«г≥дно з ординал≥стичною теор≥Їю споживач≥ прагнуть максим≥зувати загальну корисн≥сть, проте вони не можуть к≥льк≥сно обчислити корисн≥сть, а лише здатн≥ визначити, €к≥ товари (чи набори товар≥в) Ї дл€ них б≥льш корисними. якщо вони не можуть надати перевагу одному з набор≥в товар≥в, вважаЇтьс€, що ц≥ набори задовольн€ють потреби споживача однаковою м≥рою, тобто характеризуютьс€ однаковою корисн≥стю.
ќрдинал≥стська теор≥€ споживацького вибору ірунтуЇтьс€ на таких постулатах:
1. ћножинн≥сть вид≥в споживанн€. ожен споживач бажаЇ споживати безл≥ч р≥зноман≥тних ≥ндив≥дуальних благ.
2. Ќенасичен≥сть. —поживач прагне мати €комога б≥льшу к≥льк≥сть будь-€ких товар≥в ≥ послуг, в≥н не пересичуЇтьс€ жодним ≥з них. √ранична корисн≥сть ус≥х економ≥чних благ завжди позитивна.
3. “ранзитивн≥сть. “еор≥€ споживчого вибору виходить з≥ сталост≥ ≥ визначеноњ погодженост≥ смак≥в споживача. Ћог≥чно це може бути виражено в такий спос≥б: €кщо ј, ¬ ≥ — Ї комб≥нац≥€ми €кихось благ ≥ споживач байдужий у вибор≥ м≥ж наборами ј ≥ ¬ та м≥ж ¬ ≥ —, то в≥н також байдужий у вибор≥ м≥ж ј ≥ —.
4. —убституц≥€. —поживач згодний в≥дмовитис€ в≥д невеликоњ к≥лькост≥ певного блага, €кщо йому запропонують натом≥сть б≥льшу к≥льк≥сть блага-субститута. —убститути Ц це взаЇмозам≥ним≥ товари.
5. —падна гранична корисн≥сть. √ранична корисн≥сть кожноњ наступноњ одиниц≥ блага, що споживаЇтьс€, зменшуЇтьс€ в м≥ру його споживанн€.
ѕредставники ординал≥стськоњ теор≥њ розробили п≥дходи до анал≥зу повед≥нки споживач≥в без безпосереднього к≥льк≥сного вим≥рюванн€ корисност≥. ќсновними ≥нструментами, що використовуютьс€ в ц≥й теор≥њ, Ї граф≥ки бюджетних можливостей споживач≥в (бюджетн≥ л≥н≥њ) та крив≥ байдужост≥.
рива байдужост≥ (indifference curve) Ц граф≥к, на €кому представлен≥ р≥зн≥ комб≥нац≥њ двох економ≥чних благ, що мають однакову корисн≥сть дл€ споживача.
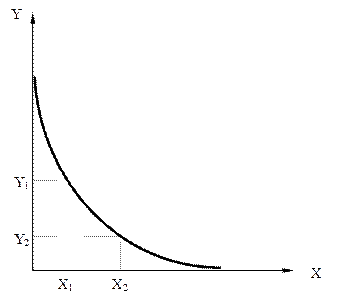
–ис. 2. рива байдужост≥
„им прав≥ше ≥ вище розм≥щена крива байдужост≥, тим б≥льшою корисн≥стю дл€ споживача характеризуютьс€ представлен≥ нею комб≥нац≥њ двох благ. ћножина кривих байдужост≥ називаЇтьс€ картою кривих байдужост≥ (рис. 3).
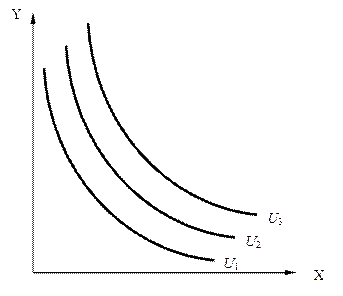
–ис. 3. арта кривих байдужост≥
рив≥ байдужост≥ мають в≥дТЇмний нахил, Ї опуклими в≥дносно початку координат ≥ н≥коли не перетинаютьс€ одна з одною. “ому через будь-€ку точку можна провести лише одну криву байдужост≥.
ƒл€ характеристики взаЇмозам≥нност≥ товар≥в на р≥зних в≥др≥зках кривоњ байдужост≥ використовуЇтьс€ пон€тт€ граничноњ норми зам≥щенн€ товар≥в.
√ранична норма зам≥щенн€ (marginal rate of substitution Ц MRS) Ц к≥льк≥сть, на €ку споживанн€ одного з двох благ маЇ бути зб≥льшене (чи зменшене), щоб ц≥лком компенсувати споживачу зменшенн€ (чи зб≥льшенн€) споживанн€ ≥ншого блага на одну додаткову (граничну) одиницю.
