Periodization of the history of the English language. The criteria for the periodization. Who suggest the linguistic criterion of the periodization.
3 периода:
1)древнеанглийский (период от начала письм. пам€тников VIIв. до конца XI в.)
2) среднеанглийский XII-XVв. Ќекоторые считают XV век переходным между средним и новоанглийским
3) новоанглийский XVIв. Ц наши дни. 16 и 17в.-ранненовоанглийский период
ритерий Ц событи€ внешней истории јнглии, €вл€ющиес€ веками в смене экономических формаций и политических форм управлени€. —ередина 11в Ц нормандское завоевание. 15в- война јлой и Ѕелой –озы, распад феодального государства.
√. —уит Ц прин€та€ периодизаци€ соответствует морфологии - Е строю различных эпох
ƒревнеанглийский Ц период полных окончаний
—реднеанглийский Ц период редуцировани€ окончаний
Ќовоанглийский Ц период утраченных окончаний
2. What keltic tribes inhabited Britain in the VII c. BC?
ельты Ц индоевропейские племена, поселившиес€ в Ѕритании в 7в. до н.э.
3. What name is earlier, Britain or England?
Britain.
4. What is the starting point of the English language?
ѕо€вление древнеанглийской письменности
Name the OE dialects
”эсесисский, ћерсийский, Ќортумбрийский, ентский (Uessex, Mercia, Northumbria, Kent)
Name the OE written records
Ѕольше всего на уэссексом диалекте. ѕо диалектам:
- ”эсисский:
јнглосаксонска€ хроника Ц летописи, начина€ с7 в.
УCura PastoralesФ Ц произведение папы √ригори€ I
¬семирна€ истори€ Ц испанского монаха ќроси€ + повествование јльфреда о путешестви€х ќтхере и ¬ульфсона
”тешение философии Ц Ѕоэци€
- ћерийский:
ѕеревод псалтыр€ (9в), гласы(8в), церковные чилины (?)
- Ќортумбрийский:
Ћатинским алфавитом написан перевод евангели€, гимн монаха эдмона и предсмертна€ песнь Ѕэды
÷ерковна€ истори€ английского народа
- ентский:
ѕеревод псалмов и юридические документы
ѕоэтические пам€тники нельз€ отнести к одному определенному диалекту. ѕоэма УЅеовульфФ (автор неизвестен), поэмы монаха юневульфа У≈ленаФ, УёлианаФ УјндрейФ
ѕоэма УёдифьФ (автор неизвестен)
7. Name of the OE epic poem.
ЂЅеовульфї (автор неизвестесн)
8.Name the morphological classes of the OE verbs. —ильные, слабые, претерито-презентные и неправильные глаголы (strong, weak, preterite-present and irregular verbs).
9.What is the characteristic feature of the OE strong verbs? »меют 4 формы: инфинитив, прошедшее ед., прошедшее мн. и причастие II. —ильные глаголы образуют прошедшее врем€ и причастие II чередованием гласных.
infinitive past sing. past pl. participle II
writan [i:] wrat [a:] writon [o] written [i]
ceosan [eo:] ceas [ea] curon [u] coren [o]
drinkan [i] drank [a(o)] druncon [u] drunken [u]
stelan [e] stæl [æ] stælon [æ] stolen [o]
specan [e] spæc [æ] spæcon [æ] specen [e]
faran [a] for [o] foron [o] faren [a]
10.How many classes of the OE strong verbs do you know?
1.writan (УwriteФ)
|
|
|
2.ceosan (УchooseФ)
3.drinkan (УdrinkФ)
4.stelan (УstealФ)
5.specan (УspeakФ)
6.faran (УgoФ)
7.hatan (УcallФ)
11.What Mod.E morphological do the OE strong verbs correspond to?
ќни соответствую неправильным глаголам.
12.What is the characteristic feature of the OE weak verbs?
»меют 3 формы. ¬се слабые глаголы образуют формы претерита и причасти€ II прибавлением дентального суффикса. –азличие в способе прибавлени€ суффикса. —уществует 3 класса:
Inf. Ц past sing. Ц participle II
1 класс: deman Ц demde Ц demd УjudgeФ (suffix Цi/j) past pl.
2 класс: lufian Ц lufode Ц lufod УloveФ (suffix Цoj) вместо Цe
3 класс: habban Ц hæfde Ц hæfd УhaveФ (suffix Цai) ставитс€ Цon
13.What Mod.E morphological class do the OE weak verbs correspond to?
