“ема є 1. Ђѕатофизиологическа€ характеристика воспалительных заболеваний мочевыделительной системы. ќбструктивные уропатии.
ѕатогенез мочевого синдромаї (3час).
÷ели зан€ти€:
Ј ‘ормирование знаний по этиологии и† патогенезу воспалительных заболеваний мочевыделительной системы
Ј —овершенствование практических навыков патофизиологического анализа клинико-лабораторных данных
Ј —овершенствование коммуникативных компетенций студентов
«адачи обучени€:
Ј —формировать знани€ по общим механизмам нарушений функции нефрона, этиологии и патогенезу мочевого синдрома, воспалительных заболеваний мочевыделительной системы.
Ј —овершенствовать практические навыки патофизиологического анализа клинико-лабораторных данных
Ј —овершенствовать коммуникативные навыки работы в группе при проведении дискуссии по вопросам темы зан€ти€
ќсновные вопросы темы:
1. ѕричины, вызывающие нарушени€ функций почек. Etiology of renal functions disorders каз вар добавить
2. ”величение и уменьшение клубочковой фильтрации, причины, механизмы развити€, последстви€.
3. Ќарушение канальциевой реабсорбции. “убулопатии, виды, причины, патогенез.
4. »зменени€ относительной плотности мочи (гипер-, гипо-, изостенури€), механизмы развити€.
5. ѕолиури€, олигури€ и анури€, виды по происхождению, механизмы развити€.(на казахском €зыке)
6. ачественные изменени€ состава мочи. ѕротеинури€,†††††††††††††††††††† цилиндрури€, гематури€, пиури€, механизмы развити€.
7. Ётиологи€ и патогенез обструктивных уропатий.
8. Ётиологи€ и патогенез воспалительных заболеваний почек на примере пиелонефритов
ћетоды обучени€ и преподавани€:

ƒискусси€ по вопросам темы, работа в малых группах, тестирование.
ѕрактическа€ работа
«адание є 1. «аполните таблицу ЂЁтиологи€ и патогенез
ѕиелонефритаї.
| Ќаиболее часта€ причина пиелонефрита | |
| ѕути проникновение инфекции | |
| ”риногенный путь проникновени€ инфекции | |
| √ематогенный путь проникновени€ инфекции | |
| ‘акторы, предрасполагающие к возникновению пиелонефрита | |
| ѕатогенез | |
| »зменени€ в крови | |
| ћочевой синдром |
«адание є 2 »спользу€ приведенный рисунок, назовите все возможные варианты формировани€ обструктивной уропатии
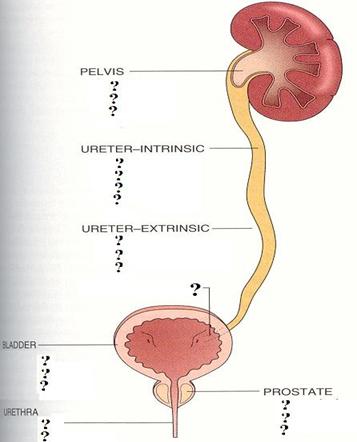 |
«адание є 3. ейс-стади
«адача є 1.
ќпишите представленные в задании данные медицинскими терминами. Ќа основании анализа данных сформулируйте заключение о форме патологии почек.
ƒиурез Ц 420 мл в сутки ѕлотность Ц 1011
Ѕелок Ц 2,0 г/л
≈диничные в поле зрени€ выщелоченные эритроциты √иалиновые, восковидные, зернистые цилиндры
јƒ Ц 175/95 мм рт.ст. ќстаточный азот Ц 190 мг%
«адача 2
Ѕольной ћ., 42 лет поступил в клинику с симптомами: температура тела 380—, боли, а по€снице. ќбщий анализ мочи: суточный диурез 2 л, моча мутна€. –еакци€ кисла€, относительна€ плотность 1020, белок 0,033%, эритроциты 2-3 в поле зрени€, лейкоциты Ц 20-30 в поле зрени€. ћного клеток Ўтернгеймера-ћальбина, эпителиальные клетки Ц 10-20, единичные зернистые цилиндры в поле зрени€, выраженна€ бактериури€.
|
|
|
1. ќ каком заболевании можно думать?