√ранична норма зам≥щенн€ товару X товаром Y визначаЇтьс€ за такою формулою:
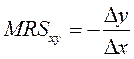 , або, €кщо розраховуЇтьс€ гранична норма зам≥щенн€ в певн≥й точц≥ кривоњ байдужост≥,
, або, €кщо розраховуЇтьс€ гранична норма зам≥щенн€ в певн≥й точц≥ кривоњ байдужост≥, 
якщо два товари Ї абсолютними зам≥нниками, гранична норма зам≥щенн€ Ї дл€ них сталою величиною, а крива байдужост≥ маЇ вигл€д пр€моњ л≥н≥њ. якщо товари доповнюють один одного в споживанн≥, то MRS = 0 ≥ крива байдужост≥ маЇ вигл€д пр€мого кута.
|
|
|
ƒл€ незалежних товар≥в гранична норма зам≥щенн€ зменшуЇтьс€ в м≥ру споживанн€ одного з товар≥в, що по€снюЇтьс€ законом спадноњ граничноњ корисност≥.
√ранична норма зам≥щенн€ може також трактуватис€ €к сп≥вв≥дношенн€ граничних корисностей благ. ѕрипустимо, що споживач в≥дмовл€Їтьс€ в≥д DY одиниць блага Y заради D’ одиниць блага ’. якщо корисн≥сть кожноњ одиниц≥ блага Y дор≥внюЇ MUY, а корисн≥сть кожноњ одиниц≥ блага ’ дор≥внюЇ MU’, то це означаЇ, що в≥н в≥дмовл€Їтьс€ в≥д обс€гу корисност≥ DYMUy ≥ одержуЇ додаткову корисн≥сть в обс€з≥ D’MU’. ќск≥льки споживач залишаЇтьс€ на т≥й сам≥й крив≥й байдужост≥, корисн≥сть обох набор≥в дл€ нього Ї однаковою:
DYMUy = − D’MU’, або 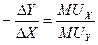 ,
,
оск≥льки 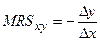 , то MRSxy =
, то MRSxy = 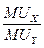 .
.
√ранична норма зам≥щенн€ Ї додатною величиною ≥ за абсолютним значенн€м дор≥внюЇ тангенсу кута нахилу кривоњ байдужост≥. ¬ ординал≥стськ≥й теор≥њ гранична норма зам≥щенн€ виконуЇ т≥ сам≥ функц≥њ, що й гранична корисн≥сть у кардинал≥стськ≥й теор≥њ.
Ѕюджетна л≥н≥€ (budget line)Ц граф≥к, на €кому зображен≥ комб≥нац≥њ двох економ≥чних благ, €к≥ можна придбати за певну суму грошей.
якщо ≤ Ц дох≥д споживача, ’ та Y Ц товари, на €к≥ витрачаЇтьс€ цей дох≥д, –х Ц ц≥на блага X, –y Ц ц≥на блага Y, то р≥вн€нн€ бюджетного обмеженн€ набуде вигл€ду:
≤ = –x’ + PyY,
або (у б≥льш звичному вигл€д≥)
Y = 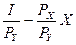 ,
,
де –x /–y Ц кутовий коеф≥ц≥Їнт, що вим≥рюЇ нахил бюджетноњ л≥н≥њ до ос≥ абсцис.
якщо ’ = 0, Y = ≤/Py, тобто весь дох≥д споживача витрачаЇтьс€ на благо Y. якщо Y = 0, X = ≤/Px. ѕоЇднавши точки максимального споживанн€ благ, отримуЇмо л≥н≥ю бюджетного обмеженн€ (budget constraint):

–ис. 4. Ѕюджетне обмеженн€
“очка дотику найвищоњ з доступних кривих байдужост≥ з бюджетним обмеженн€м визначаЇ стан р≥вноваги споживача (consumer equilibrium) (ситуац≥ю, коли в нього немаЇ стимул≥в зм≥нювати наб≥р спожитих благ, оск≥льки в≥н споживаЇ на найвищому р≥вн≥ корисност≥):
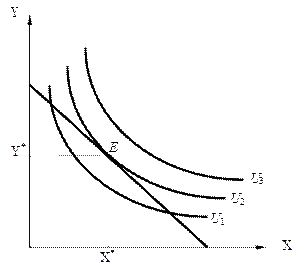
–ис. 5. –≥вновага споживача
√ранична норма зам≥щенн€ в стан≥ р≥вноваги споживача дор≥внюЇ тангенсу кута нахилу бюджетноњ л≥н≥њ:
MRSxy = 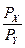 .