ѕравильные глаголы.
14.How many classes of the OE weak verbs do you know?
3 класса (вопрос 12)
15.Name the OE weak verbs of the 3d class?
Inf. Ц past.sing. Ц participle II
УhaveФ habban Ц hæfde Ц hæfd
УliveФ libban Ц lifde Ц lifd
УsayФ seeʒan Ц sægde (sæde) Ц sæʒd (sæd)
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21. What is declension? How many cases there were in OE?
—клонение Ч словоизменение именных частей речи (сущ, прил, числ) по числам родам и падежам.
¬ древнеанглийском было п€ть падежей Ч номинатив (им), генетив (род), датив (дат), аккузатив (вин) и инструментатив (тв)
22. What is conjugation?
—пр€жение Ч изменение глаголов по числам, лицам и временам.
23. What Verbals were there in OE? How where they formed?
¬ древнеанглийском были такие безличные формы глагола как:
1. »нфинитив Ч две формы
а) простой инфинитив с окончанием -an
b) датив инфинитив Ч после предлога to и имел окончание Цanne
bindan Ц to bindanne, deman Ц to demanne
2. ѕартисипл 1 Ч имел окончание Цende и склон€лс€ по правилам склонени€ слабых глоголов
3. ѕартисипл 2 Ч имел окончание Цn или Цed/-od в зависимости от типа глагола (сильный или слабый). —клон€лс€ как прилагательное
24. Three declensions: the strong declension, the weak declension and the root-stem declension. The strong declension included nouns with vocalic stems (-a, -o, -i, -u), the weak declension comprises Цn-stem nouns only.
25. A special type, called root-stem, formed several cases by changing the root vowel due to mutation, and not by adding an inflexion.
26. Adjectives in OE had the grammatical categories of gender (masculine, feminine, neuter), number (singular and plural), case (nominative, genitive, dative, accusative and, partly, instrumental), and degrees of comparison. Every adjective could be declined both according to the strong declension and the weak declension. The weak declension forms were used when the adjective was preceded by a demonstrative pronoun. In all other contexts strong declension forms were used.
How were the degrees of comparison of the old English adjectives formed.
The comparison degree: -ra(re) ќбычна€ степень сравнени€
The superlative degree: -ost(est) превосходна€ степень
»сключени€:
Suppletive forms(суплетивные формы)
God-betera-betst У goodФ
Micel-mara-maest УbigФ
Lytel-laessa-laest УlittleФ
Yfel-wiersa-wierest ФbadФ
|
|
|
28) What classes of the Old English pronouns do you know?






29. ¬ древнеанглийском существовали две группы указательных местоимений. 1 группа распадаетс€ в среднеанглийском, а 2а€ проходит через исторические изменени€, и до наших дней форма среднего рода this вытесн€ет остальные формы. ќт неЄ уже по€вл€ютс€ формы those, these, them
30. «начение будущего времени зачастую выражалось формой насто€щего времени. » будущее какое мы привыкли видеть, как таковое не существовало в древнеанглийском. «начение будущего времени выражалось с помощью формы - насто€щего в сочетании с временным наречием или сочетанием модального глагола с инфинитивом.
31. —реднеанглийский период начинаетс€ с ’I века. Ќормандское завоевание "открыло" этот период. Ќорманди€ €вл€лась герцогством феодальной ‘ранции; скандинавы ассимилировались с местным населением и перенимали их€зык и культуру.
32 What was the state language in Britain in ME? What language was taught at schools? What language was spoken at university?
‘ранцузский €зык был официальным €зыком јнглии при поражении англичан в битве при √астингсе в 1066 году, победу одержали французы.
¬ школах изучали Ћатынь, а в университете говорили на јнглийском и иногда на Ћатыни.
36. In what position was the vowel levelled in ME? And in OE?
 ¬ инфинитиве изменилось окончание на en (звук ә
¬ инфинитиве изменилось окончание на en (звук ә
37. In what position could a long vowel occur in ME? And in OE?
”длинение гласных происходило перед сочетани€ми звуков /ld/, /nd/, /mb/. Ќо если после сочетаний /ld/, /nd/, /mb/ по€вл€лс€ еще один согласный, то удлинени€ не происходило.
Ѕуква e часто прибавл€лась к словам, которые изначально ее не имели, чтобы показать исторически долгий корневой гласный.
