“ема є 1. Ђѕатофизиологи€ воспалительных и дистрофических поражений опорно-двигательного аппарата и кожиї.
. ÷≈Ћ№ зан€ти€:
‘ормирование †знаний †п†††† патофизиологии опорно-двигательной системы, практических навыков интерпретации клинико-лабораторных данных при решении ситуационных задач по патологии опорно-двигательной системы, совершенствование коммуникативных навыков общени€ в группе, навыков самосовершенствовани€.
.«адачи обучени€:
ü —формирование знание этиологии и патогенеза основных симптомов и синдромов поражени€ опорно-двигательной системы, кожи и придатков кожи
ü сформировать практические навыки интерпретации клинико-лабораторных данных при заболевани€х опорно-двигательной системы и кожи
ü развивать коммуникативные навыки ведени€ дискуссии при разборе теоретического материала
ü развивать навыки самосто€тельной работы с научной, учебной и справочной литературой, сайтами интернета при подготовке к зан€ти€м и —–— по предложенным и инициативным темам
.ќсновные вопросы темы:
1. Ётиологи€ и патогенез нарушений развити€ костной ткани. —үйек т≥н≥ дамуы бұзылысының этиологи€сы және патогенез≥. Etiology and pathogenesis of disorders of bone development (вопрос разбираетс€ на трех €зыках по выбору студентов)
2. Ќарушение регул€ции активности остеогенных клеток. –оль обмена кальци€ и фосфора в патогенезе остеопороза и остеомал€ций.
3. “иповые нарушени€ опорно-двигательного аппарата. ќстеопатии, пон€тие, виды, этиологи€, патогенез. ѕон€тие о болезни –еклингаузена, ѕеджета, несовершенном остеогенезе
4. ¬оспалительные и дегенеративные изменени€ суставов (артропатии). ѕон€тие об артритах и артрозах, этиологи€, механизмы развити€. ѕон€тие о ревматоидном артрите.
5. ќбща€ этиологи€ заболеваний кожи. ¬заимосв€зь местных и общих факторов в патогенезе заболеваний кожи.
.ћетоды обучени€ и преподавани€:
ƒискусси€ по вопросам темы, работа в малых группах: кейс-стади, заполнение Ђнемыхї таблиц, схем патогенеза; тестирование
ѕрактическа€ работа
«адание є 1.†††† «аполнить† таблицу,† указать† патогенез† наиболее† часто встречающихс€ остеопатий
| Ќаследственно-обусловленные | |
| јхондроплази€ | |

| Ќесовершенный остеогенез | |
| —индром ћарфана | |
| –ахитоподобные заболевани€ | |
| ѕриобретенные | |
| —тарческие | |
| јлиментарные | |
| √ормональные | |
| Ќефрогенные | |
| ¬оспалительные | |
јртропатии
- повреждени€ суставов, характеризующиес€ альтерацией хр€щевых суставных поверхностей, синовиальных оболочек и утратой интегративной функции поддерживающих структур суставов.
| ¬ид нарушени€ | ѕатогенез |
| јртроз - первичный дегенеративный процесс в пределах гиалинового хр€ща 1. ѕервичный (идиопатический) 2. ¬торичный (в результате системных заболеваний Ц сахарный диабет, гемохроматоз, ожирение) | |
| јртрит Ц воспалительные заболевани€ суставов |
|
|
|
«адание є 2.†† ейс-стади
«адача є 1
¬ поликлинику обратилась пациентка –. 45 лет с жалобами на умеренные боли в суставах кистей и лучезап€стных суставах обеих рук, их припухлость и ощущение скованности по утрам. Ѕоли возникают чаще при движени€х. роме того, больную беспоко€т повышение температуры до 37,5 Ц 38,0˚ по вечерам, сердцебиение, одышка при физической нагрузке, слабость, недомогание, похудание. »з анамнеза вы€снено, что боли в суставах беспоко€т последние 3 мес€ца, когда перенесла острую респираторно-вирусную инфекцию. ѕовышение температуры, сердцебиение, похудание стала замечать в течение мес€ца.“огда же стала отмечать припухлость и скованность в суставах кистей. Ќе лечилась. –одители умерли в преклонном возрасте, но пациентка отмечает, что мать часто жаловалась на боли в суставах рук и ног.