.
“еор≥€ попиту
ѕопит ≥ пропозиц≥€ Ї найб≥льш уживаними пон€тт€ми в м≥кроеконом≥ц≥. „ерез взаЇмод≥ю попиту ≥ пропозиц≥њ розкриваЇтьс€ д≥€ ринкового механ≥зму, њх анал≥з Ї ун≥версальним ≥нструментом досл≥дженн€ повед≥нки будь-€ких економ≥чних субТЇкт≥в.
ћ≥кроеконом≥ка досл≥джуЇ повед≥нку ц≥н у р≥зних умовах, ви€вл€Ї законом≥рност≥ ц≥Їњ повед≥нки п≥д впливом попиту ≥ пропозиц≥њ.
Ќа думку ј. ћаршала, можна з однаковим усп≥хом сперечатис€ про те, чим визначаЇтьс€ варт≥сть товару Ц корисн≥стю чи витратами виробництва, €к ≥ про те, €ким к≥нцем ножиць розр≥заЇтьс€ лист паперу. ¬≥дпов≥дно до його п≥дходу ц≥на товару визначаЇтьс€ €к факторами корисност≥ (через в≥дпов≥дний попит), так ≥ факторами витрат (через формуванн€ пропозиц≥њ товару).
ѕопит (demand) Ц це к≥льк≥сть (обс€г) товару чи послуги, €ку споживач≥ готов≥ (бажають та спроможн≥) придбати за кожного р≥вн€ ц≥н (за ≥нших однакових умов) у визначений пер≥од часу.
–озр≥зн€ють ≥ндив≥дуальний (individual demand) та ринковий (market demand) попит. ќстанн≥й Ї сумою ≥ндив≥дуальних попит≥в.
¬еличина попиту (quantity demanded) Ц це максимальна к≥льк≥сть товару, €ку погоджуютьс€ придбати споживач≥ за певною ц≥ною при певних умовах у певний час.
|
|
|
÷≥на попиту (demand price) Ц це найвища ц≥на, €ку згодн≥ заплатити споживач≥ за певну к≥льк≥сть товару.
ќбернена залежн≥сть м≥ж ц≥ною товару ≥ величиною попиту на нього називаЇтьс€ законом попиту (law of demand). ¬ основу закону попиту покладен≥:
1. ≈фект доходу (income effect) Ц при зниженн≥ ц≥ни товар≥в споживач≥, €ким не вистачало грошей на њх куп≥влю (чи на куп≥влю њх у б≥льш≥й к≥лькост≥), тепер можуть це зробити.
2. ≈фект зам≥ни (зам≥щенн€) (substitution effect) Ц при зниженн≥ ц≥ни товар≥в у споживач≥в зТ€вл€Їтьс€ бажанн€ придбати дешевш≥ товари зам≥сть аналог≥чних дорожчих.
3. «акон спадноњ граничноњ корисност≥ (law of diminishing marginal utility) стверджуЇ, що кожна наступна одиниц€ товару приносить споживачев≥ меншу корисн≥сть. ¬≥дпов≥дно, кожну наступну одиницю товару (зб≥льшуючи величину попиту) споживач≥ погод€тьс€ купувати за умови, що ц≥на товару зменшуватиметьс€.
≤снуЇ вин€ток ≥з закону попиту. ”перше на цей факт звернув увагу англ≥йський економ≥ст –оберт √≥ффен (1837Ц1910). ¬ивчаючи ц≥ноутворенн€ в ≤рланд≥њ, в≥н пом≥тив парадоксальне €вище. ѕ≥д час катастроф≥чного неврожаю картопл≥, що була основним продуктом харчуванн€ ≥рландських б≥дн€к≥в, при зб≥льшенн≥ ц≥ни товару попит на нього теж зб≥льшивс€. ÷ей факт по€снюЇтьс€ тим, що п≥д час неврожаю б≥дн€кам довелос€ в≥дмовитис€ в≥д р€ду ≥нших, б≥льш високо€к≥сних товар≥в (мТ€со, риба тощо) та споживати т≥льки картоплю. “овари, дл€ €ких закон попиту не виконуЇтьс€ (зазвичай це товари, що займають велику частку в бюджет≥ б≥дних споживач≥в), називаютьс€ товарами √≥ффена.