2. ”кажите этиологию и патогенез данного заболевани€
3. —делайте патофизиологический анализ клинико-лабораторных данных
4. ќбоснуйте принципы этитропной и патогенетической терапии
√лоссарий
| лиренс - объем плазмы, очищенный почками от какого- либо вещества в единицу времени C = (U/P) x V; — Ц клиренс; U - концентраци€ тест-вещества в моче; P - концентраци€ тест- вещества в плазме крови; V Ц величина минутного диуреза —корость†††††††††††† клубочковой фильтраци膆 у†† здорового человека††††† п††† клиренсу эндогенного креатинина | лиренс Ц уақыт б≥рл≥г≥нде қандай да б≥р заттан бүйректермен тазартылған плазманың көлем≥ C = (U/P) x V; — Ц клиренс; U - заттың несептег≥ мөлшер≥; P - заттың қан сары суындағы мөлшер≥; V Цминуттық диурезд≥ң көлем≥. ƒен≥ сау адамда эндогенд≥ креатинин клиренс≥ бойынша шумақтық††††††††††††††††††† сүз≥лу жылдамдығы 80 Ц 120 мл/мин құрайды. | Clearance Ц is the volume of plasma cleared from any substance per minute C = (U/P) x V; — Ц clearance;†††††† U†††††† - concentration of the test - substance in urine P - concentration of the test - substance in plasma of blood; V - minute diuresis составл€ет 80 Ц 120 мл/мин |
| “убулопати膆† - нарушение функции канальцев | “убулопати€лар Ц өзекшелер қызмет≥н≥ң бұзылыстары | Tubulopathy - impairment of tubular functions Ц |
| Cиндром де “они Ц ƒебре Ц ‘анкони - наследственна€ тубулопати€, обусловленна€ нарушением функции проксимальных канальцев почек, нарушена реабсорбци€ глюкозы, фосфатов, гидрокарбонатов. | де “они Ц ƒебре Ц‘анкони синдромы†††††† - бүйрект≥ң проксималды††††† өзекшелер≥ қызмет≥ бұзылуынан глюкоза, фосфат, гидрокарбонаттардың кер≥ с≥ң≥р≥лу≥ бұзылуымен сипатталатын тұқымқуатын тубулопати€. | FanconyТs syndrome - is inherited tubulopathy due to impaired function of proximal†††††††††††† tubules, decreased reabcorbtion of glucose, amino acids, phosphates, hydrocarbonates |
| Ќаследственный фосфатный почечны醆††††† диабет††††††† Ц наследственна€ тубулопати€, при которой нарушена реабсорбц舆†††††††† фосфатовЃ фосфатури€ и гипофосфатеми€; кальциури€,†††††††††††††††††††† рахит (гипофосфатемический вит.D резистентный) | “ұқымқуатын фосфаттық бүйрект≥к диабет Ц фосфаттың кер≥ с≥ң≥р≥лу≥ бұзылуы Ѓ фосфатури€ және гипофосфатеми€; кальциури€, рахит (гипофосфатеми€лық вит.D төз≥мд≥) дамуымен сипатталатын тұқымқуатын тубулопати€. | Inherited renal phosphate diabetes Ц is hereditary tubulopathy with reduced phosphate reabsorption Ѓ phosphaturia, hypophosphatemia, calciuria,††††††††††† rachitis, osteomalacia††††††††† (vitD resistant) |
| ѕолиури€ Ц увеличение диуреза более 2,0л | ѕолиури€ Ц диурезд≥ң 2,0л-ден артық көбею≥. | Polyuria - is increase †in diuresis (more than 2 liters) |
| ќлигури€ Ц снижение диуреза менее 500мл | ќлигури€ Ц диурезд≥ң 500мл- ден кем болуы | Oliguria - is reduction of daily diuresis less than 500ml |
| јнури€ Ц снижение диуреза менее 50мл | јнурри€ Ц диурезд≥ң 50мл-ден аз болуы | Anuria - absence of urine formation and urination (diuresis is less than 50 ml) |
