додаткова вартість
vending machine operator ['vendιŋ mə'Ji:n 'opəreιtə] оператор
торговельних апаратів
volume ['voljum] обсяг; кількість
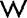
wage [weιdj] заробітна πnaτə; фонди заробітної плати warehousing ['wεəhauzιŋ] складування (товарів)
warranty ['worəntι] гарантія; порука waste [weιst] n безкорисна витрата, збитки; v витрачати марно wastes [weιsts] відходи wealth [welθ] багатство wear out [wcə aut] зношуватися
welfare ['welfeə] добробут; достаток
welfare programme ['weifeə 'prougraem] добродійна програма
well-being ['wel'bi:ιŋ] добробут wholesale unit ['houlseιl 'ju:nιt] об'єднання оптової торгівлі wholesaling ['houlseιlιŋ] оптова торгівля will [wil] бажання; сила волі; заповіт

yield [ji:ld] прибуток
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION 5
Lesson 1. What is Economics? 7