≤снують також соц≥альн≥ ефекти, €к≥ призвод€ть до специф≥чних нефункц≥ональних зм≥н попиту. ≈фект ¬еблена (названий за ≥мТ€м американського вченого “орстейна ¬еблена) описуЇ демонстративне споживанн€, коли ц≥на придбаного товару демонструЇ р≥вень доход≥в та статус (ел≥тн≥сть) покупц€. Ќаприклад, автомоб≥ль Ferrari або коштовност≥ De Beers. ≈фект сноба (на в≥дм≥ну в≥д ефекту приЇднанн€ до б≥льшост≥, чи, ≥ншими словами, ефекту насл≥дуванн€ (band wagon effect)), демонструЇ бажанн€ покупц€ купувати товари, €к≥ в≥др≥зн€ютьс€ в≥д товар≥в, €к≥ купують ≥нш≥ споживач≥.
√раф≥к попиту в≥дображаЇ залежн≥сть м≥ж ц≥ною та обс€гом попиту (рис 6).
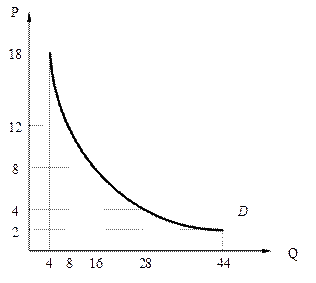
–ис. 6. рива попиту (demand curve)
√раф≥к ринкового попиту зазвичай Ї вв≥гнутим в≥дносно початку координат, оск≥льки становить суму ≥ндив≥дуальних попит≥в, к≥льк≥сть €ких зростаЇ при зменшенн≥ ц≥ни.
«алежн≥сть величини попиту в≥д фактор≥в, що њњ визначають, називаЇтьс€ функц≥Їю попиту (demand function). ѕерш за все величина попиту на товар визначаЇтьс€ його ц≥ною. јнал≥тичним способом л≥н≥йна функц≥€ попиту може бути записана таким чином:
Qd = f(P) = a Ц bp,
де P Ц ц≥на за одиницю товару;
Qd Ц величина попиту на товар;
а, b Ц константи, €к≥ в абсолютн≥й б≥льшост≥ випадк≥в Ї додатними
(a > 0, b > 0).
¬ економ≥ц≥ (на в≥дм≥ну в≥д традиц≥йноњ математики) незалежна зм≥нна зазвичай розм≥щуЇтьс€ на ос≥ ординат, тод≥ €к залежна Ц на ос≥ абсцис. ўо стосуЇтьс€ граф≥к≥в попиту, це повТ€зано з тим, що на початку розвитку теор≥њ ринкового попиту вчен≥ анал≥зували залежн≥сть ц≥ни попиту в≥д к≥лькост≥ товару, на€вного на ринку. ” сучасн≥й терм≥нолог≥њ так≥ функц≥њ називаютьс€ оберненими функц≥€ми попиту Pd = f(Q) (под≥бн≥ функц≥њ можна знайти в прац€х ј. ћаршалла). ѕ≥зн≥ше з метою розширенн€ анал≥зу незалежна ≥ залежна зм≥нн≥ пом≥н€лис€ м≥сц€ми, тод≥ €к граф≥чне зображенн€ залишилос€ незм≥нним.
ќск≥льки методолог≥чн≥ основи м≥кроеконом≥ки закладалис€ в англомовному середовищ≥, то базов≥ терм≥ни позначаютьс€ першими л≥терами в≥дпов≥дних сл≥в англ≥йськоњ мови. Ќаприклад: P(price) Ц ц≥на, Q(quantity) Ц к≥льк≥сть, D (demand) Ц попит.
ћожна вид≥лити основн≥ групи фактор≥в, що впливають на попит (детерм≥нанти попиту (determinants of demand)):
1. ≥льк≥сть споживач≥в.
2. ƒоходи споживач≥в.
3. Ќакопичене багатство.
|
|
|
4. —маки та уподобанн€ споживач≥в (субТЇктивн≥ фактори).
5. ÷≥ни на товари-зам≥нники (субститути) та доповнююч≥ (комплементарн≥) товари.
6. ÷≥нов≥ та деф≥цитн≥ оч≥куванн€ споживач≥в.
” загальному вигл€д≥ функц≥€ попиту Ї функц≥Їю вс≥х фактор≥в, що його визначають:
Qd = f (–, N, ≤, W, F, PS, PC, E),
де Qd Ц величина попиту;
P Ц ц≥на товару;
N Ц к≥льк≥сть споживач≥в;
≤ Ц доходи споживач≥в.
W Ц накопичене багатство;
F Ц смаки та уподобанн€ споживач≥в;
PS Ц ц≥ни на товари-зам≥нники (субститути) (substitute goods, substitutes);
PC Ц ц≥ни на товари-доповнювач≥ (комплементи) (complementary goods, complements);
E Ц ц≥нов≥ та деф≥цитн≥ оч≥куванн€.
