medium (pi. media) Ч носитель; среда capacity Ч емкость; объем (пам€ти); пропускна€ спо≠собность
media capacity Ч емкость носител€
data access time Ч врем€ доступа к данным
per bit Ч на единицу информации
to transferЧ передавать(с€); переносить(с€); пересы-лать(с€)
archival storage Ч архивное «”; архивна€ пам€ть to depend Ч зависеть от; полагатьс€, рассчитывать на to rotate Ч вращать(с€); чередовать(с€); смен€ть(с€) reason Ч причина; основание; довод; обосновывать;
делать вывод
solid-state device Ч твердотельный прибор magnetic core Ч магнитный сердечник
јнглийский €зык. ќсновы компьютерной грамотности 90
 bipolar semiconductor Ч бипол€рный полупроводник
bipolar semiconductor Ч бипол€рный полупроводник
metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) Ч структура металл-оксид-полупроводник randomly Ч произвольно
random-access memory (RAM) Ч оперативное запомина≠ющее устройство (ќ«”)
sound recording Ч звукозапись
to arrange Ч размещать; располагать; устанавливать;
монтировать tape device Ч «” на магнитной ленте
to range Ч классифицировать; располагать в пор€дке; лежать в диапазоне
magnetic disc storage Ч «” на магнитном диске
moving-head device Ч устройство с двигающейс€ голов≠кой
predominant Ч преобладающий; доминирующий flexible Чгибкий; настраиваемый; измен€емый floppy (disk) Ч гибкий диск(ета); «” на гибком диске to meet the demands Ч удовлетвор€ть потребности
9. ѕрочтите текст 2 и скажите, как вы понимаете термин Ђзапоминающа€ средаї и какие компоненты ее состав≠л€ют. ѕереведите текст.
Text 2. STORAGE DEVICES
Storage media are classified as primary storage or secondary storage on the basis of combinations*of cost, capacity, and ac≠cess time. The cost of storage devices is expressed as the cost per bit of data stored. The most common units of cost are cents, millicents (0.001 cents) and microcents (0.000001 cents). The time required for the computer to locate and transfer data to and from a storage medium is called the access time for that medi≠um. Capacities range from a few hundred bytes of primary stor≠age for very small computers to many billions of bytes of archi≠val storage for very large computer systems.
Memories may be classified as electronic or electromechani≠cal. Electronic memories have no moving mechanical parts, and
91 Unit 7. Storage
 data can be transferred into and out of them at very high speeds. Electromechanical memories depend upon moving mechanical parts for their operation, such as mechanisms for rotating mag≠netic tapes and disks. Their data access time is longer than is that of electronic memories; however they cost less per bit stored and have larger capacities for data storage. For these reasons most computer systems use electronic memory for primary storage and electromechanical memory for secondary storage.
data can be transferred into and out of them at very high speeds. Electromechanical memories depend upon moving mechanical parts for their operation, such as mechanisms for rotating mag≠netic tapes and disks. Their data access time is longer than is that of electronic memories; however they cost less per bit stored and have larger capacities for data storage. For these reasons most computer systems use electronic memory for primary storage and electromechanical memory for secondary storage.
Primary storage has the least capacity and is the most expen≠sive; however, it has the fastest access time. The principal pri≠mary storage circuit elements are solid-state devices: magnetic cores and semiconductors. For many years magnetic cores were the principal elements used in digital computers for primary storage. The two principal types of semiconductors used for memory are bipolar and metal-oxide semiconductors (MOS). The former is faster, the latter is more commonly used at present. Because data can be accessed randomly, semiconduc≠tor memories are referred to as random-access memory, or RAM.
|
|
|
There is a wide range of secondary storage devices. Typical hardware devices are rotating electromechanical devices. Mag≠netic tapes, disks, and drums are the secondary storage hardware most often used in computer systems for sequential processing. Magnetic tape, which was invented by the Germans during World War II for sound recording, is the oldest secondary stor≠age medium in common use. Data are recorded in the form of small magnetized "dots" that can be arranged to represent coded patterns of bits.
Tape devices range from large-capacity, high-data-rate units used with large data processing systems to cassettes and cartridges used with small systems. Magnetic disk storage, introduced in the early 1960s, has replaced magnetic tape as the main meth≠od of secondary storage. As contrasted with magnetic tapes, magnetic discs can perform both sequential and random pro≠cessing. They are classified as moving-head, fixed-head, or com≠bination moving-head and fixed-head devices. Magnetic discs are the predominant secondary storage media. They include flexible, or floppy discs, called diskettes. The "floppies" were introduced by IBM in 1972 and are still a popular storage me≠dium to meet the demands of the microcomputer market.
|
јнглийский €зык. ќсновы компьютерной грамотности 92
 10. ќтветьте на вопросы, использу€ информацию текста.
10. ќтветьте на вопросы, использу€ информацию текста.
1. How are storage media classified? 2. How is the cost of storage devices expressed? 3. What is the access time for stor≠age media? 4. How does the storage capacity range? 5. What are the two main types of storage devices? 6. What are electronic storage devices? 7. What are the principal primary storage cir≠cuit elements? 8. What are the main secondary storage devic≠es? 9. What is the oldest secondary medium and when was it invented? 10. What is a floppy?
11. Ќайдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих
словосочетаний:
«апоминающие устройства; носители пам€ти; первич≠ные «”; вторичные «”; врем€ доступа; стоимость «”; диа≠пазон емкости пам€ти; архивна€ пам€ть; движущиес€ ме≠ханические части; вращающиес€ магнитные ленты и диски; по этим причинам; твердотельные устройства; маг≠нитные сердечники; полупроводники; оперативное «”; аппаратное обеспечение вторичной пам€ти; звукозапись;. намагниченные точки; представл€ть зашифрованную ком≠бинацию единиц информации; в отличие от магнитных лент; последовательна€ и произвольна€ обработка; устрой≠ства с движущейс€ и фиксированной головкой; удовлет≠вор€ть потребности; гибкий диск.
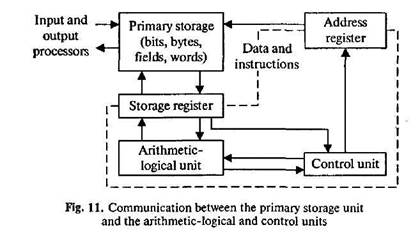
ќпишите схему.
93__________________________________ Unit 7. Storage
13. ѕереведите предложени€, содержащие всевозможные
формы причастий: Participle I, Participle II, Perfect
Participle Active и Perfect Participle Passive.
1. Electromechanical memories depend upon moving me≠chanical parts for their operation. 2. The time required for the computer to locate and transfer data to and from a storage me≠dium is called the access time. 3. Being not visible software makes possible the effective operation of computer system. 4. Having invented magnetic tapes the Germans used them as the secondary storage medium. 5. When properly programmed computers don't make computational errors. 6. Having been in≠troduced in the early 1960s magnetic disc storage has replaced magnetic tape storage. 7. The control unit interpreting instruc≠tions is one of the important parts of any computer system. 8. Data recorded in the form of magnetized dots can be arranged to represent coded patterns of bits. 9. As contrasted with mag≠netic tapes magnetic discs can perform both sequential and ran≠dom processing. 10. While having no moving mechanical parts electronic memories can transfer data at very high speed.
|
|
|
¬ыполните письменный перевод текста по вариантам.