ƒанные обследовани€: –ост Ц 168 см, вес - 48 кг, “емпература Ц 37,6; јƒ Ц 90/60 мм.рт.ст.,
ѕульс - 100/мин, „ƒ - 20/мин. остно-мышечна€ система: проксимальные
межфаланговые, п€стно-фаланговые и лучезап€стные суставы обеих кистей припухые, умеренно деформированы, кожа гиперемирована, движени€ несколько ограничены из-за болей. ѕальцы рук имеют веретенообразный вид. ќтмечаетс€ умеренна€ атрофи€ мышц кистей и подкожные узелки на разгибательной поверхности локтевых суставов.
јнализ крови:

Ёритроциты 3,0 х1012
√емоглобин 100 г/л
÷ветовой показатель 0,8
Ћейкоциты††††††† 10,0 х 109 /л
Ёозинофилы††††† 3, 0 %, ѕалочко€дерные 8 %; с/€ - 67 %
Ћимфоциты†††††† 18 %; ћоноциты - 4 %
–етикулоциты†† 5 Й †; †“ромбоциты††††† 240 х109 /л; —ќЁ -35 мм/час ¬ мазке - гипохроми€ - ++;
Ѕиохимические анализы крови: —-реактивный белок† +++
ѕротеинограмма
норма
ќбщий белоꆆ†††††††††††††† 50 г/놆††††††††††††††††††† 65 Ц 85 г/л
јльбумины††††††††††††††††††† 30 г/놆†††††††††††††††††††† 40 - 50 г/л
√лобулины†††††††††††††††††††† 42 г/놆†††††††††††††††††††† 30 - 40 г/л
‘ибриноге톆††††††††††††††††† 6 г/놆†††††††††††††††††††††† 2 - 4 г/л
»нструментальные исследовани€
–езультаты инструментальных исследований: Ќа рентгенограмме остеопороз суставных концов костей составл€ющих п€стно Ц фаланговые суставы. раевые узуры в головке III Ц п€стной кости и в основании проксимальной фаланги II Ц пальца правой кисти. «аметное сужение суставной щели п€стно-фаланговых суставов II Ц и III- пальце правой кисти.
1. ќ каком заболевании можно думать?
2. ќбъ€сните этиологию и патогенез заболевани€.
3. ƒайте патофизиологический анализ клинических про€влений.
4. ƒайте патофизиологический анализ лабораторных данных
«адача є 2
–ебенок 2 лет доставлен в приемный покой больницы с переломом плечевой кости. ѕри исследовании обнаружены Ђстарыеї переломы ребер, деформаци€ костей, разболтанность суставов, изменение формы зубов Ђ€нтарные зубыї, Ђголубыеї склеры, нарушение костей среднего и внутреннего уха, глухота.
1. ќ каком заболевании можно думать?
2. какой группе остеопатий по этиологии относитс€ это заболевание? ѕриведите примеры других заболеваний этой же группы?
3. ќбъ€сните патогенез повреждени€ костной ткани у данного больного.
«адача є 3
Ѕольна€ ћ., 65 лет длительное врем€ наблюдалась у врача по поводу мочекаменной болезни. Ќа рентгенограмме костной ткани отмечены фиброзные изменени€. –езорбци€ костной ткани превышает остеосинтез. ѕоставлен диагноз первичный гиперпаратиреоз (болезнь –еклингаузена)
|
|
|
1. ак изменитс€ концентраци€ паратгормона, кальци€, фосфатов в крови больной?
2. ќбъ€сните патогенез изменений костной ткани.
3. ќбъ€сните патогенез образовани€ камней в почках.
«адача є 4
Ѕольной ћ., 35 лет обратилс€ к врачу с жалобами на зуд кожи в межпальцевых складках, на сгибательной поверхности лучезап€стных суставов, снижение работоспособности,

нарушение сна. ѕри осмотре обнаружено (см. рисунок): извилистые ходы, по ходу которых отмечаютс€ расчесы, покрытые чешуйками и корочками. ¬еро€тнее всего у больного:
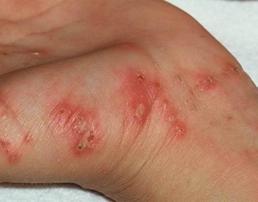
A) контактный дерматит
B) волчаночный дерматит
C) крапивница
D) пиодерми€
E) чесотка
«адача є5.