” раз≥ зб≥льшенн≥ к≥лькост≥ споживач≥в, њхн≥х доход≥в та накопиченого багатства, зниженн€ ц≥н на доповнююч≥ товари ≥ п≥двищенн€ ц≥н на товари-зам≥нники, а також позитивних зм≥н в уподобанн€х, оч≥куванн€ п≥двищенн€ ц≥н чи деф≥циту попит на даний товар зростаЇ. ѕротилежна зм≥на фактор≥в зменшуЇ попит на товар.
«м≥на ц≥ни товару зумовлюЇ зм≥ни величини попиту (change in quantity demanded) ≥ в≥дображаЇтьс€ рухом уздовж кривоњ попиту, тод≥ €к зм≥на нец≥нових фактор≥в викликаЇ зм≥ни попиту (change in demand) ≥ зм≥щенн€ самого граф≥ка попиту. «б≥льшенн€ попиту на товар в≥дображаЇ зм≥щенн€ граф≥ка попиту праворуч-угору (зростанн€ величини попиту при кожному р≥вн≥ ц≥н), у раз≥ зменшенн€ попиту його граф≥к зм≥щуЇтьс€ л≥воруч-униз (зменшенн€ величини попиту при кожному р≥вн≥ ц≥н).
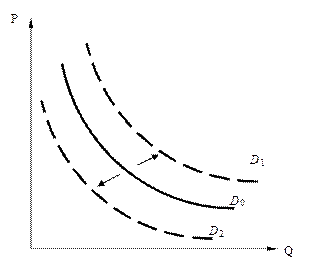
–ис. 7. «ростанн€ попиту (D 1) та зниженн€ попиту (D 2)
«алежно в≥д д≥њ закону попиту вс≥ товари можна под≥лити на нормальн≥ (normal goods) (€кщо закон попиту виконуЇтьс€) та товари √≥ффена (Giffen goods) (€кщо закон попиту не виконуЇтьс€).
«алежно в≥д реакц≥њ попиту на зм≥ну доход≥в споживача розр≥зн€ють товари вищоњ категор≥њ (попит на €к≥ зростаЇ в раз≥ зб≥льшенн€ доход≥в споживача) та товари нижчоњ категор≥њ (попит на €к≥ зменшуЇтьс€ в раз≥ зростанн€ доход≥в споживача).
“овари √≥ффена Ї товарами нижчоњ категор≥њ, на €к≥ малозабезпечен≥ споживач≥ витрачають значну частку свого бюджету. ѕроте не вс≥ товари нижчоњ категор≥њ Ї товарами √≥ффена.
ќск≥льки ≥снуЇ багато фактор≥в, що впливають на попит, то постаЇ питанн€ про ступ≥нь впливу кожного фактора на величину попиту. « ц≥Їю метою використовуютьс€ в≥дпов≥дн≥ показники (коеф≥ц≥Їнти) еластичност≥ попиту (elasticity of demand).
оеф≥ц≥Їнт еластичност≥ попиту за ц≥ною (coefficient of price elasticity of demand)показуЇ, на ск≥льки в≥дсотк≥в зм≥нитьс€ величина попиту в раз≥ зм≥ни ц≥ни товару на 1%. «агальна формула дл€ визначенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта ц≥новоњ еластичност≥
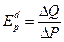 ,
,
де ≈dp Ц значенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта еластичност≥;
∆Q Ц зм≥на величини попиту, %;
∆– Ц зм≥на ц≥ни, %.
оеф≥ц≥Їнт еластичност≥ попиту за доходом (coefficient of income elasticity of demand)показуЇ, на ск≥льки в≥дсотк≥в зм≥нитьс€ величина попиту в раз≥ зм≥ни доходу споживача товару на 1%:
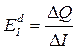 ,
,
де ≈dI Ц значенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта еластичност≥;
∆Q Ц зм≥на величини попиту, %;
∆≤ Ц зм≥на доходу, %.
оеф≥ц≥Їнт перехресноњ еластичност≥ попиту (coefficient of cross elasticity of demand)показуЇ, на ск≥льки в≥дсотк≥в зм≥нитьс€ величина попиту на товар ’ в раз≥ зм≥ни ц≥ни товару Y на 1%:
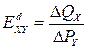 ,
,
де ≈dXY Ц значенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта еластичност≥;
∆QX Ц зм≥на величини попиту на товар ’, %;
∆PY Ц зм≥на ц≥ни на товар Y, %.
¬≥дсоткова зм≥на величин, €к≥ застосовуютьс€ при обчисленн≥ коеф≥ц≥Їнт≥в еластичност≥, використовуЇтьс€ дл€ приведенн€ у взаЇмну в≥дпов≥дн≥сть величин, що мають р≥зн≥ одиниц≥ вим≥ру (наприклад, ц≥ни вим≥рюютьс€ в грошових одиниц€х, тод≥ €к величина попиту Ц у натуральних).
