Spoken English And Broken English
(after G.B.Shaw)
If you are learning English because you intend to travel in England and wish to be understood there, you _____ not try to speak English perfectly because, if you do it, no one _____to understand you.
Though there is no such thing as perfectly correct English, there is presentable English which we call УGood EnglishФ, but in London nine hundred and ninety-nine out of every thousand people not only speak bad English but speak even that very badly. You _____ say that even if they _____ not speak English well themselves, they at least _____ understand it when it is well spoken. They _____ when the speaker is English; but when the speaker is a foreigner, the better he _____ speak, the harder it is to understand him. Therefore the first thing you _____ to do is to speak with a strong foreign accent. You _____ speak broken English, that is English without any Grammar. Then every English person will think that you _____ be a foreigner, and try to understand you and be ready to help.
He will not expect you to be polite and to use correct grammatical phrases. He will be interested in you because you are a foreigner. If you say, У_____ you have the goodness, sir, to direct me to the railway station at Charing CrossФ, pronouncing all the vowels and consonants beautifully, nobody _____ to understand you and will think you to be a beggar. But if you shout, УPlease! Charing Cross! Which way?Ф, you will have no difficulty. Half a dozen people will give you directions at once.
¬–≈ћ≈Ќј јЌ√Ћ»…— »’ √Ћј√ќЋќ¬
¬ систему глагольных времЄн вход€т времена следующих групп: Indefinite (Simple), Continuous (Progressive), Perfect, Perfect Continuous.
ENGLISH TENSES
| INDEFINITE (repeated, customary action) | CONTINUOUS (action/process going on at the moment of speech) | PERFECT (completed action connected with the present; result) | PERFECT CONTINOUOS (action/process which began in the past and is still going on) | |
| P R E S E N T | Еverb ask(s) |
be + V-ing
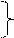 am
is asking
are am
is asking
are
| have + V in III form
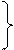 have
asked
has have
asked
has
| have been + V-ing
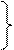 have
been asking
has have
been asking
has
|
| P A S T | asked took | was asking were asking | had asked | had been asking |
| F U T U R E | will ask | will be asking | will have asked | will have been asking |
ЌеопределЄнные (простые) времена действительного залога
(The Indefinite (Simple) Tenses)
¬ремена группы Indefinite обозначают факт совершени€ действи€ в насто€щем, прошедшем или будущем. ¬ этой группе 3 времени: Present Indefinite, Past Indefinite, Future Indefinite.
Ќасто€щее неопределЄнное (простое) врем€
(The Present Simple Tense)
Ќасто€щее неопределЄнное (простое) врем€ обозначает посто€нное, обычное, регул€рно повтор€ющеес€ действие, общеизвестный факт, признак, посто€нно характеризующий предмет, а также действие, заранее запланированное на будущее согласно договорЄнности или расписанию, плану. Ёто врем€ переводитс€ на русский €зык глаголом несовершенного вида в насто€щем времени.
|
|
|
I go to the Institute every day. я хожу в институт каждый день.
Present Indefinite совпадает с первой основной формой глагола (инфинитивом) без частицы to дл€ всех лиц и чисел, кроме 3 лица единственного числа. ¬ этой форме к основе инфинитива прибавл€етс€ окончание Цs или Цes.
ќкончание Цs прибавл€етс€ к основе большинства глаголов:
(to) write Ц he writ es писать Ц он пишет
(to) work Ц he work s работать Ц он работает
ќкончание Цes используетс€, если глагол в инфинитиве оканчиваетс€ на:
1) s, ss, ch, tch, x, o:
(to) dress Ц he dre sses одеватьс€ Ц он одеваетс€
(to) watch Ц he wa tches наблюдать Ц он наблюдает
2) y, перед которой стоит согласна€; при этом буква Цy мен€етс€ на Цi:
(to) try Ц he tr ies пытатьс€, старатьс€ Ц он пытаетс€
(to) cry Ц he cr ies плакать Ц он плачет
ѕримечание: если глагол оканчиваетс€ на Цy с предшествующей гласной, то в третьем лице единственного числа он получает окончание Цs: (to) play Ц he pla ys. ѕри этом гласна€ Цy не измен€етс€.
ќкончание третьего лица единственного числа читаетс€ по-разному:
1) после глухих согласных [s]: he stops;
2) после звонких согласных и гласных [z]: she sees, he lives;
3) после буквосочетаний Цss, -s, -ch, -tch, -sh, -x [iz]: she teaches, he passes.
¬опросительна€ форма Present Indefinite образуетс€ при помощи вспомогательных глаголов does (в третьем лице единственного числа) и do (во всех остальных лицах и числах). ¬спомогательные глаголы став€тс€ перед подлежащим. ѕри этом в третьем лице единственного числа у основного глагола исчезает окончание Цs/-es. ќтрицательна€ форма образуетс€ с помощью отрицательной частицы not, котора€ ставитс€ после вспомогательных глаголов do или does.
He speaks English. ќн говорит по-английски.
Does he speak English? √оворит ли он по-английски?
He does not (doesnТt) speak English. ќн не говорит по-английски.
They like ice cream. ќни люб€т мороженое.
Do they like ice cream? Ћюб€т ли они мороженое?
They do not (donТt) like ice cream. ќни не люб€т мороженое.
ƒл€ указани€ на повторный характер действи€ часто употребл€ютс€ следующие обсто€тельства времени: often (часто), usually (обычно), seldom (редко), always (всегда), sometimes (иногда), never (никогда), а также словосочетани€ со словом every (каждый): every day/week/month/year/Monday (каждый день/неделю/мес€ц/год/понедельник).
Ќаречи€ often, seldom, always, never, usually обычно став€тс€ перед глаголом-сказуемым. ≈сли же сказуемым €вл€етс€ глагол to be, то они сто€т после него.
I often read books. я часто читаю книги.
He is always very busy. ќн всегда очень зан€т.
”пражнени€
ќтветьте на следующие вопросы по образцу.
Model: What does a driver do? He drives.
What do drivers do? They drive.
1. What does a singer do? 2 What does a runner do? 3 What do students do? 4.What does a dancer do? 5. What do cooks do? 6. What do dancers do? 7. What does a painter do? 8. What do teachers do? 9. What does a typist do? 10. What do painters do? 11. What do writers do?