¬ детское отделение поступил больной ќ., 3 лет. ѕри осмотре наблюдаетс€ шатка€
Ђутина€ї походка, адинами€, низкорослость, ќ-образное искривление голеней. —о слов родителей ребенок родилс€ в срок, роды протекали нормально. ѕервые признаки
заболевани€ начали про€вл€тьс€ с двухлетнего возраста. ”частковым врачом был поставлен диагноз рахит и назначен витамин ƒ, но эффекта от лечени€ не было. ѕри обследовании обнаружено: незначительна€ гипокальциеми€, выраженна€ гипофосфатеми€, повышенна€ активность щелочной фосфатазы, уровень l,25(OH)2D3 крови снижен, фосфатури€
1. ќ каком заболевании можно думать?
2. ќбъ€сните этиологию и патогенез вы€вленного заболевани€.
3. ƒайте патофизиологический анализ клинико-лабораторных данных
«адача є 6
Ќа прием к дерматологу обратилс€ пациент ј., 24 года, с жалобами на по€вление сыпи на коже кистей. –аботает стоматологом один год. ѕодобна€ сыпь, но менее выраженна€, была шесть мес€цев назад. ѕосле смазывани€ ее преднизолоновой мазью быстро исчезла. ¬рач поставил диагноз: аллергический контактный дерматит.
1. ћожет ли возникновение сыпи быть св€зано с профессиональной де€тельностью пациента?
2. ѕочему после применени€ преднизолоновой мази сыпь исчезла?
3. какому типу аллергических реакций (ƒжелл и умбс) относитс€ аллергический контактный дерматит?
4. аков патогенез этого дерматита?
 √лоссарий
√лоссарий
| –емоделирование костной ткани Ц непрерывный процесс перестройки костной ткани: резорбци и образовани€ костной ткани | —үйек т≥ндер≥н қайта үлг≥леу - сүйек т≥ндер≥н≥ң үзд≥кс≥з қайта құрылу үрд≥с≥: сорып алу және сүйек т≥н≥ түз≥лу≥ | Remodeling of bone tissue is the breakdown and renewal of bone that are responsible for skeletal maintenance | |||
| –езорбци€ кости Ц | —үйект≥ң | кер≥ | сорылуы | Ц | †Resorbtion Ц is the process of |
| растворение минерального компонента кости и гидролиз органического матрикса | сүйект≥ң минералдық құрам бөл≥г≥н≥ң††††† еру≥††††† және органикалық†††††† матрикс≥н гидролиздеу | mineral†† component†††††††††††††† and organic matrix breakdown |
| ќстеоид Ц неминерализованный межклеточный органический матрикс кости | ќстеоид -†††††††††††††† сүйект≥ң минералданбаған жасуша аралық органикалық матрикс≥ | Osteoid Ц is nonmineralyzed intercellular organic matrix of the bone |
| ќстеопатии (греч. osteon Ц кость + patos- страдание, болезнь) Ц любые поражени€ костной системы без уточнени€ их характера | ќстеопати€лар (грек сөз≥нен Osteon-сүйек + patos- азап шегу, ауру) Цсипаты анықталмаған сүйек жүйес≥н≥ң кез-келген зақымдануы | Osteopathya Ц (osteon Ц bone + pathos - suffering, illness) Ц any defeats of bone system without specification of their character |
| ќстеомал€ци€ (греч. osteon Ц кость + malakia Ц м€гкость; синоним: разм€гчение костей) Ц разм€гчение костей вследствие уменьшени€ в них солей кальци€ и фосфора. ѕри остеомал€ции остеоид образуетс€, но не минерализуетс€ | ќстеомал€ци€ (грек сөз≥нен Osteon -сүйек + malakia- жұмсақтық; иноним: сүйектерд≥ң жұмсаруы) Ц сүйекте кальций және фосфор тұздарының азаюы салдарынан сүйектерд≥ң жұмсаруы | Osteomalacia Ц is defect in matrix mineralization due to decreased contents of Ca- and P Цsalts/ Osteoid is formatted? But there is no mineralization |