| ѕоллакиур舆†††† Ц††††† частое мочеиспускание (при циститах, аденом円††††††† предстательной железы) | ѕоллакиури€ Ц зәрд≥ жи≥ шығару (қуық қабынуында, қуықасты†††††††††††††††††† без≥н≥ң аденомасында) | Pollakiuria Ц is frequent urination (at cystitis, prostate adenoma) |
| Ќиктур舆†††††† - увеличение выделени€ мочи в ночное врем€ (при заболевани€х почек и сердечно-сосудистой системы) | Ќиктури€ - түнге қарай зәр шығарудың артуы (бүйрек, жүрек-қантамыр††††††† жүйес≥ ауруларында) | Nocturia is predominant night diuresis (at renal diseases and heart failure) |
| ѕротеинури€ Ц белок моче | ѕротеинури€ Ц зәрде нәруыз болуы | Proteinuria Ц is protein in urine |
| —елективна€ протеинури€ - в моче альбумины и трансферрин, развиваетс€ вследствие потери отрицательног†††††††††† зар€да гломерул€рного фильтра | “алғамды протеинури€ Ц зәрде альбумин және трансферрин пайда болуы, шумақтық сүзг≥н≥ң тер≥с зар€ды жоғалуы салдарынан дамиды. | Selective proteinuria - is observed at loss of a negative charge by glomerular filter. There are albumins and transferrin in the urine |
| Ќеселективна€ протеинури€ развиваетс€††††††††††† вследствие увеличени€ проницаемости гломерул€рного фильтра, в моче нар€ду с альбуминами и трансферино솆†††† по€вл€ютс€ крупнодисперсные белки (IgG) | “алғамсы熆††††† протеинури€ шумақтық†††††††††††††††† сүзг≥н≥ң өтк≥зг≥шт≥г≥ артуынан дамиды, зәрде альбумин және трансферрин болуымен қатар ≥р≥ дисперст≥ нәруыздар (IgG) пайда болады. | Nonselective proteinuria is due †to†††††††††† increased permeability of glomerular filter, there are albumins, transferrin and high molecular proteins (IgG) in urine |
| √ематур舆†† Ц††† по€вление эритроцитов в моче | √ематур舆††††† Ц†††††† зәрде эритроциттерд≥ң пайда болуы | Hematuria -†††† means erythrocytes in urine |
| ѕиури€ Ц большое содержание лейкоцитов в моче (гной в моче), количество лейкоцитов более 200 в п/зр | ѕиур舆†††††††† Ц††††††††† зәрде лейкоциттерд≥ң көп мөлшерде (зәрде ≥р≥ң), лейкоциттер саны көру аймағында 200-ден артық кездесу≥ | Pyuria means pus in urine (number of leukocytes in urine more than 200under microscope) |
| √ипостенури€ - понижение относительной плотности мочи (менее 1010 во всех порци€х пробы «имницкого) | √ипостенури€ Ц зәрд≥ң салыстырмалы тығыздығы төмендеу≥ («имницкийд≥ң барлық сынауында 1010 Цден төмен) | Hyposthenuria†††††††††††† is decreased specific gravity of urine less than 1.010 in all portions of ZimnitzkyТs test |
| √иперстенури€ - повышение относительной плотности мочи | √иперстенури€ Ц зәрд≥ң салыстырмалы тығыздығы жоғарылауы | Hypersthenuria††††††††††† is increased specific gravity of urine (is observed at diabetes mellitus) |
| »зостенури€ - одинакова€ в течение суток относительна€ плотность мочи, равна€ плотности первичной мочи (1010 Ц1012), свидетельствует оᆆ††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† отсутствии концентрационной способности почек | »зостенури€ - тәул≥к бойына зәрд≥ң††††††††††† салыстырмалы тығыздығы†††††††† өзгермеген, алғашқы††††††††††††††††††††† зәрд≥ң тығыздығының б≥рдей болуы (1010 Ц1012), бүйрект≥ң қоюландыр󆆆††† қаб≥лет≥н≥ң жоқтығын мәл≥мдейд≥. | Isosthenuria is constant specific gravity and equal the specific gravity of the primary urine (ultrafiltrate) Ц††††† 1.010-††††† 1.012. Isosthenuria reflects the failure†††††† of††††† renal concentration ability |