якщо коеф≥ц≥Їнт еластичност≥ за модулем б≥льше одиниц≥, попит вважаЇтьс€ еластичним, €кщо менше одиниц≥ Ц нееластичним, €кщо ≈ = 1, це св≥дчить про те, що попит маЇ одиничну еластичн≥сть.
|
|
|
р≥м того, певну ≥нформац≥ю несе сам знак коеф≥ц≥Їнта еластичност≥: дл€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта ц≥новоњ еластичност≥ дл€ нормальних товар≥в в≥н маЇ знак ЂЦї, дл€ товар≥в √≥ффена Ц знак Ђ+ї. ƒодатне значенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта еластичност≥ попиту за доходом вказуЇ на товар вищоњ категор≥њ, в≥дТЇмне Ц на нижчу категор≥ю. ƒодатне значенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта перехресноњ еластичност≥ вказуЇ на взаЇмозам≥нн≥сть товар≥в, в≥дТЇмне Ц показуЇ, що товари доповнюють один одного в споживанн≥
Ќайб≥льш практичне застосуванн€ маЇ коеф≥ц≥Їнт еластичност≥ попиту за ц≥ною (дл€ б≥льш детального вивченн€ питанн€ див. рекомендовану л≥тературу.
√раф≥чне в≥дображенн€ еластичност≥ попиту наведене на рис. 8.
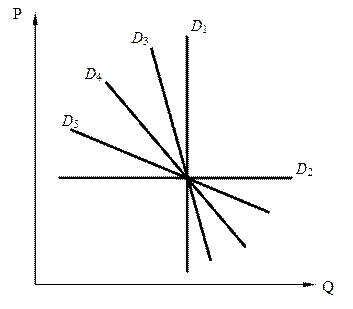
–ис. 8. ≈ластичн≥сть попиту
D 1 Ц абсолютно нееластичний попит (perfectly inelastic demand) (висока нагальн≥сть потреби), коеф≥ц≥Їнт ц≥новоњ еластичност≥ ≈ = 0.
D 2 Ц абсолютно еластичний попит (perfectly elastic demand) (будь-€ка к≥льк≥сть товару може бути продана за даною ц≥ною), ≈ = ∞.
D 3 Ц в≥дносно нееластичний попит (inelastic demand), ≈ < 1.
D 4Ц граф≥к попиту з одиничною еластичн≥стю (unit (or unitary) elastic demand), ≈ = 1.
D 5 Ц в≥дносно еластичний попит (elastic demand), ≈ > 1.
√раф≥чне в≥дображенн€ ц≥новоњ еластичност≥ попиту за допомогою л≥н≥йних функц≥й Ї умовним, оск≥льки п≥д час руху вздовж кривоњ попиту, заданоњ пр€мою л≥н≥Їю, еластичн≥сть попиту за ц≥ною зменшуЇтьс€ зверху вниз. “ому мову можна вести т≥льки про в≥дносно еластичний попит.
‘актори, що визначають ц≥нову еластичн≥сть попиту:
1. «ам≥нн≥сть товар≥в дл€ споживач≥в. „им вищий ступ≥нь зам≥нност≥ товару або послуги дл€ споживача, тим попит на товар або послугу еластичн≥ший.
2. Ѕагатофункц≥ональн≥сть товару Ц робить попит на нього б≥льш еластичним.
3. Ќагальн≥сть потреби Ц робить попит на товар б≥льш нееластичним.
4. „астка витрат на даний товар у бюджет≥ споживача. „им ц€ частка Ї вищою, тим б≥льша еластичн≥сть попиту на даний товар. якщо покупець витрачаЇ незначну частку свого бюджету, зм≥на ц≥н на даний товар мало впливаЇ на величину попиту.
5. ‘актор часу: чим б≥льший час, за €кий потр≥бно зробити покупку, тим б≥льш еластичним Ї попит на товар.
≤снуЇ звТ€зок м≥ж ц≥новою еластичн≥стю попиту та доходом в≥д реал≥зац≥њ продукц≥њ. якщо попит на товар нееластичний, а ц≥на на нього п≥двищуЇтьс€, то при цьому дох≥д в≥д реал≥зац≥њ (TR (total revenue)) зросте, ≥ навпаки.
якщо попит на товар еластичний, а ц≥на на нього зростаЇ, то при цьому дох≥д в≥д реал≥зац≥њ (TR) зменшитьс€, ≥ навпаки.