| ќстеопороз ( греч. osteon Ц кость + poros - пора) Ц снижение плотности кости. ѕри остеопорозе снижаетс€ и образование остеоида, и его минерализаци€. | ќстеопороз ( греч. osteon Ц сүйек + poros - тес≥к) Цсүйек тығыздығының төмендеу≥. ќстеопороз кез≥нде остеоид түз≥лу≥ де және оның минералдануы да төмендейд≥ | Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by increased porosity of the skeleton resulting from reduced bone mass. |
| —уставной синдром Ц сочетание нескольких субъективных и объективных признаков поражени€ опорно-двигательного аппарата | Ѕуын синдромы- т≥рек-қимыл аппараты зақымдануының б≥рнеше субъективт≥ және объективт≥††††††† белг≥лер≥н≥ң қабаттасуы. | Arthritic syndrome Ц is the combination of several subjective and objective signs of musculoskeletal system damage |
| јртрит Ц воспаление сустава, в основном синовиальной оболочки | јртрит Ц буынның, нег≥з≥нен синовиалды қабығының қабынуы | Arthritis Ц is a joint inflammation. In the heart of it there is synovitis |
| –евматоидный артрит Ц аутоиммунное ревматическое заболевание неизвестной этиологии, характеризующеес€ хроническим эрозивным артритом (cиновитом) и системным поражением внутренних органов | Құздамалық артрит Ц созылмалы жаралы (эрози€лы) буын қабынумен және ≥шк≥ мүшелерд≥ң жүйел≥к зақымдануымен сипатталатын, себеб≥ белг≥с≥з аутоиммундық құздамалық буын қабынуы | Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a autoimmune rheumatic disease of unknown etiology is characterized by chronic erosive arthritis (synovitis) and systemic defeats of many tissues and organsЧskin, blood vessels, heart, lungs, and muscles |
| –евматоидный фактор Ц белок сыворотки крови и | Құздамалық жайт (фактор)- иммммуноглобулин G Цге | Rheumatoid factor - is blood and synovial fluid protein, †is |

|
|
|
| синовиальной жидкости, €вл€ющийс€†††††† антителом против иммуноглобулинов G. ¬ы€вл€етс€ у 70 - 80% больных†††††† ревматоидным артритом (серопозитивный ревматоидный артрит) | қарсы антидене болып табылатын қан сарсуының және синовиалдық сұйықтың нәруызы. Құздамалық жайт буын қабынуымен ауыратын адамдардың 70-80 % анықталады (серопозитивт≥ құздамалық артрит). | antibody against Ig. Is determined in 70-80% patients with Rheumatoid arthritis (seropositive Rheumatoid arthritis) |
| ѕаннус (лат. рannus Ц лоскут, кусок ткани) Ц агрессивна€ гранул€ционна€ ткань в суставе при ревматоидном артрите | ѕаннус- (латынша pannus Ц қиық, кесек мата (т≥н) Ц құздамалық буын қабынуы кез≥ндег≥ буындағы агрессивт≥ б≥те (жазыла) бастаған т≥н | Pannus is aggressive granulation tissue rich in inflammatory cells, enzymes, mediators. It produces sustained, irreversible cartilage destruction and erosion of subchondral bone |
| јнкилоз (ankylos Ц согнутый, изогнутый) Ц неподвижность сустава вследствие сращени€ суставных поверхностей | јнкилоз (ankylos- бүг≥лген, майысқан)- буын беттер≥н≥ң б≥р-б≥р≥не жабысып б≥т≥п кету≥нен буын қимыл- қозғалысының шектелу≥ | Ankylosis - is a stiffness of a joint due to abnormal adhesion and rigidity of the bones of the joint, which may be the result of injury or disease |