Ћ»“≈–ј“”–ј:
|
|
|
† ќсновна€
|
|
|
1. ѕатофизиологи€: ”чебник дл€ мед.вузов под/ред ¬.¬. Ќовицкого и ≈.ƒ. √ольдберга ќ.». ”разовой- ћ.: √Ёќ“ј–-ћ≈ƒ, т.2, 2013.-—.460-467
2. ѕатофизиологи€: ”чебник под/ред Ћитвицкого ѕ.‘.Цћ.: √эотар-ћеди€. - 2010.-—. 428 - 432
† ƒополнительна€
3. ѕатофизиологи€ в схемах и таблицах: урс лекций: ”чебное пособие. ѕод ред. ј.Ќ.Ќурмухамбетова. Ц јлматы: ≥тап, 2004. Ц —. 212 Ц 221
4. ƒжеймс ј. Ўейман. ѕатофизиологи€ почки. ћ. Ц—ѕб: изд-во Ѕ»Ќќћ, 2002.- 206с
5. V.Kumar, A. Abbas, J. C. Aster. Pathologic basis of disease/Elsevier.- 2015.- Ch.20
онтроль (тестовые задани€)
¬арианты тестовых заданий составлены на основе сборника Ђ“естовые задани€ по патологической физиологииї./под ред “.ѕ. ”дарцевой и Ќ.Ќ. –ыспековой. -јлматы, 2007.-—. 400-414
“ема є 2. Ђѕатофизиологическа€ характеристика отдельных форм патологии почек (острые и хронические гломерулонефриты,
нефротический синдром)ї. (3 час)
÷ель зан€ти€:
‘ормирование знаний по этиологии и патогенезу гломерулонефритов, нефротического †синдрома,††††† совершенствование коммуникативных компетенций студентов, совершенствование практических навыков патофизиологического анализа клинико-лабораторных данных
«адачи обучени€:
Ј —формировать знани€ по этиологии и патогенезу острых и хронических гломерулонефритов, нефротическому синдрому.
Ј —овершенствовать практические навыки патофизиологического анализа клинико-лабораторных данных
Ј —овершенствовать коммуникативные навыки работы в группе при проведении дискуссии по вопросам темы зан€ти€
ќсновные вопросы темы:
1. ѕатогенез повреждени€ клубочков почек
2. Ќефротический синдром, пон€тие, патогенез
3. Ётиологи€ и патогенез острого гломерулонефрита
4. Ётиологи€ и патогенез хронического гломерулонефрита. Etiology and pathogenesis of chronic glomerulonephritis. (на казахском €зыке)
5. »зменени€ в крови и моче при гломерулонефрите.
6. ѕатогенез клинических про€влений при гломерулонефритах (отеки, повышение јƒ, анеми€ и др.)
.ћетоды обучени€ и преподавани€:
ƒискусси€ по вопросам темы, работа в малых группах, заполнение схем патогенеза, кейс-стади, тестирование.
ѕрактическа€ работа
«адание є 1. —оставить схему патогенеза иммунного повреждени€ фильтрующей мембраны клубочков почек.
ќтразить характер антигена, локализацию комплексов антиген+антитело, основные медиаторы, механизм повреждени€ фильтрующей мембраны
1. »ммуннокомплексный механизм повреждени€
2. ÷итотоксический механизм повреждени€
3. леточно-опосредованный механизм повреждени€
«адание є 2 ейс-стади
«адача є 1
ѕациенту Ќ 2 года назад был поставлен диагноз Ђострый диффузный гломерулонефритї. ¬ насто€щее врем€ отмечаютс€ слабость, головные боли, головокружение, слабовыраженные отеки.
јнализ мочи:
ѕлотность 1008, белок - 0,2%, единичные эритроциты в поле зрени€, гиалиновые цилиндры в малом количестве. —уточный диурез Ц 3100 мл.
јнализ крови:
ќстаточный азот 90 ммоль/л, общий белок 59г/л (норма 65-85г/л), клиренс эндогенного креатинина Ц 40 мл/мин (90-170 мл/мин)
јƒ Ц 180/100 мм рт.ст.
