(cognitive linguistics vs. generative grammar)
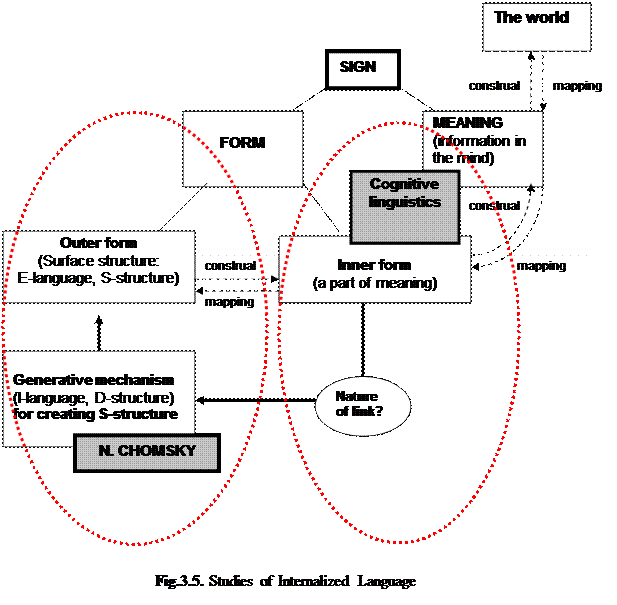
In the East European tradition, the studies of Internalized Language employ such basic notions as the conceptual model of the world, and the linguistic model of the world. The conceptual model of the world is the totality of different kinds of information (both conscious and unconscious) retained in the mind. The linguistic model of the world is that part of the conceptual model which is conscious, and which is constituted by concepts manifested through language. The linguistic model of the world is a structured multidimensional network, where linguistic entities are interrelated formally, semantically, and functionally. This model is presumed to integrate two domains of knowledge: (1) knowledge about language as a system of linguistic forms, and (2) knowledge in language, which is obtained through cognizing the world, and exposed in the system of linguistic meanings. Hence, there are two approaches Ц formal and semantic Ц to interpreting the IL. In the Western tradition, the formal approach to IL is taken by generative grammar, and the semantic approach is taken by cognitive linguistics. These two paradigms disagree on the question about the nature of link between the two domains of knowledge represented in language. Generative linguistics considers them to be autonomous: the generative mechanism (D-structure) that creates the surface syntactic structure (S-structure) of linguistic expressions is just СconnectedТ to the system of thoughts through some СinterfaceТ. Cognitive linguistics views conceptual structures and linguistic structures as iconic: the structures of language are similar to the structures of thought (Fig. 3.5).
Fig. 3.5. demonstrates creation and interpretation of a linguistic sign as viewed by cognitive linguistics. Creation of a sign is associated with the Speaker (the onomasiological approach Сfrom the meaning to a linguistic formТ), and interpretation of a sign is associated with the Listener (the semasiological approach Сfrom the linguistic form to its meaningТ). Creation of a sign involves cognitive mapping as an incomplete, fragmentary representation of the signified entity. Interpretation of a sign involves cognitive construal of its meaning.
In language, mapping has three major directions (1) the experienced world à the thought / meaning of a linguistic sign; (2) the meaning of a linguistic sign à the signТs inner form; (3) the signТs inner form à the signТs outer form:
Ј WORLD à THOUGHT / MEANING OF A SIGN. Cognitive mapping of the world is grounded on attention patterns,whichsingle outparticular related fragments of the experienced entity. Such fragments, registered by the mind, become meanings of linguistic signs.
Ј MEANING à LINGUISTIC FORM / inner form. A motivated sign has its outer and inner forms. The outer formis the sound form of a sign. The innerform is a fragment of meaning immediately represented in the outer form; e.g. cat-chaser Сa dogТ.
Ј LINGUISTIC FORM: inner form à outer form. The inner form of a sign is structured with an onomasiological model which includes the basis (the target concept), the feature (characteristics of the basis), and the link(the relation between the basis and its feature). The outer form of a linguistic sign may represent its onomasiological model fragmentarily; e.g. theinner form: УBIKE (basis) HAS (link) THREE WHEELS (feature)Ф à the outer form: three-wheeler (the link is missing), three wheels (the link and the basis are missing).
 |
Therefore, cognitive linguistics hypothesizes that emergence of language as a system of signs may results from cognitive mapping: our thought is mapped upon the experienced world, thus yielding the meanings of linguistic signs; inner forms of linguistic signs are mapped upon their meanings, and the outer forms of linguistic signs are mapped upon their inner forms.