| ќстеоартроз (в зарубежной литературе называетс€ остеоартритом) Ц дегенеративно- дистрофическое поражение суставного хр€ща. ¬торично поражаютс€ субхондральна€ кость, синовиальна€ оболочка, св€зки, капсула, околосуставные мышцы | ќстеоартроз (шетел әдебиеттер≥нде остеоартрит деп айтады)- буын шем≥ршег≥н≥ң дегенеративт≥- дистрофи€лық зақымдануы | Osteoarthritis is degeneration of cartilage. There is secondary damage to subchondral bones, sinovia, ligaments, capsule and muscles |
| ƒерматозы (греч. derma Ц кожа;† синоним† кожные болезни) Ц общее название болезней кожи различной этиологии и† патогенеза (наследственны円††††††††††††† и приобретенные; воспалительные, дистрофические, аллергические и др.). | ƒерматоздар (грек derma- тер≥ синоним тер≥ аурулары)- тер≥н≥ң себеб≥ мен даму тет≥г≥ әртүрл≥ тұқымқуалайтын, жүре пайда болған; қабынулық дистрофи€лық, аллерги€лық ауруларының жалпы аталуы | Dermatoses is common definition of different diseases of different etiology and pathogenesis (inherited and acquired,††††††† inflammatory, diastrophic, allergic ets.) |
| ƒерматит - воспаление кож膆††† ↆ††† результате непосредствен ного контакта с внешними патогенными факторами | ƒерматит- сыртқы дертт≥к ықпалдармен т≥келей жанасулар нәтижес≥ндег≥ тер≥ қабынуы. | Dermatitis Ц is skin inflammation due to direct contact with exogenous pathogenic factors |
| ѕиодерми€ или пиодермит (от греч. рyon Ц гной, derma - кожа)†† Ц †гнойничковые заболеван舆†††††††††††††† кожи, | ѕиодерми€ немесе пиодермит (грек сөз≥ pyon-≥р≥ң, derma- тер≥)- ≥р≥ң тудыратын микроорганизмдерд≥ң | Pyodermitis - are purulant skin diseases due to pyogenous microbes. Are divided into staphylodermias, |
| обусловленные экзогенным внедрение솆††††††††††††††††††††††† гноеродных микроорганизмов. —оставл€ют 80% заболеваний кожи у взрослых, у детей Ц 30%. ѕо этиологии дел€тс€ на†††††††††††††† стафилодермии, стрептодермии, смешанные | сырттан ену≥нен тер≥н≥ң майда ≥р≥ңд≥ аурулары. ≈ресек адамдарда тер≥ ауруларының -80%ын, балаларда- 30% құрайды. —ебептер≥ бойынша стафилодерми€ға, стрептодерми€ға, аралас түрлер≥не бөл≥нед≥ | streptodermias, miscellanies. |
| √идраденит - гнойное воспаление апокриновых потовых желез | √идроаденит- апокринт≥к тер бездер≥н≥ң ≥р≥ңд≥ қабынуы | Hidradenitis is purulant inflammation of apocrine glands |
| ћикозы - заболевани€ кожи, вызванные патогенными грибами | ћикоздар- дерт тудырушы саңырауқұлақтардан туындаған тер≥ аурулары. | Mycosis Цis skin disease due to fungal infection |
| андидозы Ц поражение слизистых††††††††††† оболочек, внутренних органов, ногтей, обусловленное экзогенным внедрением грибов рода Candida | андидоздар- Candida тект≥ саңырауқұлақтардың экзогенд≥ ену≥не байланысты шырышты қабықтардың, ≥шк≥ ағзааалардың, тырнақтардың зақымдануы | Candidosis Ц is defeat of mucous membranes, organs, nails, caused by Candida fungi |
| рапивница Ц аллергическое заболевание, характеризующеес€ быстрым высыпание솆 на††† коже зуд€щих волдырей (I тип аллергических реакций по ƒжеллу† и† умбсу† - реагиновый). | рапивница- тер≥де қышитын күлд≥реулерд≥ң тез пайда болуыме톆††† сипатталатын аллерги€лық ауру (ƒжелл және † умбс††††† бойынша аллерги€лық серп≥л≥стерд≥ң 1 түр≥ Ц реагинд≥к түр≥). | Urticaria (hives) Ц is allergic disease, is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps (Allergic reactions of the I type - reagenic) |