1. Ќе противоречит ли наличие полиурии диагнозу Ђострый гломерулонефритї, поставленному 2 года назад?
2. аковы механизмы развити€ полиурии и гипостенурии в данной ситуации?
3. аково значение развившейс€ у больного полиурии?
«адача є 2
” пациентки . 22 года через 2 нед после перенесЄнной в т€жЄлой форме ангины по€вились боли в области по€сницы, одышка, сердцебиение, головна€ боль. «а 4 дн€ прибавила в весе на 5 кг. ќбъективно: лицо бледное; веки мешкообразные и вздуты, глазные щели сужены, голени и стопы пастозны, границы сердца расширены, јƒ 140/95 мм рт.ст., диурез резко снижен, в моче в большом количестве эритроциты, лейкоциты, зернистые цилиндры, высокое содержание белка. ¬ крови повышены титры антистрептолизина ќ и антигиалуронидазы.
|
|
|
1. ќ каком заболевании можно думать у данной больной
2. ¬ чЄм причина и каковы механизмы нарушени€ функции почек? ѕриведите доказательства ¬ашей версии.
3. аковы механизмы каждого из симптомов, имеющихс€ у пациентки? „то привело к развитию гипергидратации: снижение экскреторной функции почек и/или внепочечные механизмы задержки жидкости в организме? ќтвет обоснуйте.
«адача є 3
” больного, 40 лет с хроническим гломерулонефритом на рентгенограмме вы€влен обширный остеопороз. артина деминерализации костей напоминает рахит. Ќазначение больному витамина ƒ не принесло желаемого результата
1. аков механизм наблюдаемых изменений костной ткани?
2. ќбъ€снить резистентность к витамину ƒ (Ќарушение образовани€ активной формы витамина ƒ -1, 25 (ќЌ)2ƒ3
«адача є 4

” больного стойкое повышение јƒ, жалобы на головные боли, нарушение зрени€. јƒ 190/110 мм рт.ст.; „—— 110 в мин.; отеки на лице под глазами по утрам. ¬ периферической крови: эритроциты-3,2х1012/л, гемоглобин
Ц 105 г/л, ретикулоциты Ц 0,02%:, лейкоциты -5,6х109/л. ¬ плазме крови: общий белок Ц 56г/л, альбумины Ц 16г/л (норма 40-50 г/л), глобулины Ц 40 г/л (норма 20-30 г/л), остаточный азот Ц 39 ммоль/л, мочевина Ц 11,4 ммоль/л (норма 3,3-
8,3 ммоль/л), креатинин 14 мг/л (норма 12-14 мг/л).
–еакци€ мочи кисла€, концентраци€ белка 0,85 г/л, реакци€ на сахар отрицательна€. ѕри микроскопии осадка: эритроциты 2-3 в поле зрени€, гиалиновые цилиндры 7-9 в поле зрени€. ƒиурез 1000мл
1. ќ чем свидетельствуют качественные изменени€ мочи у данного больного?
2. ќ чем свидетельствуют изменение биохимических показателей крови?
3. аков патогенез гипертензии и анемии у данного больного?
4. —делайте общее заключение по задаче.