38. In what position could a short vowel occur in ME? And in OE?
в ћ≈ перед двойным согласным гласна€ становитс€ краткой, в то врем€ как в ќ≈ эта гласна€ была долгой

36 - levelling
37 Ц lengthenting
38 Ц shortening
39) How did the declension system change in ME period? How many cases survived? What are they called? And in Mod.E?
¬ древнем английском существительные склон€лись по 4 падежам(им.,род.,дат.,вин.), по числам и полу(мж.р.,жен.,р.,ср.р.) » учитывались основы слов *см вопрос про сущ в ƒревн.англ.
¬ сред.јнгл. существительные склон€ютс€ только по »м. и –од. ѕадежу, по числам (ед.ч.,мн.ч)
¬се типы склонени€ остались неизменными после древнего (strong,root,weak).
40) How did the verb system change in the ME period? What is simplified? ¬ др.английском было 7 классов сильных глаголов. 
ј также произошли изменени€ в окончани€х глаголов насто€щего и прошедшего времен.
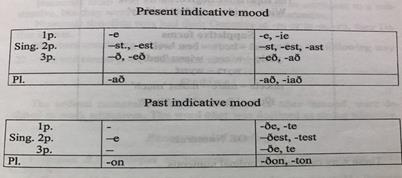
41) What is an analytical form? And what period did they appear in the English language? And what analytical forms in Mod. Eng do you know?
јналитическа€ форма Ц это составна€ форма, состо€ща€ из 2 компонентов: вспомогательного глагола, лишенного лексического значени€ и выражающего только грамматическое значение и неличной формы глагола Ц носител€ как лексического, так и грамматического значени€.¬озникли в древнем английском. ¬ современном английском аналитические формы встречаютс€ в перфектных временах, пассивном залоге, составных временах, таких как континиус. ѕрим: have come; was taken; will be doing
42 What is a synthetic form? Give some examples Synthetic forms unite both lexical and grammatical meanings in one word. Grammatical forms may be synthetical and analytical. Synthetical:1. inflection (morphemic changes without changing their lexical meaning: sentence, sentences, sentenced);2. suppletivity (combining different roots: be, am, is/are, was/were). oe
43 At what period did the verb forms expressing future action appear in the English language? How did they develop?
—реднеанглийский. ¬ыражалось наст временем, модальные глаголы и инфинитив начинали утрачивать свое лексическое значение. ср анг Ц shall will
|
|
|
44 At what period did the Continuous forms appear in the English language? How did they develop?
—овременный английский. beon weordan Цпредшествовали современным длительным формам. носили неопределенный характер, не было ограничени€ во времени, описательное значение
45 at what period did the perfect verb forms appear in the English language? How did they develop?
—тановление past и present perfect можно проследить с древнеанглийского периода, с самого его начала встречаютс€ сочетани€ глаголов beon и habban с причастием II.
¬ течение ранненовоанглийского периода происходит ограничение употреблени€ глагола to be в качестве вспомогательного глагола аналитической формы глагола перфекта. ¬ литературном €зыке XVII и XVIII века встречаютс€ редкие употреблени€ с глаголом to be, в этот период происходит размежевание значений претерита и перфекта. началу XVIII века в present perfect полностью закрепл€етс€ в современном употреблении. «начение предшествующее Past perfect четко устанавливаетс€ еще в XVI веке. Ќо широкого использование оно не получило, если из контекста и благодар€ союзам было €сно, что одно действие совершалось раньше другого, то употребл€лась форма past indefinite. “акое употребление сохранилось и сейчас (после when, as soon as, after). концу ранненовоанглийского периода окончательно оформл€етс€ и второе значение past perfect(действие завершенное к определенному времени в прошлом).
46 at what period did the articles forms appear in the English language? How did they develop?
¬ среднеанглийском из числительного Ђanї (один), сто€щего в безударной позиции, обособл€етс€ неопределенный артикль. ќбособление формы вызвано сокращением [а:] вне ударени€; [n] сохран€етс€ перед гласными, перед согласными оно отпадает.
¬ древнеанглийском €зыке в период между V и X веками существовали указательные местоимени€ мужского рода se, женского рода seo и среднего рода thæt. концу древнеанглийского периода в XI-XII века артикли стали выступать как служебные части речи, указывающие на частный, единичный характер предмета, обозначаемого существительным, с которым они употребл€лись. в Middle English: формы падежа и рода измен€лись в сторону упрощени€ из-за оглушени€ согласных (редукции) и разрушени€ системы склонений имен существительных. –анее в староанглийском €зыке у каждого окончани€ существительных была сво€ система склонений, котора€ также отличалась в единственном и множественном числах. ќднако из-за утраты среднеанглийским €зыком системы рода формы определений также упростились: и определЄнный артикль the и указательные местоимени€ this, that, these, those с XII века и по наши дни используютс€ независимо от рода определ€емого существительного. ¬ староанглийском €зыке система родов была сложной не только из-за согласовани€ с определител€ми, но и из-за нелогичности делени€ существительных по родам: многие существительные, несмотр€ на то, что обозначали лицо или предмет женского или мужского родов, в древнеанглийском €зыке относились к среднему роду.