| ќтеꆆ†††††† винк円†††††† Ц аллергический отек дермы и подкожной клетчатки лица | винке ≥с≥ну≥ - бетт≥ң тер≥с≥ мен шелмайының аллерги€лық ≥с≥ну≥. | Quincke's edema is the rapid swelling (edema) of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, mucosa and submucosal tissues. It is very similar to urticaria, but urticaria, commonly known as hives, occurs in the upper dermis (Allergic reactions of the I type -reagenic). |
| »хтиоз (кожа аллигатора, от греч. ichthy - рыба) Ц группа гетерогенных заболеваний, характеризующихс€ диффузным нарушением ороговени€ кожи по типу гиперкератоза вследствие мутаци膆†††††††††††††††††† генов, | »хтиоз-††††††††††††† (аллигатор тер≥с≥,ichty- балық деген грек сөз≥нен шыққан)- кератинн≥ң әртүрл≥ түрлер≥н≥ң түз≥лу≥не жауапты††††††††††††††† тектерд≥ң (гендерд≥ң)†††††††† мутаци€сы салдарынан гиперкератоз түр≥нде тер≥ †мүй≥здену≥н≥ң | Ichthyosis Ц (from the Greek root ichthy -, meaning fishy) is the group of genetically inherited disorders associated with excessive keratin build-up (hyperkeratosis) that results clinically in fishlike scales |
| ответственных††††††††††††††††† за образование различных форм кератина. Ёто приводит к образованию на коже чешуек, напоминающих чешую рыбы | жайылмалы бұзылыстарымен сипатталатын гетерогенд≥ аурулар тобы. Ѕалықтың қабыршықтары톆†††††††† еске түс≥рет≥ндей,††††††††††††† тер≥де қабыршықтар пайда боуына әкелед≥ | |
| Ёкзема ( от греч.eczema Ц вскипать,†††† †††††††††† кипеть)†††††††††††††† Ц воспалени円†††††††† поверхностных слоев кожи, имеющее нейро - аллергическое происхождени円††††††††††††††† и хроническое рецидивирующее течение | Ёкзема- (eczema-††††† қайнау, қатты қайнау деген грек сөз≥нен алынған)- пайда болуы†††††† жүйкел≥ꆆ†††† Ц аллерги€лық,†††††††††††† ағымы созылмалы- қайталанбалы, тер≥н≥ң бетк≥ қабаттарының қабынуы | Eczema Ц (The Greek word eczema, means "to boil over") is skin inflammation of †neuro Цallergic origin, has chronic current. It is characterized by red, papulovesicular, oozing, and crusted lesions early on that, with persistence, develop into raised, scaling plaques. In time, acute spongiotic dermatitis may evolve to a more chronic form in which epidermal hyperplasia and excessive scale, rather †than blistering, dominate the clinical and histologic picture |
| ѕсориаз или чешуйчатый лиша醆 Ц††††††††††††† хронический дерматоз, характеризующийс€ пролиферацие醆††††† клеток эпидермиса, нарушением кератинизации, воспалением в дерме | ѕсориаз- немесе қабыршақты тем≥ретк≥-††††††††††††††††††††††††††† эпидермис жасушаларының†††††††††† өс≥п өну≥мен, кератиндену≥менн, бұзылуларымен, дермадағы қабынулармен сипатталатын созылмалы дерматоз | Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory dermatosis. Psoriasis is characterized by proliferation of epidermatic cells,†††††† disorders†††††† of keratinization, dermatitis. The most typical lesion is a well- demarcated, pink to salmon- colored plaque covered by loosely adherent scales that are characteristically silver-white in color |