«а одиничноњ еластичност≥ попиту дох≥д в≥д реал≥зац≥њ залишаЇтьс€ незм≥нним за будь-€коњ зм≥ни ц≥ни.
“еор≥€ пропозиц≥њ
ѕропозиц≥€ (supply) Ц це к≥льк≥сть (обс€г) товару або послуги, €ку виробники готов≥ (бажають ≥ спроможн≥) поставити дл€ продажу на ринок при кожному р≥вн≥ ц≥н (за ≥нших однакових умов) у визначений пер≥од часу.
–озр≥зн€ють ≥ндив≥дуальну та ринкову пропозиц≥ю (individual and market supply). –инкова пропозиц≥€ Ї сумою ≥ндив≥дуальних пропозиц≥й виробник≥в.
¬еличина пропозиц≥њ (quantity supplied) Ц це максимальна к≥льк≥сть товару, €ку погоджуютьс€ виготовити виробники за певною ц≥ною за певних умов у певний час.
÷≥на пропозиц≥њ (supply price) Ц це найнижча ц≥на, за €ку виробники згодн≥ виробити певну к≥льк≥сть товару.
ѕр€ма залежн≥сть м≥ж ц≥ною товару ≥ величиною попиту на нього д≥стала назву закону пропозиц≥њ (law of supply).
ѕр€му залежн≥сть м≥ж ц≥ною та величиною пропозиц≥њ теоретично можна по€снити так:
1. ” раз≥ зростанн€ ц≥ни виробник може п≥двищити пропозиц≥ю даного товару шл€хом залученн€ незад≥€них ран≥ше малоефективних ресурс≥в. …ого втрати через використанн€ дорожчих технолог≥й, менш квал≥ф≥кованоњ робочоњ сили, дорожчих або менш €к≥сних природних ресурс≥в ≥ комплектуючих покриватимутьс€ завд€ки п≥двищенню ц≥ни товару.
2. ¬иробник, нарощуючи залученн€ моб≥льних ресурс≥в (робоча сила, сировина ≥ матер≥али, комплектуюч≥, ≥нструменти) з часом стикаЇтьс€ з проблемою нарощуванн€ стац≥онарних ресурс≥в. ¬ерстати, стац≥онарн≥ виробнич≥ площ≥ ви€вл€ютьс€ перевантаженими, унасл≥док чого ефективн≥сть виробництва знижуЇтьс€, а витрати на виробництво кожноњ наступноњ одиниц≥ зростають. ÷е зростанн€ можна покрити шл€хом п≥двищенн€ ц≥н.
√раф≥к пропозиц≥њ в≥дображаЇ залежн≥сть м≥ж ц≥ною та величиною пропозиц≥њ (рис. 9)
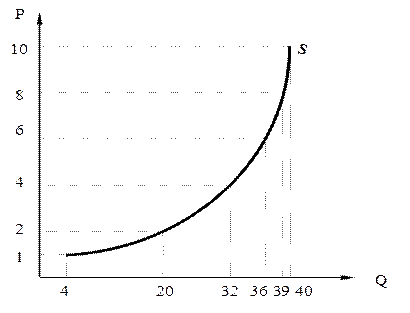
–ис. 9. √раф≥к пропозиц≥њ
«алежн≥сть величини пропозиц≥њ в≥д фактор≥в, що њњ визначають, називаЇтьс€ функц≥Їю пропозиц≥њ (supply function). јнал≥тичним способом л≥н≥йна функц≥€ пропозиц≥њ може бути записана за допомогою формули
|
|
|
Qs =f (P) = Ц с + dp,
де P Ц ц≥на за одиницю товару;
Qd Ц величина пропозиц≥њ товару;
c, d Ц додатн≥ константи (c > 0, d > 0).
ћожна вид≥лити так≥ основн≥ групи фактор≥в, що впливають на пропозиц≥ю (детерм≥нанти пропозиц≥њ):
1) к≥льк≥сть виробник≥в;
2) ц≥ни на виробнич≥ ресурси;
3) технолог≥€ виробництва;
4) природно-кл≥матичн≥ умови виробництва;
5) державн≥ податки та субсид≥њ;
6) ц≥нов≥ та деф≥цитн≥ оч≥куванн€ виробник≥в.
” загальному вигл€д≥ функц≥€ пропозиц≥њ Ї функц≥Їю вс≥х фактор≥в, що њњ визначають:
Qs = f (P, N, Pres, Tech, , T/S, E),
де Qs Ц величина пропозиц≥њ;
P Ц ц≥на товару;
N Ц к≥льк≥сть виробник≥в;
Pres Ц ц≥ни на ресурси;
Tech Ц р≥вень розвитку технолог≥њ;
K Ц вплив природно-кл≥матичних умов;
T/S Ц податки та субсид≥њ;
E Ц оч≥куванн€ виробник≥в.