47 at what period did the gerund forms appear in the English language? How did they develop?
ѕо€вление герунди€ в английском €зыке €вл€етс€ результатом взаимодействи€ первого причасти€ и отглагольного существительного на Ц ing. ѕервое причастие заимствовало этот суффикс у отглагольного существительного (e.g.: huntende > hunting). ¬ результате в €зыке развивалась лексико-грамматическа€ омоними€ (hunting - герундий; hunting - причастие). ¬ свою очередь, уподобившись в своей форме отглагольному существительному, причастие стало активно воздействовать на него. ѕод вли€нием причасти€ отглагольное существительное стало приобретать глагольные черты: в среднеанглийский период эта форма стала использоватьс€ с пр€мым дополнением и обсто€тельствами; в новоанглийский период герундий приобрел аналитические формы перфекта и пассива.
|
|
|
48. French lexical borrowings in the ME period. What social spheres were they found in?
»стори€ французского €зыка в английском началась в 1066 году после завоевани€ јнглии норманнами во главе с герцогом Ќормандии ¬ильгельмом. »менно тогда €зыком знати стал французский, а простолюдинов Ц английский. Ќа прот€жении трех столетий (XI-XIV) эти два €зыка конкурировали друг с другом. ‘ранцузский €вно доминировал, привнос€ в английский все новую и новую лексику. ≈го распространенность в кругах аристократии обусловила тематику заимствований. ‘ранцузские заимствовани€ были особенно распространены в сфере государственного управлени€ (такие слова как government, prince/princess, empire, state €вл€ютс€ заимствовани€ми), в юриспруденции (justice, equity, plaintiff, judge и многие другие), а так же в кулинарии (venison, beef, veal, mutton, port, bacon)
49. The rise of the English language. The first document written in English. When did the English language became a state language?
ќксфордские постановлени€ (1258) Ц первый официальный документ на английском €зыке. ¬ 1362 король Ёдвард III впервые обратилс€ к ѕарламенту на английском. 14 веку английский €зык стал государственным.
50 (51). The starting point of modern English. What historical event is it usually associated with?
¬еликий сдвиг гласных (англ. Great Vowel Shift) Ч фонетическое изменение, произошедшее в английском €зыке в XIVЧXV вв. »зменени€ случившиес€ в процессе великого сдвига гласных превратили среднеанглийский в новоанглийский. —овременный английский во варианте, максимально приближенном к тому, что мы знаем сейчас, по€вилс€ около 17 века. ѕо€вление книгопечатани€ (1475). “ворчество поэтов, писателей (Ўекспир, Ѕлейк). –ост колониальной империи и установление св€зей с новыми странами(заимствовани€).
52. The great vowel shift ("the narrowing"). What is its phonological characterictic? How did it affect the English pronunciation?
¬еликий —двиг гласных - изменение, которое произошло в 14th- 16thc. и затронуло все длинные монофтонги + дифтонг [Au]. ¬ результате долге гласные:
-дифтонгизировались (дифтонгизаци€ узких длинных гласных звуков)
-сузились - стали более закрытыми (сужение всех долгих гласных)
Narrowing:
1. o: - u:
2. {шва}: - e: - i:
The Great Vowel Shift was not followed by any regular spelling changes which contribute greatly to the present discrepancy between the spoken and written English. The Great Vowel Shift didnТt add any new sounds to the vowel system.
Ћюди постепенно стали произносить слова немного по-другому и новое произношение быстро распространилось по всему острову. »менно благодар€ Ђвеликому сдвигу гласныхї слова boot, feet, make произнос€тс€ так как они произнос€тс€.
ѕри этом письменна€ речь Ц удел немногих грамотных аристократов и ученых, не спешила за изменением речи устной и оставалась такой, как есть. Ќе последнюю роль в этом сыграло и изобретение печатного станка Ц переделать печатный текст совсем не просто, книги сохран€ли древнее правописание слова, несмотр€ на новое произношение.