| “оксикодерми€ Ц поражение кожи, вызванное гематогенно попавшим膆†††† ↆ†††† нее аллергенами или токсинами | “оксикодерми€-††††††††† тер≥ге гематогенд≥ жолмен түскен аллергендерден немесе уытты заттардан туындаған тер≥н≥ң зақымдануы. | Toxicodermitis Ц is skin disease†††††††††††††††††† caused†††††† by hematogenous invasion by toxins or allergens |
| ¬итилиго (vitiligo Ц пега€ кожа, песь) Ц хроническое заболевание, про€вл€ющеес€ образованием депигментированных п€тен на различных участках кожного покрова. | ¬итилиго (vitiligo- ала тер≥, пес)- тер≥н≥ң әртүрл≥ бөл≥ктер≥нде түсс≥з дақтар пайда болуымен көр≥нет≥н созылмалы ауру. | Vitiligo is a chronic disorder characterized by partial or complete loss of pigment- producing melanocytes within the epidermis. |
| —ебор分†† Ц†† нарушение функции сальных желез, | —еборе€- пайдасыз †(құнсыз) тер≥ майының бөл≥н≥п †шығуы | Malassezia furfur. Seborrhoeic dermatitis (also |
| характеризующеес€ | күшею≥ме톆† сипатталатын | seborrheic dermatitis AmE, |
| усиленны솆††† выделением | тер≥дег≥†† май† бездер≥н≥ң | seborrhea) (also known as |
| неполноценног кожного | қызмет≥н≥ң††††† бұзылулары. | "seborrheic eczema") is an |
| сала. Ётиологи€ неизвестна, | —ебеб≥ белг≥с≥з, дегенмен | inflammatory skin disorder |
| однако предполагаетс€ роль | Malassezi††††††††††††††††††††† furfur | affecting the scalp, face, and |
| грибка | саңырауқұлағының††††† рол≥ | torso. The probable cause is |
| болжамдалады | Malassezia furfur. Malassezia | |
| hydrolyze human††† sebum | ||
| releasing a mixture of non- | ||
| uniform structure saturated and | ||
| unsaturated fatty acids which | ||
| breach the skin's barrier | ||
| function. This barrier breach | ||
| induces an irritation response, | ||
| leading to dandruff and | ||
| seborrheic dermatitis. | ||
| ‘отодерматозы | ‘отодерматоздар | Photodermatitis is skin disease |
| (фотодерматиты)†††††††††††††† Ц | (фотодерматиттер)-†††††† күн | sometimes referred to as sun |
| заболевани€ кожи, вызванные | сәулес≥н円 сез≥мталдықтың | poisoning or photoallergy, is a |
| повышенной | жоғарлауынан пайда болатын | form of allergic contact |
| чувствительностью†††††††††† к | тер≥ аурулары. | dermatitis in which the |
| солнечным лучам. | allergen must be activated by | |
| light to sensitize the allergic | ||
| response |
6.1.6. Ћ»“≈–ј“”–ј:
|
|
|
|
|
|
ќсновна€:
1. ѕатофизиологи€: ”чебник дл€ мед.вузов под/ред ¬.¬. Ќовицкого и ≈.ƒ. √ольдберга ќ.». ”разовой- ћ.: √Ёќ“ј–-ћ≈ƒ, 2т., 2013. - —. 716-731
2. Ћитвицкий ѕ.‘. ѕатофизиологи€ учебник + —ƒ. Ц 4-е изд. Ц ћ., 2010. Ц с.448-450
3. линиакалық патофизиологи€: учебник Ќурмуханбетов ј.Ќ. 2010г
4. V.Kumar, A. Abbas, J. C. Aster. Pathologic basis of disease/Elsevier.- 2015.- Ch.20
ƒополнительна€
5. ѕатофизиологи€ дл€ внеаудиторной самосто€тельной работы студентов //ѕод ред. ”дарцевой “.ѕ. Ц јлматы: азЌћ” им. —.ƒ.јсфенди€рова, 2006.—.146-147, 214-216
6. ѕатофизиологи€: ”чебник дл€ мед.вузов под/ред ¬.¬. Ќовицкого и ≈.ƒ. √ольдберга - ћ.: “омск. 2006.- —. 337-340
7. ќстеоартрит//ѕод ред. Ћесн€к ќ.ћ. Ц ћ.: √Ёќ“ј– Ц ћедиа, 2006. - 176 с
8. ќстеопороз // ѕод ред. Ѕеневоленской Ћ.»., Ћесн€к ќ.ћ. Ц ћ.: √Ёќ“ј– Ц ћедиа, 2008. - 176 с
6.1.7. ќЌ“–ќЋ№
–убежный контроль (выполнение тестовых заданий, решение ситуационных задач)
»Ќ‘ќ–ћј÷»ќЌЌќ-ƒ»ƒј “»„≈— »… ЅЋќ