√лоссарий
| √ломерулонефриты - группа | √ломерулонефриттер Ц ≈к≥ | Glomerulonephritis Ц |
| заболеваний, | (қос) бүйрект≥ңде | are the group of diseases |
| характеризующихс€ развитием | шумақтарының қабынуымен | in the heart of which are |
| воспалени€ клубочков обеих | дамитын б≥р топ аурулар. | inflammatory processes |
| почек | in both kidneys | |
| јнтистрептолизинЦјSO, анти- | јнтистрептолизин ЦASO, | Antistreptolysin Ц |
| ƒЌ -аза, | анти-ƒЌ -аза, | ASO, antiDNA-ase, |
| антигиалуронидаз Ц антитела | јнтигиалуронидаз Ц жедел | antihyaluronidaseЦ are |
| против антигенов стрептококков, | стрептококт≥к | antibodies against |
| обнаруживаютс€ | гломерулонефритте байқалатын | streptococci at acute |
| при остром | антигенге қарсы антидене | poststreptococcal |
| постстрептококковом | glomerulonephritis | |
| гломерулонефрите | ||
| ѕиелонефрит Ц | ѕиелонефрит Ц Ѕүйрект≥ң | Pyelonephritis is a |
| неспецифическое инфекционное | нег≥з≥нен ми қабатында | nonspecific infection |
| воспаление почечной лоханки с | бүйрект≥ң интерстици€лық | inflammation affecting |
| системой чашечеки | т≥ндер≥нде, бүйрект≥ң | the tubules, interstitium, |
| интерстициальной ткани почки, | тостағандары мен түбектер≥нде | and renal pelvis and is |
| преимущественно в области | дамитын бейспецификалық | one of the most common |
| мозгового сло€ | жұқпалы үрд≥с. | diseases of the kidney. |
| Ќефротический синдром - | Ќефроздық синдром Цкөптеген | Nephrotic syndrome |
| симптомокомплекс, | ≥с≥нулер, шырышты қуыстарда | means complex of |
| характеризующийс€ массивной | судың жиналуымен және | symptoms with massive |
| протеинурией (более 3 гвсутки), | көлемд≥ протеинури€мен | proteinuria, |
| гипо-и диспротеинемией, | (тәул≥г≥не 3 г жоғары), гипо- | hypoalbuminemia, with |
| гиперлипидемией, | диспротеинеми€лармен, | plasma albumin levels |
| гиперхолестеринемией, | гиперлипидеми€лармен, | less than 3 g/dl. |
| распространенными отеками и | гиперхолестеринеми€лармен | generalized edema, |
| вод€нкой серозных полостей | сипатталатын симптомдық | hyperlipidemia and |
| кешен. | lipiduria | |
| ’роническа€ почечна€ | Ѕүйрект≥ң созылмалы | Chronic renal failure is |
| недостаточность (’ѕЌ) - | жетк≥л≥кс≥зд≥г≥(Ѕ—∆) Ц бүйрек | progressive and |
| прогрессирующее уменьшение | қызмет≥н≥ң үдемел≥ | irreversible deterioration |
| функций почек | жетк≥л≥кс≥зд≥г≥. | of renal function due to |
| slow destruction of renal | ||
| parenchyma | ||
| ”реми€ (от греч. uron Цмоча, | ”реми€ Ц (грекше uron - несеп, | Uremia (uremic |
| haima - кровь) Ц мочекровие, | зәр, haimaЦ қан) Ц несеп қанды, | syndrome) (from Greek. |
| синдром, возникающий при | бұл синдром бүйрек қызмет≥н≥ң | Uron- urine, haima - |
| декомпенсации функций почек | декомпенсаци€лық кезең≥нде | blood) Ц urine in |
| дамиды. | blood.End-stage kidney. | |
| Syndrome of | ||
| decompensated renal | ||
| failure |
Ћ»“≈–ј“”–ј:
|
|
|
† ќсновна€
6. ѕатофизиологи€: ”чебник дл€ мед.вузов под/ред ¬.¬. Ќовицкого и ≈.ƒ. √ольдберга ќ.». ”разовой- ћ.: √Ёќ“ј–-ћ≈ƒ, т.2, 2013.-—.460-467
7. ѕатофизиологи€: ”чебник под/ред Ћитвицкого ѕ.‘.Цћ.: √эотар-ћеди€. - 2010.-—. 428 - 432
† ƒополнительна€
8. ѕатофизиологи€ в схемах и таблицах: урс лекций: ”чебное пособие. ѕод ред. ј.Ќ.Ќурмухамбетова. Ц јлматы: ≥тап, 2004. Ц —. 212 Ц 221
9. ƒжеймс ј. Ўейман. ѕатофизиологи€ почки. ћ. Ц—ѕб: изд-во Ѕ»Ќќћ, 2002.- 206с
10.V.Kumar, A. Abbas, J. C. Aster. Pathologic basis of disease/Elsevier.- 2015.- Ch.20
онтроль (тестовые задани€)
¬арианты тестовых заданий составлены на основе сборника Ђ“естовые задани€ по патологической физиологииї./под ред “.ѕ. ”дарцевой и Ќ.Ќ. –ыспековой. -јлматы, 2007.-—. 400-414