” раз≥ зб≥льшенн€ к≥лькост≥ виробник≥в, зниженн€ ц≥н на доповнююч≥ товари, п≥двищенн€ ц≥н на ресурси, покращенн≥ технолог≥њ виробництва, позитивних зм≥нах природно-кл≥матичних умов, запровадженн€ державних субсид≥й, оч≥куванн€ зниженн€ ц≥н на попит пропозиц≥€ даного товару зростаЇ. ѕротилежна зм≥на фактор≥в зменшуЇ пропозиц≥ю на товар.
√раф≥чно зб≥льшенн€ пропозиц≥њ товару в≥дображаЇ зм≥щенн€ граф≥ка пропозиц≥њ праворуч-униз (зростанн€ величини пропозиц≥њ при кожному р≥вн≥ ц≥н), у раз≥ зменшенн€ пропозиц≥њ њњ граф≥к зм≥щуЇтьс€ л≥воруч-угору (зменшенн€ величини попиту при кожному р≥вн≥ ц≥н).
ƒл€ оц≥нки впливу р≥зних фактор≥в на величину пропозиц≥њ використовуЇтьс€ показник еластичност≥ пропозиц≥њ (elasticity of supply).Ќайб≥льш поширеним Ї показник ц≥новоњ еластичност≥ пропозиц≥њ, хоча практичне значенн€ маЇ анал≥з практично вс≥х фактор≥в (вплив зм≥ни податкового навантаженн€ чи ц≥н на ресурси).
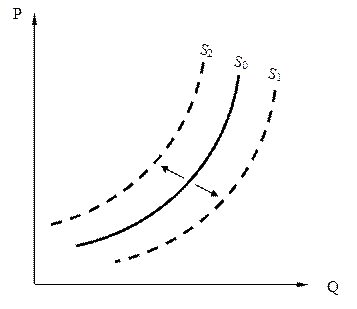
–ис. 10. «ростанн€ пропозиц≥њ (S 1) та зменшенн€ пропозиц≥њ (S 2)
оеф≥ц≥Їнт еластичност≥ пропозиц≥њ за ц≥ною (coefficient of price elasticity of supply) показуЇ, на ск≥льки в≥дсотк≥в зм≥нитьс€ величина пропозиц≥њ при зм≥н≥ ц≥ни товару на 1%. «агальна формула дл€ визначенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта ц≥новоњ еластичност≥ маЇ вигл€д:
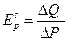 ,
,
де ≈sp Ц значенн€ коеф≥ц≥Їнта еластичност≥;
∆Q Ц зм≥на величини пропозиц≥њ, %;
∆– Ц зм≥на ц≥ни, %.
оеф≥ц≥Їнти еластичност≥ пропозиц≥њ на певному пром≥жку ц≥н (дугова еластичн≥сть) чи за даною ц≥ною (еластичн≥сть у точц≥) розраховуютьс€ за т≥Їю самою методикою, що й подан≥ вище коеф≥ц≥Їнти еластичност≥ попиту.
Ќа еластичн≥сть пропозиц≥њ впливають так≥ фактори:
1. „ас (дл€ детального вивченн€ питанн€ див. рекомендовану л≥тературу)
2. –≥вень дос€гнутого використанн€ ресурс≥в. ” раз≥ в≥дсутност≥ резерв≥в можливост≥ реагуванн€ пропозиц≥њ на зм≥ну ц≥н обмежен≥, тобто еластичн≥сть пропозиц≥њ товару буде меншою.
3. ¬исокий ступ≥нь монопол≥зац≥њ галуз≥ та незначн≥ можливост≥ переливанн€ кап≥талу з ≥нших галузей робл€ть пропозиц≥ю товару менш еластичною.
4. “ехнолог≥чн≥ особливост≥ виробництва певного товару. Ѕ≥льш складн≥ технолог≥њ виробництва робл€ть пропозиц≥ю товару менш еластичною. Ќаприклад, €кщо пор≥вн€ти буд≥вництво л≥так≥в та вип≥канн€ хл≥ба, то, безперечно, пропозиц≥€ хл≥ба буде б≥льш еластичною.
5. ÷≥ни на ≥нш≥ товари (мова йде про перехресну еластичн≥сть пропозиц≥њ). ” раз≥ п≥двищенн€ ц≥н на ресурси пропозиц≥€ основного товару зменшитьс€. ≈ластичн≥сть пропозиц≥њ товару залежатиме в≥д того, €к його виробництво реагуЇ на п≥двищенн€ ц≥н на ресурси.






